♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
- Review imaging studies
- Non-contrast head computed tomography (CT) essential for precise localization of epidural hematoma (EDH) and for detecting skull fractures
- Consider dedicated maxillofacial CT for patient with severe trauma and multiple cranial/facial fractures that may need to be addressed simultaneously with EDH.
- Skull x-ray: most often does not add additional information to head CT
- Non-contrast head computed tomography (CT) essential for precise localization of epidural hematoma (EDH) and for detecting skull fractures
- Exploratory burr holes: With the prevalence of CT scanners, situations are increasingly rare in which a patient is deteriorating so rapidly that diagnostic studies are unobtainable and placement of exploratory burr holes is necessary.
- Surgical objectives
- Removal of clot: lowers intracranial pressure (ICP) and eliminates mass effect; clot is often thick so exposure of craniotomy should allow access to entire clot
- Hemostasis
- Prevention of hematoma reaccumulation with dural tenting
- Repair skull fracture, if necessary
- Removal of clot: lowers intracranial pressure (ICP) and eliminates mass effect; clot is often thick so exposure of craniotomy should allow access to entire clot
Equipment
- Mayfield head holder: clamp or horseshoe
- Basic craniotomy tray
- High-speed drill with appropriate drill bits
- Bone flap fixation tray
- Hemostatic agents (Avitene, Gelfoam, Surgicel, bone wax)
- ICP monitor or external ventricular drain system if needed
Operating Room Set-up
- Headlight and loupes
- Bovie electrocautery
- Bipolar cautery
Anesthetic Issues
- Preoperative intravenous antibiotics administered within 30 min prior to incision (cefazolin 2 g intravenously or clindamycin 600 mg intravenously)
- With underlying brain injury, consider loading with phenytoin (15 to 18 mg/kg) administered slowly, or alternatively, levetiracetam 1000 to 1500 mg intravenously
- Communicate with anesthesiologist suspected degree of ICP elevation and if needed:
- Hyperventilation to pCO2 of 30 to 35 mm Hg
- Mannitol 0.5 to 1 g/kg infusion starting at time of skin incision
- Propofol (if indicated)
- Surgeon should warn anesthesiologist of potential hypotension at the time of clot evacuation as blood pressure is often supported by a sympathetic response to increased ICP
- Hyperventilation to pCO2 of 30 to 35 mm Hg
♦ Intraoperative
Trauma Flap (Fig. 66.1)
- Position patient assuming cervical spine injury unless C-spine was cleared preoperatively.
- Bone flap should encompass margins of hematoma and be sufficient to repair skull fractures.
Technique
- Initial burr hole is made near the area of maximal clot thickness, often in the low temporal area, to allow for prompt decompression of the hematoma.
- Craniotomy that provides adequate access to hematoma margins is then completed.
- If bleeding is from the middle meningeal artery or its branches, bipolar cautery is usually sufficient.
- If bleeding is from the foramen spinosum, the foramen is plugged with bone wax.
- If bleeding is from the middle meningeal artery or its branches, bipolar cautery is usually sufficient.
- If the brain appears tight or there is a concern for underlying SDH, a small opening in the dura is made to inspect.
- Holes are drilled along the craniotomy margins for dural tenting sutures, ~2 cm apart. Several tenting sutures are also placed in the middle of the craniotomy bone flap.
Closure
- Wounds are irrigated copiously. Antibiotic containing irrigation can be used if concern for infection.
- Bone flap is replaced with several central tenting sutures to reduce volume of epidural space and at least three-point fixation with microplates and screws
- Repair skull fractures with additional microplates or mesh, if necessary
- Subgaleal drain may be placed to minimize postoperative collections
- Temporalis muscle and fascia is closed with 0–0 Vicryl interrupted sutures
- Inverted 0–0 and 3–0 Vicryl sutures are used to close the galea
- Staples to approximate the skin edges
- Xeroform and 4 × 4 dressings should be secured with a head wrap
< div class='tao-gold-member'>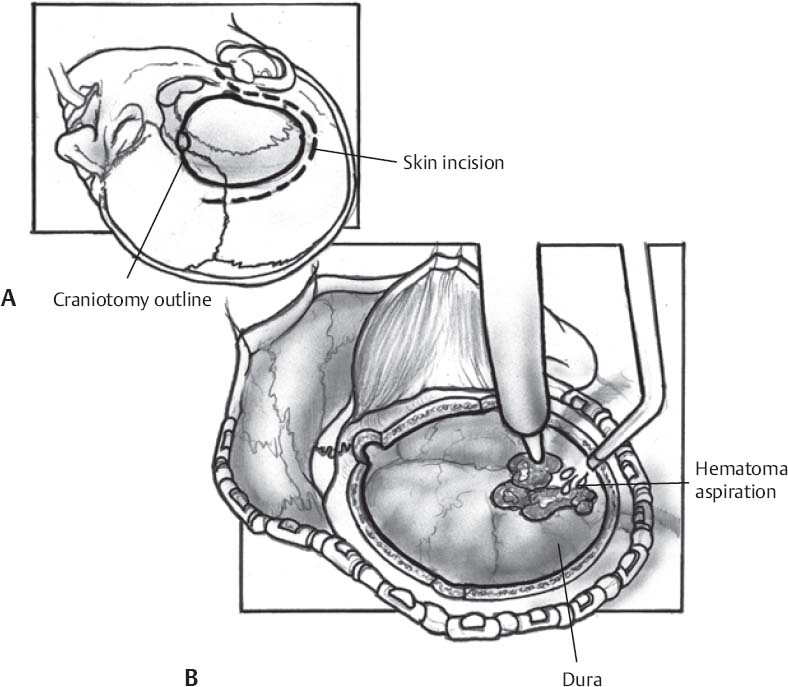 Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






