Fig. 8.1
Coronal T2-weighted MRI image of a patient who had TRMDD treated with BACI, the scan was performed within 72 h after BACI. Note the symmetrical position of the BACI lesions and surrounding oedema
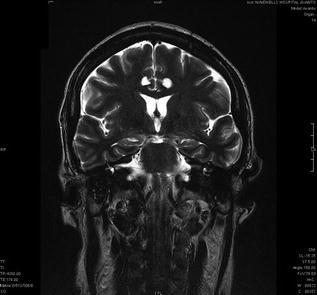
Fig. 8.2
Coronal T2-weighted MRI image 12 months after BACI, when the patient was in remission from TRMDD
Some authors reported making two further lesions in the same region on either side, what is called the six-pack BACI, however there is no strong scientific evidence to suggest that six-pack BACI is better or worse than single BACI of adequate size and precise locations.
8.3.2 Bilateral Anterior Capsulotomy (BACA)
BACA involved making lesions in the most anterior part of the anterior limb of the internal capsule on either side. The principles of BACA was first described by Talairach et al. [26] and developed as stereotactic procedure by Lars Leksell [16]. The white matter fibers connecting the frontal cortex and anterior cingulate to the thalamus, hippocampus, and amygdala are targeted during BACA by making lesions about 12 mm long as shown in Fig. 8.3.
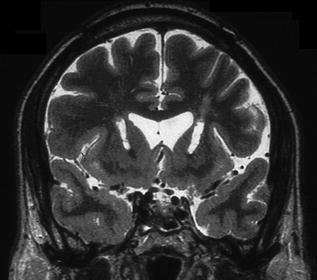

Fig. 8.3
Coronal T2-weighted MRI scan demonstrating BACA a year after the lesions were made in TRMDD
8.3.3 Bilateral Subcaudate Tractotomy (BSCT)
Geoffrey Knight performed BSCT in 1964 [7], which involved stereotactic insertion of a row of radioactive yttrium (90Y) seeds to destroy tissue below the head of the caudate nuclei in the frontal lobes. These lesions disconnect the subfontal and prefrontal cortex to the thalamus, hippocampus and amygdala. Figure 8.4 depicts BSCT.
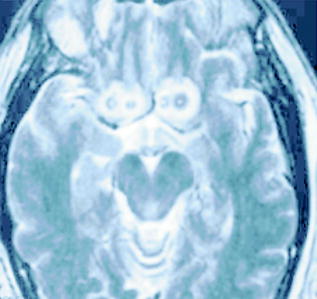

Fig. 8.4
Axial T2-weighted MRI scan image depicting BSCT
8.3.4 Bilateral Limbic Leukotomy (BLL)
BLL is essentially a combined procedure consisting of BACI and BSCT on the assumption that a combined procedure has a better chance of success than BACI or BSCT alone. This procedure was introduced in 1973 by Kelly et al. [13]. Figure 8.5 shows an MRI of BLL .
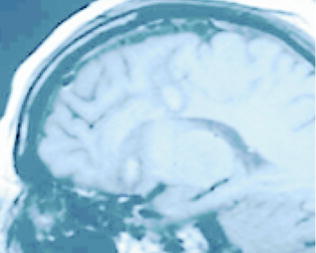

Fig. 8.5
Sagittal T1-weighted MRI image depicting BACI + BSCT = BLL
8.4 Techniques to Perform Ablative Surgery for TRMDD
Creation of a lesion at a target in the brain such as BACI, BACA, or BSCT is performed using any stereotactic frame (e.g. Cosman-Robertson-Wells (CRW), ZD or Leksell frame) and MRI or merged MRI and CT images, using stereotactic software (Fig. 8.6).
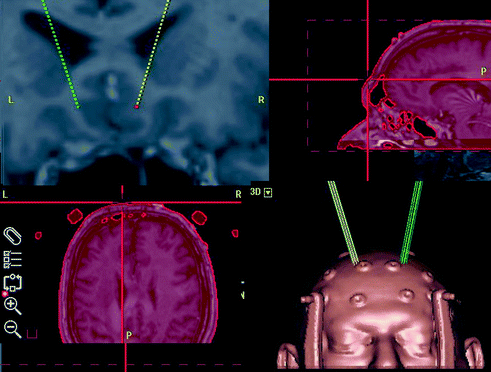

Fig. 8.6
Screen shot of stereotactic plan for subgenu cingulum (top left), fused MRI and CT (top right and bottom left) and 3D image of the plan (bottom right)
Tissue ablation can be achieved by several methods as follows.
8.4.1 Radiofrequency Thermocoagulation
Radiofrequency thermocoagulation has been used for several decades to generate lesions in the treatment of intractable pain, movement disorders and psychiatric disorders . This is the main technique I have used to generate BACI and BACA in our cohort of TRMDD. A radiofrequency electrode with 3 mm exposed tip, 3 mm in diameter was used in BACI and 6 mm exposed tip, 3 mm in diameter was used in BACA. The aim of the ablative procedure was to generate a lesion of at least 8 mm wide and 12 mm long using a lesion generator (Radionics, Boston, MA, USA). The temperature was raised to 70° for 90 s twice at the target point followed by extension along the track trajectory to cover 12 mm in length. The advantage of stereotactic thermocoagulation is its portability, immediate lesion generation, no ionizing radiation and low cost. However, there is no real time feedback regarding the location or size of the lesion, but this can be overcome by performing immediate MRI scan to assess the exact location and size of the lesion.
8.4.2 Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS)
Lars Leksell first suggested SRS in 1978, where gamma rays were focused stereotactically to generate tissue damage at the target area. The main advantage of this technique is non-invasiveness, however, it does take some time for the lesions to generate and it does not have real time monitoring of the location or size of the lesions. Although the cost of a gamma unit is prohibitive if the gamma unit is only used for low volume of surgical procedures such as BACI or BACA, most gamma units however are currently available in major centers to perform other procedures and therefore it might be more economic to use these units to perform ablative surgery for psychiatric illnesses.
8.4.3 MRI Guided High Frequency Focused Ultrasound (MgHFU)
MgHFU is an emerging technology using MRI scan for guidance and intraoperative monitoring and use high frequency focused ultrasound to create lesions in the brain. The main advantages are the non-invasiveness, no ionizing radiation, real time monitoring of the location and size of the lesions and the immediate formation of the desired lesions . However, the system is costly, not widely available and requires total head shave.
8.4.4 Stereotactic Implantation of Radioisotopes
Stereotactic implantation of radioisotopes can be used to generate lesions in the brain e.g. the use of radioactive yttrium in BSCT, however the use of radioisotopes to generate brain lesions have disappeared in recent decades because SRS is more user friendly and less invasive technology than implanting radioisotopes.
8.5 Outcome of Ablative Surgery for TRMDD
In general published data suggest that ablative stereotactic surgery for TRMDD results into 40–60 % response rate. Response is defined as 50 % or more improvement on a validated depression scoring system such as Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD) [8], or the Montgomery-Asberg Depression rating Scale (MADRS) [20].
An early report of the results of BACI was reported in 1973, where the authors classified 85 % as a “success” [1]. Another study included 198 patients with major affective disorders was reported in 1987 with a follow up average of 8.6 years. 62 % of the patients demonstrated long-term improvements [2]. Furthermore, there were no deaths and very low morbidity in this series; 1 % developed seizures, 0.3 % hemiplegia and 9 % suicide rate. All patients who committed suicide after surgery had suicidal ideation before surgery with more than 72 % had attempted suicide before surgery. Furthermore, subsequent neuropsychological assessment of a cohort of these patients found to have no diminution of intellectual function or emotional tone and no evidence of neurological or behavioral deficits except a decline in Taylor Complex Figure task [27]. A more recent study reported 53 % response rate [24]. In my own experience the response rate in patients with treatment refractory major depression that failed on average 4.6 adequate treatment trials of anti-depressive therapies including ECT (Table 8.1) 60 % responded and 40 % remitted after BACI at 12 months follow up.
Table 8.1
Clinical characteristics of TRMDD treated at the Scottish National Centre of NMD
BACI
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

| ||
|---|---|---|




