Cyst with Nodule
Troy Hutchins, MD
Karen L. Salzman, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Neurocysticercosis
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Ganglioglioma
Hemangioblastoma
Less Common
Metastases, Parenchymal
Glioblastoma Multiforme
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma
Abscess
Opportunistic Infection, AIDS, Toxoplasmosis
Parasites, Miscellaneous
DNET
Rare but Important
Desmoplastic Infantile Ganglioglioma
Schwannoma, Intraparenchymal
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Cystic lesions with solid nodular components can be divided into 2 categories
Lesions that typically demonstrate cyst with nodule morphology
Neurocysticercosis (NCC), pilocytic astrocytoma, ganglioglioma, hemangioblastoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma (PXA), desmoplastic infantile ganglioglioma (DIG), intraparenchymal schwannoma
Lesions that may demonstrate cyst with nodule morphology
Metastases, glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), abscess, toxoplasmosis, parasites, DNET, thrombosed AVM
Although metastases, abscesses, & GBMs do not classically present as “cysts with nodules”, they are included because of their overall prevalence
Statistically, the atypical form of these common diseases may be more likely than some of the other “classic” cyst with nodule lesions
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Neurocysticercosis
Cyst with “dot” inside representing scolex
Imaging appearance varies with stage; increased enhancement & edema when organism dies (inflammatory host response)
Location: Convexity subarachnoid space > > cisterns > parenchyma > ventricles
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Cerebellar cystic mass with mural nodule in a child; rarely supratentorial
T1 C+: Nodule shows intense but heterogeneous enhancement
Ganglioglioma
Cortically based, slow-growing enhancing mass in older child or young adult
Cyst with nodule most common, may be solid
Most common tumor to cause temporal lobe epilepsy
Hemangioblastoma
Parenchymal posterior fossa cyst with nodule mass in an adult
T1 C+: Nodule abuts pial surface & shows intense, homogeneous enhancement
Multiple in von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (VHL) (25-40% of hemangioblastomas)
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Metastases, Parenchymal
Discrete, gray-white interface mass(es) with adjacent vasogenic edema
Multiplicity, history of primary malignancy, helpful if present
Solitary metastasis may mimic GBM
Glioblastoma Multiforme
Malignant white matter mass with central necrosis
Predilection to spread across midline along corpus callosum; “butterfly glioma”
T1 C+: Thick, irregular, nodular enhancing margins
T2/FLAIR: Surrounding hyperintensity & mass effect reflect edema + infiltrative tumor
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma
Cortically based cyst + nodule ± involvement of adjacent meninges
T1 C+
Enhancing nodule
Look for thickening, enhancement of adjacent meninges
70% have “dural tail”
Temporal lobe predominance; young adult
Abscess
T2 Hypointense rim with surrounding edema classic
T1 C+: Enhancing capsule thinnest at ventricular side
DWI: Cystic component bright (diffusion restriction)
Opportunistic Infection, AIDS, Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis: Enhancing central nodules with peripheral rim = “target” lesions
Location: Basal ganglia > hemispheres
Clinical: Immunocompromised patient
Parasites, Miscellaneous
Multiple enhancing lesions typical
May mimic brain tumor
Travel history critical
DNET
Bubbly, wedge-shaped, cortically based mass “points” toward lateral ventricle
T2: Very hyperintense; nodular, septate; no surrounding edema
T1 C+: No to minimal enhancement, may be nodular
Temporal lobe predominance
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Desmoplastic Infantile Ganglioglioma
Supratentorial cystic/nodular mass with dominance of the cyst
Cortically based nodule with intense enhancement & dural tail
May be massive
Peak age 3-6 months
Schwannoma, Intraparenchymal
Only 1-2% of schwannomas are parenchymal
Cyst with strongly enhancing nodule
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
When hemorrhagic with partial or complete thrombosis, may present as cyst with nodule
Blood breakdown products of various ages; fluid-fluid levels
Alternative Differential Approaches
By location
Posterior fossa: Pilocytic astrocytoma, hemangioblastoma, metastasis
Temporal lobe: Ganglioglioma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, DNET
Gray-white junction: Metastases, abscess
Hemispheric: NCC, Metastases, GBM, infections, DIG, AVM
Patient age
Child & young adult: Pilocytic astrocytoma, ganglioglioma, PXA, DNET
Adult: Hemangioblastoma, GBM, metastases
Any age: Neurocysticercosis, abscess, other infections
Multiple lesions
Metastases (50-55%), NCC (50-70%), hemangioblastoma (VHL), abscesses (septic emboli), toxoplasmosis, parasites
Image Gallery
 Axial T1WI MR shows a frontal
 & left lateral ventricular & left lateral ventricular  “cyst with dot”. The “dot”, or scolex, may be T1 hyperintense “cyst with dot”. The “dot”, or scolex, may be T1 hyperintense 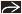 . Edema & enhancement vary with stage & host response. . Edema & enhancement vary with stage & host response.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|