Classification of mood disorders
Bipolar affective disorder
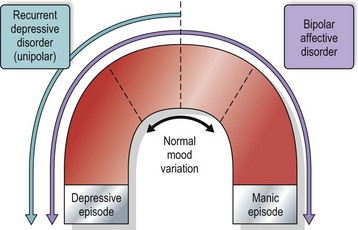
In the most commonly used classification system of mood disorders, depression and mania are viewed as representing polar extremes, as illustrated in Figure 1. ‘Bipolar’ disorders are those in which both extremes of depression and elation occur, usually in separate depressive and manic episodes, but sometimes together in what are known as mixed affective episodes. Bipolar affective disorder, previously known as manic depression, is diagnosed when a person has had two or more episodes of mood disorder in total and at least one of these has been a manic or mixed affective episode. Any of the acute affective episodes shown in Table 1 can occur during the course of the condition and, at different times in their lives, some people with bipolar disorder will experience most, if not all, of these different mood states.
Table 1 ICD10 classification of mood disorders
| Single episode | |
| Manic episode | Hypomania |
| Mania, without psychotic symptoms | |
| Mania, with psychotic symptoms | |
| Depressive episode | Mild |
| Moderate | |
| Severe, without psychotic symptoms | |
| Severe, with psychotic symptoms | |
| Mixed affective episode | |
| Recurrent episodes | |
| Bipolar affective disorder | Current episode mania |
| Current episode depressive | |
| Current episode mixed | |
| Recurrent depressive disorder | Current episode mild, moderate or severe |
| (Major Depressive Disorder in DSM4) | |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree