Fig. 1
Modified Garcia Score at 24 and 48 h (maximum score of 18). The SAH group had significantly lower modified Garcia Scores at both 24 and 48 h compared to the other three experimental groups. *p < 0.05 compared with SAH group at 24 h. **p < 0.05 compared with SAH group at 48 h. Error bars indicate standard error
Decreased Histological Evidence of Brain Injury with Valproic Acid Treatment
SAH mice treated with VPA had significantly less brain injury compared with untreated SAH mice, as measured by the number of fluoro-jade b positive cells on coronal brain sections (Fig. 2a). Also, the SAH group had significantly more fluoro-jade b positive cells compared to the Sham and Sham + VPA groups. There were no significant differences in the number of fluoro-jade b positive cells between Sham and Sham + VPA groups. ANOVA statistical analysis revealed that there were significant differences in the number of caspase-3 positive neurons between experimental groups (p = 0.04). However, after correcting for multiple statistical comparisons, there was only a trend toward decreased number of caspase-3 positive neurons in the SAH + VPA group compared with the SAH group (p = 0.01) (Fig. 2b).
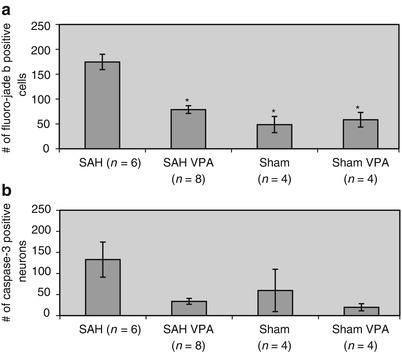

Fig. 2
Histological assessment of brain injury at 48 h. (a) Counts on coronal brain sections of fluoro-jade b positive cells. The SAH group had decreased number of fluoro-jade b positive cells compared with all the other experimental groups. (b) Counts on coronal brain sections of Caspase-3 positive neurons co-immunostained with NeuN. After correcting for multiple statistical comparisons, there was only a trend toward decreased number of Caspase-3 positive neurons in the SAH + VPA group compared with the SAH group. *p < 0.05 compared with SAH group. Error bars indicate standard error
Vasospasm Unaffected by Valproic Acid Treatment
Mice in the SAH and SAH + VPA groups had significantly increased large-vessel vasospasm on histology compared with Sham or Sham + VPA groups (Fig. 3). However there was no significant difference in vasospasm between SAH mice treated with VPA and untreated SAH mice. Also, there was no difference in vasospasm between Sham and Sham + VPA groups.
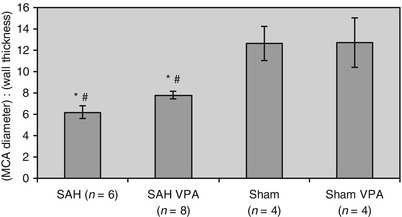

Fig. 3
Histological assessment of vasospasm. There was no significant difference in the degree of vasospasm between SAH and SAH + VPA groups. There was significantly more vasospasm in SAH and SAH + VPA groups compared with Sham and Sham + VPA groups. *p < 0.05 compared with Sham group. #p < 0.05 compared with Sham + VPA group. Error bars indicate standard error
Discussion
This preliminary study demonstrated that administration of VPA in the acute setting resulted in improved neurobehavioral outcomes and decreased histological evidence of brain injury in a prechiasmatic injection model of SAH in mice. Large-vessel vasospasm was not affected by VPA and therefore may not mediate the neuroprotective effect of VPA, although it was only measured at one time after the SAH. Because molecular studies were not performed in this study, it is not clear by which mechanism VPA decreases brain injury. In a rat model of transient focal cerebral ischemia, the investigators have suggested that VPA is neuroprotective as a result of upregulation of heat shock proteins and inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDAC) [6]. Through its inhibition of HDAC1, VPA can increase histone acetylation resulting in a relaxed chromatin configuration and an increase in overall gene transcription [1]. The increased gene expression, with some genes possibly related to neuronal survival, may explain the improved neurological outcome and decreased brain injury after SAH induction. VPA may also reduce excitotoxic damage in the neurons through its inhibition of GABA degradation [1].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





