Fig. 1
Schematic illustration of the alternate tapping task. Red-colored words mean one-octave high sounds
Each subject completed 500 trials in two conditions; the constant condition (the intervals from the subject’s tapping to the PC tapping were 600 ms) and the variable condition (the intervals were from 400 to 800 ms in five steps every 100 trials; e.g. 600 ms-400 ms-600 ms-800 ms-600 ms).
The EEG was recorded with 27 active scalp electrodes and the BrainAmp ExG MR equipment. The sampling rate was 1,000 Hz. Reference electrodes were placed on the right and left ear lobes. The independent components analyses components which were significantly correlated with the EOG were eliminated from the data as the artifact involved in eye blinks and movements [8]. And further, to reduce the effect of the spreading cortical currents due to volume conductance producing voltage maps covering large scalp areas, current source density conversion was performed. To identify the time-frequency amplitudes during the tasks, we applied wavelet transforms assuming that Morlet’s wavelet function of 7-cycles length, with frequency ranging from 1 to 40 Hz (1-Hz steps).
3 Results
According to behavioral results, both the normal and ASD subjects showed high rates of synchronization with PC’s tapping intervals (i.e. number of presentation of one octave high sound) under the constant condition. On the other hand, under the variable condition, the rates of synchronization of the normal subjects were higher than those of the ASD subjects (Fig. 2).
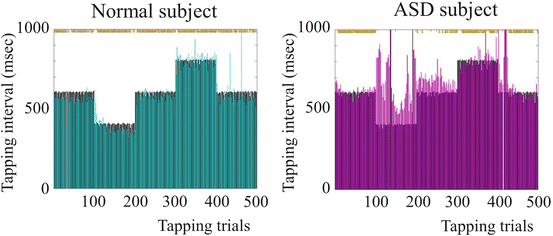

Fig. 2
Example tapping intervals under the variable condition (cyan healthy subject, magenta ASD subject, black PC). Yellow dots indicate trials which different intervals are within thresholds (50 ms)
The EEG results showed the enhancements of alpha amplitudes (10–12 Hz) in the left motor cortex at the subject’s tapping and the alpha decrements at the PC’s tapping. Interestingly, the alpha modulations in the motor cortex were larger for the normal subjects than the ASD subjects under the variable condition, whereas there was no difference under the constant condition.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







