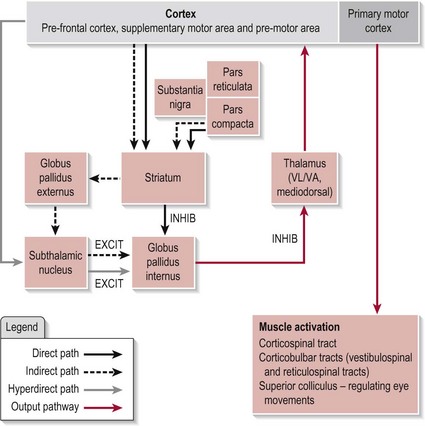
Chapter 11 The functional nuclei of the basal ganglia (BG) include: • Striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen), which receives information from all parts of the cerebral cortex except the primary visual and auditory cortices • Globus pallidus internus (GPi) • Globus pallidus externus (GPe) • Substantia nigra (SN) – pars reticulata (pr) and pars compacta (pc) which contain dopamine-producing cells. The circuitry between these functional nuclei forms several pathways, the direct, indirect and hyperdirect, the arrangement of which can be seen in Figure 11.1. The BG is also topographically arranged with each body part represented relative to its innervations. As well as the motor loop shown in Figure 11.1, there are three other loops within the BG which have their origins in different cortical areas and carry out specific functions via similar circuitry. Although previously described as discrete parallel loops, recent evidence indicates that there is a high level of interaction between these loops. However, the selection function described above is true for all of them, the motor loop (voluntary movement or learning), the limbic loop (emotions) and the associative loop (cognition and sensory integration). Based on its anatomical connections with the nociceptive system, the BG is also considered crucial in pain modulation. It appears that the interaction of several of these loops make it possible for the BG to influence several dimensions of pain (sensory discrimination, affective and cognitive) as well as the modulation of pain itself via its filtering role. The pre-frontal cortex (S2.7) provides an idea for movement, a goal, based upon the internal and external environment. A relevant movement plan is selected from learned stored programmes in the supplementary motor area (SMA) and pre-motor area (PMA) (S2.7
Basal ganglia
Basic anatomy
Function of the basal ganglia
Function of the BG in motor control
The big picture
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Basal ganglia