Electromyographic Findings in Common Neuromuscular Disorders
QUESTIONS
1. A patient presents with a right wrist drop. The acute denervation pattern can be seen in all except:
A. Abductor policis brevis
B. Brachioradialis
C. Deltoid
D. Extensor indicis proprius
View Answer
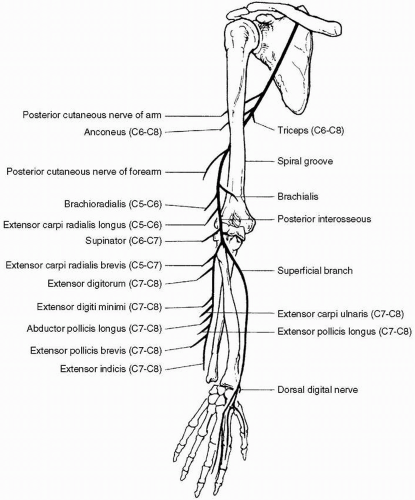
1. (A): See Figure 19.1. The anatomic localization of wrist drop can be posterior interosseous neuropathy, radial neuropathy at the spiral groove, radial neuropathy in the axilla, posterior cord brachial plexopathy, and C7 radiculopathy. These lesions will not result in an acute denervation pattern in the abductor policis brevis. However, acute denervations can be seen in the other three options with wrist drop depending where the lesion is. (Preston and Shapiro 1998, p. 294)
2. All statements regarding radial neuropathy are correct except:
A. The superficial radial sensory nerve is easy to stimulate and record
B. Most cases of posterior interosseous neuropathy are purely demyelinating in nature and a conduction block is demonstrated
C. Radial neuropathy at the spiral groove shows a conduction block with stimulation of the radial nerve proximal to the spiral groove
D. Posterior interosseous neuropathy results in a normal superficial radial sensory nerve action potential (SNAP)
View Answer
2. (B): In cases of radial neuropathy at the spiral groove, conduction block is seen with stimulation of the radial nerve proximal to the spiral groove. The relative drop in proximal to distal compound muscle action potential (CMAP) amplitude gives some indication of the proportion of fibers blocked. Most cases of posterior interosseous neuropathy are purely axonal in nature and a conduction block is usually not seen. A normal superficial radial sensory response is seen in posterior interosseous neuropathy because the superficial radial sensory nerve comes off before the posterior interosseous nerve. (Preston and Shapiro 1998, p. 296)
3. Acute denervation pattern is seen in allmuscles in radial neuropathy at the spiral groove except:
A. Brachioradialis
B. Supinator
C. Anconeus
D. Extensor carpi radialis
View Answer
3. (C): In radial neuropathy at the spiral groove acute denervation is seen in the brachioradialis, long head of the extensor carpi radialis, and supinator muscles. The branch to the anconeus comes off proximal to the spiral groove. If the lesion is at the axilla, the triceps and anconeus will be involved and acute denervation will be seen in anconeus. (Preston and Shapiro 1998, p. 299)
4. A patient presents with left foot drop from a common peroneal neuropathy at the knee. All the muscles show acute denervation except:
A. Tibialis anterior
B. Peroneus longus
C. Extensor hallucis longus
D. Tibialis posterior
View Answer
4. (D): Common peroneal neuropathy above the fibular head results in weakness and acute denervation pattern in the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, and peroneal longus muscles. However, it will not affect the tibialis posterior as it is a tibial innervated muscle. The only branch of the common peroneal nerve above the knee is to the short head of the biceps femoris. The presence of denervation pattern in the biceps femoris muscle indicates involvement of the common peroneal nerve above the knee. (Preston and Shapiro 1998, p. 314)
5. A patient presents with left foot drop with peroneal neuropathy at the fibular head. All the muscles will show acute denervation except:
A. Short head of biceps femoris
B. Peroneus longus
C. Extensor hallucis longus
D. Tibialis anterior
View Answer
5. (A): See Figure 19.2. Peroneal neuropathy at the fibular head results in a weakness and acute denervation pattern in the tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, and peroneal longus muscles. The only branch of common peroneal nerve above the knee is to biceps femoris. The presence of denervation pattern in biceps femoris indicates involvement of the common peroneal nerve above the knee and above the branch to the short head of the biceps femoris muscle, which will not be seen in this case because the lesion is at the fibular head. (Preston and Shapiro 1998, p. 314)
6. A patient presents with left foot drop from a common peroneal neuropathy in the thigh. All the muscles will show acute denervation except:
A. Long head of biceps femoris
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree