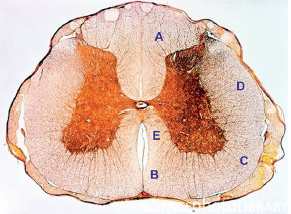
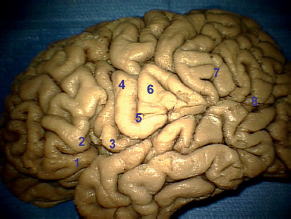
2Anatomy A lesion in the pulvinar nucleus of the thalamus can result in: A. Neglect syndromes B. Anosmia C. Contralateral sensory loss D. Endocrine dysfunction and abnormalities E. Memory difficulties A 67-year-old woman presents for follow-up 4 months after a stroke. She complains of her eyelids “twitching.” She is found to have palatal myoclonus on physical exam. Her stroke likely involved what region of the brain? A. Nucleus ambiguus B. Tectospinal tract C. Rubro-olivary tract/central tegmental tract (triangle of Mollaret) D. Body of the caudate nucleus E. Lateral lemniscus The ventral tegmental area sends projections through what neuroanatomic structure to the nucleus accumbens as part of the dopaminergic mesolimbic system (involved in reward circuitry)? A. Medial forebrain bundle B. Lateral hypothalamus C. Ventral pallidum D. Prefrontal cortex Use the following answers for questions 4 and 5: A. Area postrema B. Nucleus tractus solitarius C. Nucleus prepositus hypoglossi D. Nucleus ambiguus E. Inferior salivary nucleus What structure is the target for taste afferent fibers? What structure is the autonomic center for vomiting? What skin mechanoreceptors are best at sensing both rapid vibration and pressure? A. Ruffini endings B. Meissner corpuscles C. Merkel disks D. Pacinian corpuscles E. Free nerve endings In what ventricular structure is cerebrospinal fluid not produced by the choroid plexus? A. Roof of the fourth ventricle B. Floor of the third ventricle C. Lateral recess of the foramen of Luschka D. Temporal horn of the lateral ventricle E. Roof of the third ventricle The deep petrosal nerve is what type of nerve with what function? A. Sensory nerve that unites with the greater superficial petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal B. Sympathetic nerve that unites with the lesser superficial petrosal nerve to form the vidian nerve C. Sympathetic nerve that unites with the greater superficial petrosal nerve to form the vidian nerve D. Sensory nerve that unites with the lesser superficial petrosal nerve to form the nerve of the pterygoid canal What nerve innervates the skin between the hallux and the second toe? A. Superficial peroneal nerve B. Medial dorsal cutaneous nerve C. Intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve D. Deep peroneal nerve E. Tibial nerve What is another name for the medial distal striate artery? A. Tentorial artery (of Bernasconi and Cassinari) B. McConnell capsular artery C. Frontopolar artery D. Recurrent artery of Heubner E. Medial lenticulostriate artery What midbrain anatomic structure is responsible for pain modulation? A. Superior colliculus B. Substantia nigra C. Crus cerebri D. Red nucleus E. Periaqueductal gray matter A patient has an intractable nosebleed following transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. What artery likely is injured? A. Middle meningeal artery B. Infraorbital artery C. Internal maxillary artery D. Superior hypophyseal artery E. Anterior ethmoidal artery A patient presents with a winged scapula. What other nerve besides the long thoracic and dorsal scapular nerves may be injured? A. Suprascapular nerve B. Spinal accessory nerve C. Thoracodorsal nerve D. Lateral thoracic nerve What leptomeningeal structure is composed only of a single layer? A. Intracranial dura B. Spinal dura C. Pia mater D. Arachnoid In this spinal cord cross-sectional image, what letter corresponds to the location of the spinothalamic tract? A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E The supplementary motor area is found at what location: A. Along the midline surface of the cerebral hemisphere just anterior to the primary motor cortex leg area B. In the parietal operculum just rostral to the lateral sulcus C. Along the lateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere just anterior to the primary motor cortex arm area D. Within the pars opercularis and pars triangularis of the inferior frontal gyrus E. Along the medial surface of the cerebral hemisphere continuous with the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe Which structure runs through the petrotympanic fissure? A. Pterygoid artery B. Posterior deep temporal artery C. Chorda tympani D. Lingual nerve E. Greater superficial petrosal nerve Which bone does not contribute to both the orbit and nasal septum? A. Frontal bone B. Ethmoid bone C. Maxillary bone D. Palatine bone In the hand, what muscles are innervated by the median nerve? A. Abductor pollicis brevis B. Lumbricals 3 and 4 C. Adductor pollicis D. Opponens digiti minimi E. Abductor pollicis longus Embryologically, the pituitary is composed of the adenohypophysis and neurohypophysis. Rathke cleft cysts are derived from the persistence of what primary germ layer? A. Ectoderm B. Neuroectoderm C. Mesoderm D. Endoderm The inferior aspect of the cuneus is bounded by what structure? A. Tentorium B. Parieto-occipital sulcus C. Lingual gyrus D. Collateral eminence E. Calcarine sulcus From superior to inferior (rostral to caudal), what are the correct layers, in order, of the roof of the third ventricle? A. Fornix, tela choroidea, velum interpositum, tela choroidea, and choroid plexus B. Choroid plexus, velum interpositum, tela choroidea, and fornix C. Fornix, velum interpositum, tela choroidea, choroid plexus, and tela choroidea D. Tela choroidea, fornix, tela choroidea, velum interpositum, and choroid plexus E. Fornix, velum interpositum, and choroid plexus What structure courses between the petrous temporal bone and basilar part of the occipital bone and drains blood from the cavernous sinus to the sigmoid sinus? A. Superior petrosal sinus B. Inferior petrosal sinus C. Vein of Labbé D. Basal vein of Rosenthal E. Straight sinus Which structure primarily is responsible for carrying input to the cerebellum from the contralateral cerebral cortex? A. Inferior cerebellar peduncle B. Middle cerebellar peduncle C. Superior cerebellar peduncle D. Cerebral peduncle What structure in the medial limbic circuit is the major output of the thalamus? A. Hippocampus B. Amygdala C. Fornix D. Entorhinal cortex E. Cingulate gyrus What is an accurate description of the location of the flocculonodular lobe of the cerebellum? A. Rostral to the primary fissure B. Caudal to the primary fissure C. Anterior to and between the anterior and posterior cerebellar lobes D. Midsagittal E. Rostral to the anterior lobe and posterior to the sylvian aqueduct Afferents to the subthalamic nucleus originate in what structure? A. Thalamus B. Red nucleus C. Globus pallidus D. Cerebellum E. Substantia innominata The lateral cord of the brachial plexus is formed from what structure(s)? A. Anterior divisions of the upper and middle trunks B. Nerve roots C5, C6, and C7 C. Posterior divisions of the superior, middle, and inferior trunks D. Anterior division of the inferior trunk E. Posterior division of the superior trunk The ventral posterior nucleus of the thalamus sends information to which Brodmann area(s)? A. Areas 1, 2, and 3 B. Area 4 C. Area 17 D. Areas 39 and 40 E. Area 44 The sural nerve provides sensation to the posterolateral surface of the leg, lateral foot, and the fifth toe. It is formed by contributions from which nerve(s)? A. Tibial nerve B. Common peroneal nerve C. Tibial and common peroneal nerves D. Superficial peroneal nerve E. Tibial and superficial peroneal nerves If the facial nerve is sectioned just proximal to the nerve to the stapedius, what clinical finding would be expected other than paresis of the facial musculature? A. Decreased lacrimation B. Decreased taste in the anterior two thirds of the tongue C. Increased salivation D. Decreased sensation in the nasopharynx and palate mucous membranes What muscle is innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve? A. Flexor pollicis brevis B. Abductor pollicis brevis C. Flexor carpi radialis D. Pronator quadratus E. Abductor pollicis longus Brodmann area 39 may be considered part of what cortical area? A. Broca area B. Visual cortex C. Somatosensory association cortex D. Wernicke area E. Auditory cortex The inferior leaflet of the Liliequist membrane separates the interpeduncular from the prepontine cistern. The superior leaflet separates which two cisterns medially? A. Chiasmatic and crural cisterns B. Interpeduncular and crural cisterns C. Interpeduncular and chiasmatic cisterns D. Ambient and quadrigeminal cisterns E. Interpeduncular and ambient cisterns Innervation of the facet joints in the lumbar spine is provided by what nerve? A. Lateral branch of the dorsal ramus B. Ventral ramus C. Medial branch of the dorsal ramus D. Ramus communicans E. Dorsal root Which of the following is true regarding the cerebellothalamic tract (dentatothalamic tract)? A. It is an uncrossed tract arising from the dentate nucleus that passes through the superior cerebellar peduncle and terminates in the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus. B. It is an uncrossed tract arising from the dentate nucleus that passes through the middle cerebellar peduncle and terminates in the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus. C. It is a crossed tract arising from the dentate nucleus that passes through the superior cerebellar peduncle and terminates in the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus. D. It is a crossed tract arising from the dentate nucleus that passes through the middle cerebellar peduncle and terminates in the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus. E. It