Fig. 7.1
Young female with symptoms of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Sagittal T1-weighted image with spectral fat suppression (a) after intrathecal application of contrast agent shows accumulation of CSF (bright) in the thecal sac and in the ventral epidural space. Notice the small dural membrane between these two spaces. Axial T1-weighted image with spectral fat suppression (b) shows the pronounced collection of contrast agent along the left sheet of the nerve root
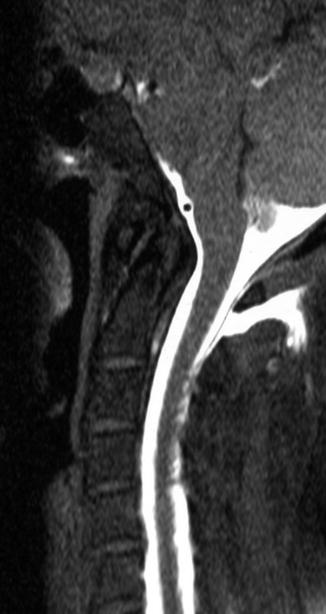
Fig. 7.2
Sagittal T1-weighted image with spectral fat suppression after intrathecal application of contrast agent in a patient with symptoms of spontaneous intracranial hypotension after chiropractic maneuver. Frank CSF collection is seen in the dorsal soft tissue. Note the dorsal dural membrane bordering upon the spinal canal
7.6 Pitfalls of Contrast-Enhanced MR Myelography
1.




Only examinations with full opacification of the thecal sac including the foramen magnum should be assessed. Cases with incomplete filling should be reevaluated with a delayed MR examination.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








