Forensic psychiatry
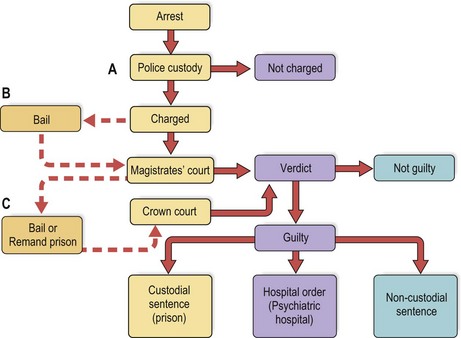
Forensic psychiatry is a sub-speciality concerned with the assessment and treatment of mentally disordered offenders. A large part of the work of forensic psychiatrists is the assessment of people held at various stages of the criminal justice system, which is portrayed in Figure 1. They may also be asked to assess patients under the care of general psychiatric services who are thought to be at high risk of committing an offence. In some areas, there are community forensic psychiatry teams that work with psychiatric patients likely to commit criminal offences.
Diversion of mentally disordered offenders
The need for forensic psychiatry is based on two important principles. The first is that if someone commits a crime because of a mental disorder, then treatment of the mental disorder is in the best interests of the individual and society. Table 1 summarises the common ways in which mental disorder leads to crime. Secondly, imprisonment usually exacerbates mental disorder and reduces the chance of rehabilitating the offender, and may result in unnecessary suffering. Therefore, it is often best for mentally disordered offenders to be dealt with by psychiatrists rather than remain within the criminal justice system. The process of getting them out of the criminal justice system is usually referred to as diversion of mentally disordered offenders.
Table 1 Crimes associated with certain mental disorders
| Disorder | Offence | Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia | Low rate of violence and homicide, but more likely than in general population | |
| Acquisitive offences | ||
| Mania | Violence (usually minor), reckless driving, deception, inappropriate sexual behaviour | |
| Depression | Homicide/infanticide, victims usually family members; often followed by suicide | As a result of guilt and hopelessness, may believe family need protecting or putting out of their misery |
| Shoplifting | ||
| ‘Cluster B’ personality disorders | Increased rate of violence, arson, sexual offences and acquisitive offences | < div class='tao-gold-member'> Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|