is an uncrossed tract arising from the dentate nucleus that passes through the inferior cerebellar peduncle and terminates in the ventral anterior nucleus of the thalamus. Pain and temperature fibers from the face are relayed to what nucleus? A. Mesencephalic nucleus of cranial nerve V B. Ventral posterior lateral nucleus of the thalamus C. Principal sensory nucleus of cranial nerve V D. Solitary nucleus E. Spinal nucleus of cranial nerve V What is the most proximal artery originating from the carotid artery distal to the ophthalmic artery? A. Posterior communicating artery B. Anterior choroidal artery C. Superior hypophyseal artery D. Inferior hypophyseal artery The vertebral artery often is divided into numbered segments. What segment exits the axis and curves posteromedially in a groove on the atlas and enters the foramen magnum? A. V2 B. V3 C. V4 D. V5 What type of nerve ending is slowly adapting? A. Meissner corpuscle B. Pacinian corpuscle C. Merkel disk D. Hair follicle receptor E. A-delta free nerve ending What anatomic reference points form the stephanion? A. Junction of the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones B. Junction of the lambdoid, occipitomastoid, and parietomastoid sutures C. Junction of the coronal and sagittal sutures D. Junction of the coronal suture and superior temporal line The stria medullaris thalami connect what neural structures? A. Globus pallidus and the field of Forel H B. Septal nuclei and the habenular nuclei C. Globus pallidus interna and the thalamic fasciculus D. Amygdalae E. Ventral tegmental area and the nucleus accumbens Corticospinal tracts terminate on which structures in the spinal cord? A. Spinal gray interneurons in Rexed lamina IX B. Alpha motor neurons in Rexed lamina VII C. Gamma motor neurons in the anterior gray horn D. Spinal gray interneurons in Rexed lamina VII E. Gamma motor neurons in Rexed lamina IX Proprioception sense is carried in what decussating tract? A. Spinothalamic tract B. Posterior columns C. Dorsal spinocerebellar tract D. Ventral spinocerebellar tract E. Corticobulbar tract The acoustic reflex to loud sound involves what circuitry? A. Cranial nerve V to the tensor veli palatini muscle B. Cranial nerve V to the stapedius muscle C. Cranial nerve V to the levator palatini muscle and cranial nerve VII to the posterior belly of the digastrics muscle D. Cranial nerve V to the tensor tympani muscle and cranial nerve VII to the stapedius muscle The transverse component of the transverse ligament of the atlas attaches to what structure? A. Occipital condyle B. Medial surface of the lateral mass of C1 C. Medial surface of the pars interarticularis of C2 D. Posterior aspect of the body of C2 E. Posterior arch of C1 Damage to the anterior hypothalamus may cause what dysfunction? A. Obesity B. Cachexia C. Hypothermia D. Impaired memory E. Hyperthermia The amygdala projects to which area of the insula? A. Operculum B. Anterior short gyri C. Posterior long gyrus D. Cingulate E. Claustrum What deep cerebellar nucleus is located most laterally? A. Dentate B. Globose C. Fastigial D. Emboliform E. Inferior olivary nucleus What percentage of people have a balanced configuration of the circle of Willis? A. 5% B. 20% C. 40% D. 60% E. 80% The nucleus pulposus is the remnant of what embryonic structure? A. Neural tube B. Anterior neuropore C. Posterior neuropore D. Neural plate E. Notochord What is the arterial supply for the optic tract? A. Ophthalmic artery B. Anterior communicating, posterior communicating, and posterior cerebral arteries C. Posterior communicating, posterior cerebral, and anterior choroidal arteries D. Lateral posterior choroidal artery What Brodmann area corresponds to primary visual cortex? A. Area 41 B. Area 19 C. Area 17 D. Area 39 How many primary ossification centers are present for the C1 (atlas) and C2 (axis) vertebrae, respectively? A. One and three B. Two and four C. Three and five D. Five and three E. Three and one The afferent and efferent projections to and from the medial geniculate body, respectively, are from what structures? A. Superior colliculus; visual cortex B. Retina; visual cortex C. Reticular formation; dorsal thalamic nuclei D. Inferior colliculus; auditory cortex E. Mammillary bodies; cingulum What blood vessel is at risk of injury during a Chiari decompression? A. Lateral medullary segment of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery B. Telovelotonsillar segment of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery C. Tonsillomedullary segment of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery D. Posterior spinal artery E. V2 segment of the vertebral artery Number 2 in this image represents what structure?
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree