CPA Mass, Adult
H. Ric Harnsberger, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Vestibular Schwannoma
Less Common
Meningioma, CPA-IAC
Epidermoid Cyst, CPA-IAC
Aneurysm, CPA-IAC
Arachnoid Cyst, CPA-IAC
Metastases, CPA-IAC
Rare but Important
Neurofibromatosis 2, CPA-IAC
Sarcoidosis, CPA-IAC
Choroid Plexus Papilloma, CPA
Lipoma, CPA-IAC
Ependymoma, CPA
Pseudotumor, Intracranial
Schwannoma, Facial Nerve, CPA-IAC
Schwannoma, Jugular Foramen
Hemangioma, IAC
Neurenteric Cyst
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Idealized imaging protocol in evaluating CPA mass lesions
T1 C+ fat-saturated MR is gold standard
Fat-saturation differentiates lipoma from vestibular schwannoma
Add DWI for possible epidermoid
Add GRE for aneurysm wall clot & calcification; tumor calcifications
T2 thin-section, high-resolution, MR gives more surgical data when vestibular schwannoma diagnosed
Amount of CSF cap in lateral IAC
Assessment of relationship to cochlear nerve canal
If small schwannoma, nerve of origin
Knowledge of relative incidence of lesions key in cerebellopontine angle
Vestibular schwannoma ˜ 90% all CPA-IAC masses
Meningioma, epidermoid cyst, aneurysm, arachnoid cyst together represent ˜ 8% all CPA-IAC masses
All other diagnoses in differential list ˜ 2% of CPA-IAC masses
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Vestibular Schwannoma
Morphology: Ovoid intracanalicular mass (IAC); “Ice cream on cone” shape (CPA-IAC)
T1 C+ MR: Enhancing ± intramural cysts
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Meningioma, CPA-IAC
Morphology: “Mushroom” dural-based mass capping IAC asymmetrically
T1 C+ MR: Enhancing ± dural “tails” ± CSF-vascular cleft if CPA component is larger
25% of CPA meningiomas have extension/dural tail into IAC
Epidermoid Cyst, CPA-IAC
Morphology: Insinuating ± scalloping brainstem margin
T1 C+ MR: Nonenhancing; may be difficult to see
DWI: Restricted diffusion (high signal) makes diagnosis
Aneurysm, CPA-IAC
Morphology: Ovoid or fusiform; rarely IAC
T1 & T1 C+ MR: Complex signal mass from wall calcification, clot & flow
MRA, CTA, or angiography sort out diagnosis
Arachnoid Cyst, CPA-IAC
Morphology: Fills cistern with rounded margins
Imaging
T1 C+ MR: No enhancement
FLAIR attenuates
DWI: No restricted diffusion
Metastases, CPA-IAC
Morphology: Irregular, invasive margins
T1 C+ MR: Single or multiple enhancing masses in CPA area
4 sites primarily involved: Flocculus, choroid plexus, arachnoid-dura, or pia
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Neurofibromatosis 2, CPA-IAC
Morphology: Bilateral ovoid IAC or “ice cream on cone” CPA-IAC masses
T1 C+ MR
Bilateral enhancing CPA-IAC masses pathognomonic of NF2
Other schwannomas & meningiomas may be present
Sarcoidosis, CPA-IAC
Laboratory: CSF lymphocytosis; ↑ ↑ blood angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE)
Morphology: En plaque or nodular dural lesion(s)
T1 C+ MR: Enhancing multifocal dural-based lesions
Choroid Plexus Papilloma, CPA
Morphology: Dumbbell shape with 4th ventricle and CPA cistern components
Pear-shaped if begins in foramen of Luschka
T1 C+ MR: Avidly enhancing mass in 4th ventricle projecting through foramen of Luschka into CPA cistern
Lipoma, CPA-IAC
Morphology: Ovoid if IAC; CPA lesion may be broad-based against brainstem
CT: Fat-density lesion of CPA ± IAC ± inner ear
T1 MR: High signal lesion disappears with fat-saturation
Caveat: If T1 C+ without fat-saturation, may be mistaken for vestibular schwannoma
Ependymoma, CPA
Morphology: Irregular soft tumor squeezes out through 4th ventricle foramen of Luschka into CPA cistern
Tumor margins amorphous
CT: Calcifications in 50%
T1 C+ MR: Heterogeneous enhancement of solid tumor components
Marginal enhancement of tumor cyst wall
Pseudotumor, Intracranial
Morphology: En plaque
T1 C+ MR: Thickened, enhancing dura
Caveat: May mimic meningioma, sarcoidosis or metastatic disease
Schwannoma, Facial Nerve, CPA-IAC
Morphology: CPA-IAC mass with “labyrinthine tail”
CT: Labyrinthine segment CN7 may be enlarged
T1 C+ MR: Enhancing tubular mass in CPA-IAC and labyrinthine segment CN7
Caveat: If not labyrinthine segment CN7 involvement, cannot differentiate from vestibular schwannoma
Schwannoma, Jugular Foramen
T1 C+ MR: Enhancing mass arising from jugular foramen
Mass projects cephalad into CPA cistern
Hemangioma, IAC
Morphology: Ovoid IAC mass with punctate calcifications
CT: Punctate calcifications in IAC mass
T1 C+ MR: Enhancing IAC mass with focal low signal foci (calcifications)
Neurenteric Cyst
Morphology: Rounded ovoid mass in prepontine cistern
MR: Intermediate to high signal T1 prepontine mass
Caveat: T1 increased signal differentiates from epidermoid cyst
Image Gallery
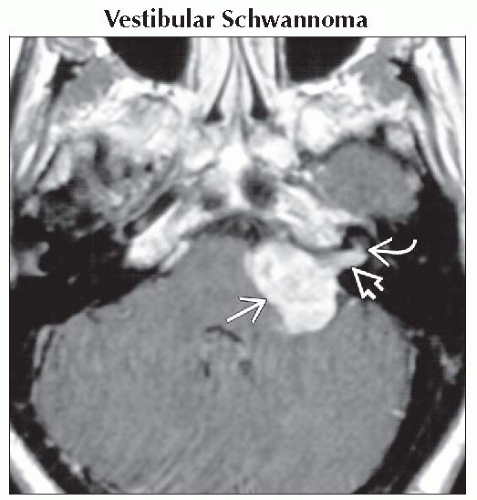 Axial T1 C+ MR reveals enhancing mass filling the CPA
 & internal auditory canal & internal auditory canal  . Note the cochlear nerve canal is involved . Note the cochlear nerve canal is involved  , making resection with hearing preservation difficult. , making resection with hearing preservation difficult.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|