Fig. 1
(a) SAH grade in the SAH + vehicle and the SAH + anti-VEGF antibody groups. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. No significant difference between the groups. Mann-Whitney U tests. (b) Neurological score in the sham, SAH + vehicle and SAH + anti-VEGF antibody groups. Data were expressed as median ± 25th–75th percentiles. p Value, Kruskal-Wallis test
Neurological score in the SAH + vehicle group was significantly impaired compared with the sham group after 24 h of surgery. In the SAH mice treated with anti-VEGF antibody, neurological score (Fig. 1b) was significantly improved compared with the SAH + vehicle group (p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U or Kruskal–Wallis test).
Anti-VEGF Antibody Alleviates Brain Edema after 24 h of SAH
Brain water content analysis showed that the brain edema that was caused by SAH occurred only in the left cerebral hemisphere and was significantly alleviated after treated with anti-VEGF antibody compared with the SAH + vehicle group (p < 0.05, ANOVA, Fig. 2).
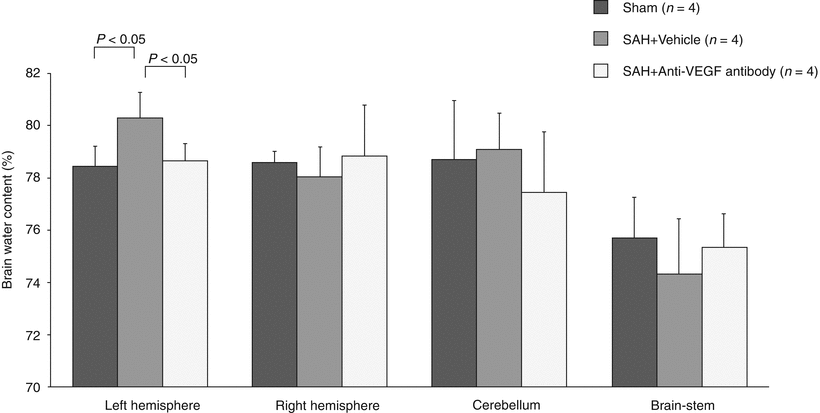

Fig. 2
Brain water content in the left cerebral hemisphere, right cerebral hemisphere, cerebellum, and brain stem in the sham, SAH + vehicle, and SAH + anti-VEGF antibody groups. Data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. p Value, ANOVA
IgG Extravasation in Brain Tissue Is Inhibited by Anti-VEGF Antibody
Based on the result of brain water content analyses, anti-VEGF antibody was administered using an icv injection, and BBB permeability of the left cerebral hemisphere was evaluated by IgG immunohistochemistry. IgG immunohistochemistry analysis showed that BBB disruption markedly occurred in the left cerebral cortex, especially the temporal cortex, in the SAH + vehicle group compared with the sham-operated group. After treatment with anti-VEGF antibody, the IgG extravasation was markedly suppressed compared with the SAH + vehicle group (Fig. 3).
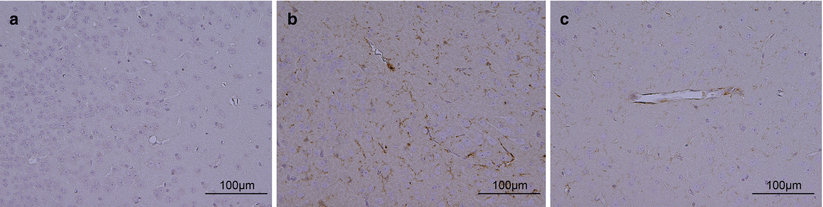

Fig. 3
IgG immunohistochemistry in the sham (a), SAH + vehicle (b), and SAH + anti-VEGF antibody (c) groups
Discussion
In this study, we investigated the protective effect of anti-VEGF antibody on brain edema formation after SAH. The findings indicated that VEGF is involved in brain edema formation after SAH, and that anti-VEGF antibody can improve neurobehavioral outcome, decrease BBB permeability and ameliorate brain edema after 24 h of SAH in mice.
BBB is the basic unit between the peripheral circulation and central nervous system and regulates the homeostasis of brain [12]. Some researchers have demonstrated that the BBB disruption was a critical pathologic manifestation that occurred in an early stage of SAH and allowed numerous inflammatory mediators to transfer into brain parenchyma, leading to brain edema formation and further brain parenchymal damage [13]. The mechanisms of brain edema formation are complex and still indistinct, though many specific molecules have been identified during the pathological procedure of SAH.
VEGF is a pivotal regulator of angiogenesis that controls vascular growth under physiological and pathological conditions and, meanwhile, promotes vascular permeability [3]. It has been reported that the expression of VEGF was upregulated after ischemic or hemorrhagic brain injury and responsible for increased BBB permeability [7, 14, 15]. One report stated that application of appropriate dosages of exogenous human VEGF165 increased BBB permeability in normal mice [5]. Some researchers also have demonstrated that inhibition of endogenous VEGF with topical application of anti-VEGF antibody attenuated BBB disruption in focal cerebral ischemia [16]. However, there is no previous study on experimental SAH in which the effects of inhibition of VEGF on BBB disruption were investigated.
In the present study, we demonstrated our hypothesis that VEGF is a key molecule that causes BBB disruption and induces brain edema formation, and thus, that suppressing VEGF after SAH is a possible way to protect BBB and to reduce brain edema. It is suggested that neutralization of VEGF protein using anti-VEGF antibody may be a prospect for SAH therapy, though the detailed mechanisms responsible for the attenuated brain edema formation remain unclear.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








