Cranial Nerves V and VII
The Face
BACKGROUND
Facial nerve: VII
Peripheral function can be summarised as ‘face, ear, taste, tear’:
With lower motor neurone (LMN) facial weakness, all muscles are affected.
With upper motor neurone (UMN) facial weakness, the forehead is relatively preserved.
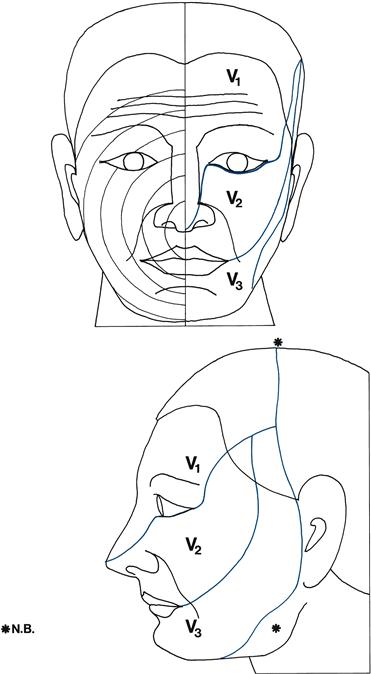
Trigeminal nerve: V
Motor
The trigeminal nerve supplies the muscles of mastication.
What to do
Look at the face generally.
FACIAL NERVE: WHAT TO DO
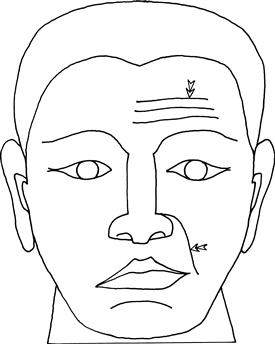
Look at the symmetry of the face.
Ask the patient to:
• show you his teeth (demonstrate)
• whistle
• close his eyes tightly as if he had soap in them (demonstrate)
– assess the strength by trying to open his eyes with your fingers
Look out for symmetrical movement.
Compare the strength of the forehead and lower face.
In LMN lesions you can see the eye turn upwards on attempted closure—Bell’s phenomenon.
Other functions of the facial nerve
Look at the external auditory meatus—the cutaneous distribution of VII. Note any vesicles suggestive of herpes zoster.
Provides taste to the anterior two-thirds of tongue.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree