Staining method
Pathology
Hematoxylin–eosin (HE)
Evaluation of muscle fiber size and shape, vascular and nerve structures, infiltrates, general histology (Fig. 9.1)
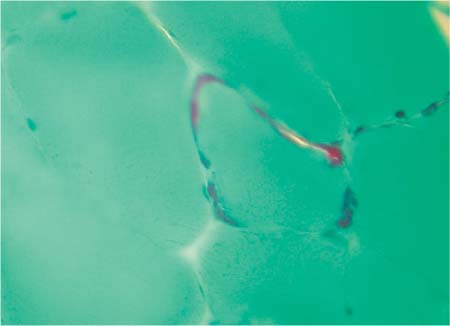
Gomori trichrome
Detection of ragged red fibers (mitochondrial dysfunction, Fig. 9.2), rimmed vacuoles (inclusion bodies, Fig. 9.3)
Oil red O
Evaluation of lipid deposition (Fig. 9.4)
Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS)
Glycogen deposition
Acid phosphatase
Lysosomal enzyme, indicative of degenerative changes of muscle fibers
Cytochrome C oxidase (COX)
Mitochondrial enzyme (Fig. 9.6)
Succinate dehydrogenase (SDH)
Mitochondrial enzyme
ATPase
Differentiation between type I and type II muscle fibers;.ber type grouping (Fig. 9.7)
NADH-tetrazolium reductase (NADH-TR)
Enzyme in mitochondria, T tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum, target fibers
Fig. 9.1 Histology of normal muscle (HE stain). The section shows muscle fibers of normal size and shape, and normal vascular and nerve structures. Infiltrates are absent.
Fig. 9.2
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree