Fig. 1
Topological properties of whole brain network metrics of each group using 3 min sliding time-window. (a) Clustering coefficient (b) local efficiency (c) modularity (d) global efficiency (e) degree of whole brain network for ADHD and control groups as a function of cost
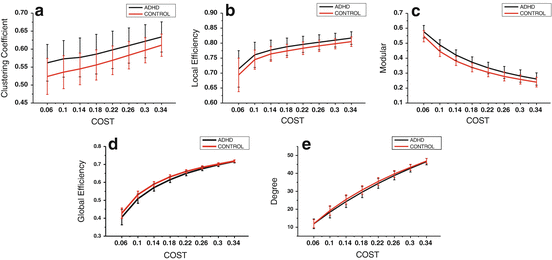
Fig. 2
Topological properties of whole brain network metrics of each group using 1 min sliding time-window. (a) Clustering coefficient (b) local efficiency (c) modularity (d) global efficiency (e) degree of whole brain network for ADHD and control groups as a function of cost
In addition, in order to study the difference of overall properties between two groups, we calculated the characteristic coefficients within the all sliding time-windows at each value over a wide range of cost. Figure 3 shows that, from the overall level of sliding time-window, the clustering coefficient, local efficiency and modularity of ADHD group are larger than that of control group for the costs, but it is converse to global efficiency and degree.
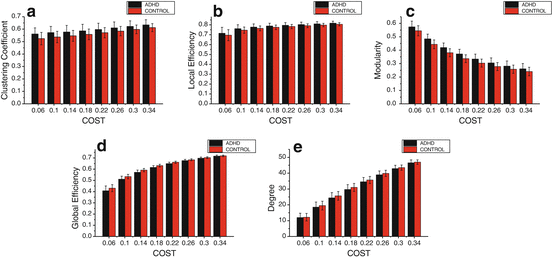

Fig. 3
Topological properties of whole brain network metrics of each group for all sliding time-windows. (a) Clustering coefficient (b) local efficiency (c) modularity (d) global efficiency (e) degree of whole brain network for ADHD and control groups as a function of cost
The clustering coefficient, local efficiency and modularity of ADHD group are always larger than that of control group, and global efficiency and degree of ADHD group are always smaller than that of control group at different widths of sliding time-window or all sliding time-windows for each value over a wide range of cost.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






