Fig. 1
Effects of TNC on cerebral arteries during the 72-h observation period. (a) Representative India-ink angiograms 24 h after injection; arrow, left internal carotid artery (ICA). (b) Vessel diameter of left intracranial ICA at 24, 48, and 72 h after injection. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean; P value, unpaired t tests. (c) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the left intracranial ICA
Effects of p38 MAPK Inhibitor on TNC-Induced Contraction of the Left ICA in Rats
SB203580 itself had no effects on the vessel diameter of the untreated left ICAs in rats (Fig. 2). In the TNC plus SB203580 group, the vessel diameter of the intracranial ICA was significantly greater than that in the TNC-only group at 24 h after injection (unpaired t tests; Fig. 3a). In histological examination of the intracranial ICA, vasoconstriction was observed in the TNC-only group, but was abolished in the SB203580-treated groups (Fig. 3b).
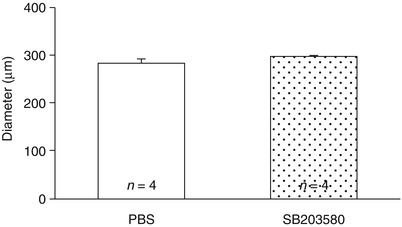
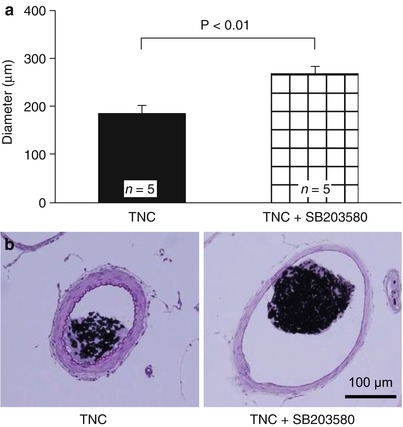

Fig. 2
Effects of p38 MAPK inhibitor on normal cerebral arteries at 24 h after injection. Vessel diameter of the left intracranial internal carotid artery. Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. No significant difference is seen between the two groups

Fig. 3
Effects of p38 MAPK inhibitors on TNC-induced cerebral arterial constriction at 24 h after injection. (a) Vessel diameter of the left intracranial internal carotid artery (ICA). Data are expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean; P value, unpaired t tests. (b) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of the left intracranial ICA
Discussion
The main findings of this study are as follows: (1) an intracisternal injection of TNC caused constriction of the rat intracranial ICA at least for 72 h; and (2) SB203580, a p38 MAPK inhibitor, abolished the vasoconstriction induced by TNC.
TNC, a matricellular protein, is highly expressed during embryogenesis and is absent or much reduced in normal adult tissue, but reappears in many diseases including cancer, chronic inflammation, and tissue injury. TNC is induced by cytokines, growth factors, mechanical stress, and hypoxia, and exerts diverse functions through direct binding to cell surface receptors and other matrix proteins [2].
MAPKs including p38 MAPK are present in vascular smooth muscle cells and considered likely modulators of prolonged smooth muscle contraction through caldesmon, calponin, and heat shock protein 27 [7]. In cerebral vasospasm after SAH, Pan et al. [3] reported that phosphorylated p38 MAPK in the rabbit basilar arteries was expressed at significantly higher levels in the SAH group than in the control group, and SB20350 attenuated vasospasm associated with decreased expression of phosphorylated p38 MAPK in the basilar arteries.
TNC has been found to activate MAPK signaling [4]. Wang et al. [9] reported that integrin β3, TNC, phosphorylated p38 MAPK, and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) were expressed in breast invasive ductal carcinoma, and expression of phosphorylated p38 MAPK and uPA in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells decreased after the addition of integrin β3 antibody and TNC antibody. In addition, interestingly, not only TNC does influence intracellular MAPK activation, but MAPKs also regulate TNC transcription and deposition [10]. Our previous experimental study showed that expression of TNC and phosphorylated p38 MAPK increased in the spastic cerebral artery wall in a rat SAH model, and that inhibition of post-SAH upregulation of TNC by imatinib mesylate prevented cerebral vasospasm associated with inactivation of p38 MAPK. In this study, TNC constricted rat intracranial ICA and activated p38 MAPK in the constricted artery wall. Taken together, TNC may play an important role in post-SAH vasospasm development by p38 MAPK activation.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





