SECTION I GENERAL APPROACH TO HISTORY AND EXAMINATION
NERVOUS SYSTEM – EXAMINATION
Neurological disease may produce systemic signs and systemic disease may affect the nervous system. A complete general examination must therefore accompany that of the central nervous system. In particular, note the following
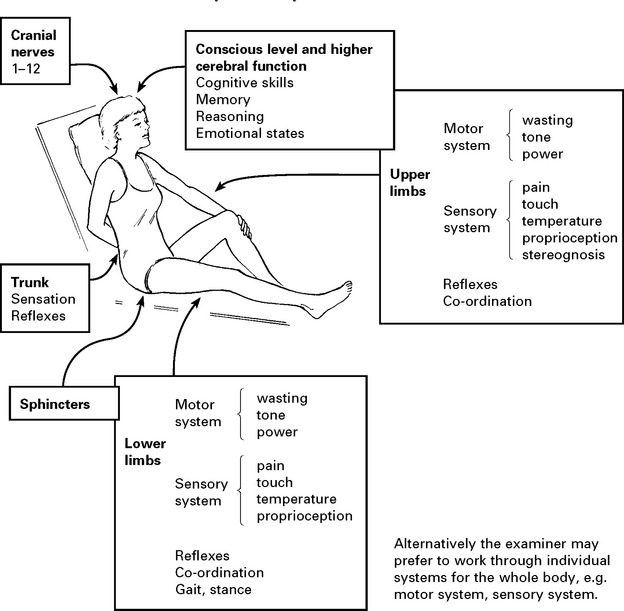
CNS examination is described systematically from the head downwards and includes:
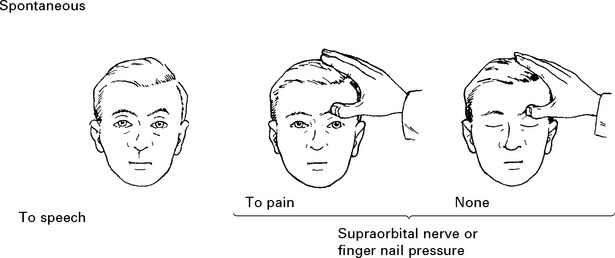
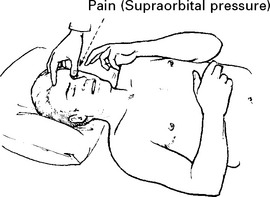
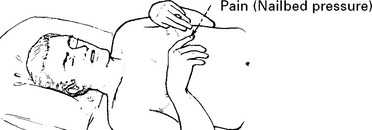
EXAMINATION – CONSCIOUS LEVEL ASSESSMENT
EXAMINATION – HIGHER CEREBRAL FUNCTION
COGNITIVE SKILL
Dominant hemisphere disorders
| Listen to language pattern | Expressive dysphasia | |
| Receptive dysphasia | ||
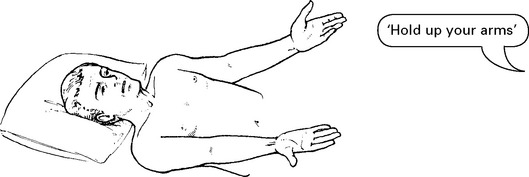
| Does the patient understand simple/complex spoken commands? e.g. ‘Hold up both arms, touch the right ear with the left fifth finger.’ | Receptive dysphasia | |
| Ask the patient to name objects. | Nominal dysphasia | |
| Does the patient read correctly? | Dyslexia | |
| Does the patient write correctly? | Dysgraphia | |
| Ask the patient to perform a numerical calculation, e.g. serial 7 test, where 7 is subtracted serially from 100. | Dyscalculia | |
| Can the patient recognise objects? e.g. ask patient to select an object from a group. | Agnosia | |
Non-dominant hemisphere disorders
| Note patient’s ability to find his way around the ward or his home. | Geographical agnosia |
| Can the patient dress himself? | Dressing apraxia |
| Note the patient’s ability to copy a geometric pattern, e.g. ask patient to form a star with matches or copy a drawing of a cube. | Constructional apraxia |
Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) is used in the assessment of DEMENTIA (page 127).
REASONING AND PROBLEM SOLVING
Ask patient to reverse 3 or 4 random numbers.
Ask patient to explain proverbs.
Ask patient to sort playing cards into suits.
CRANIAL NERVE EXAMINATION
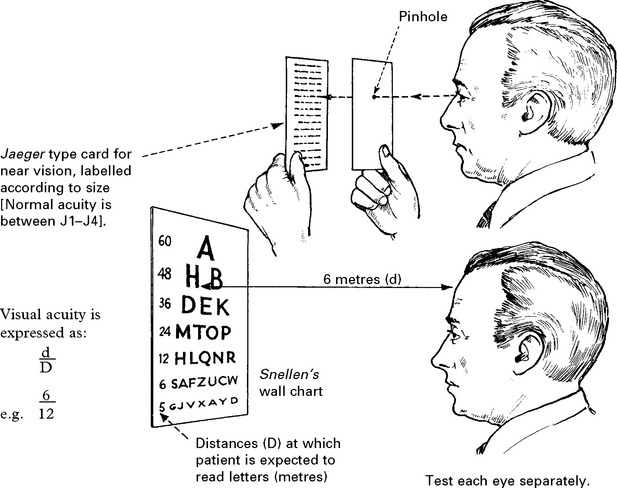
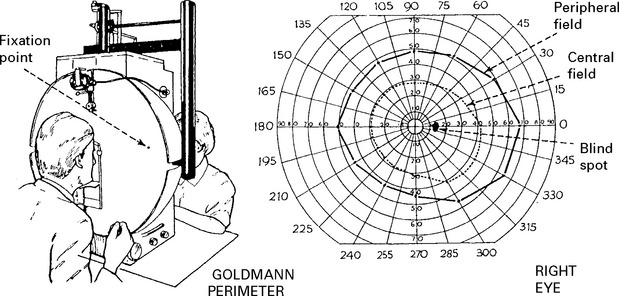
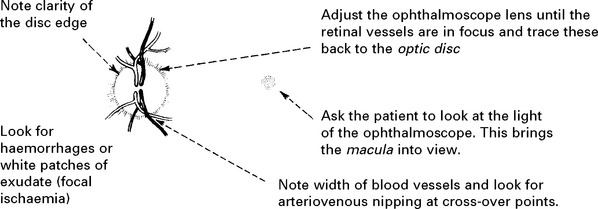
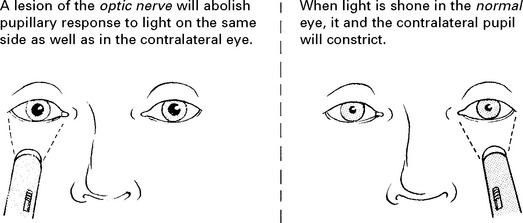
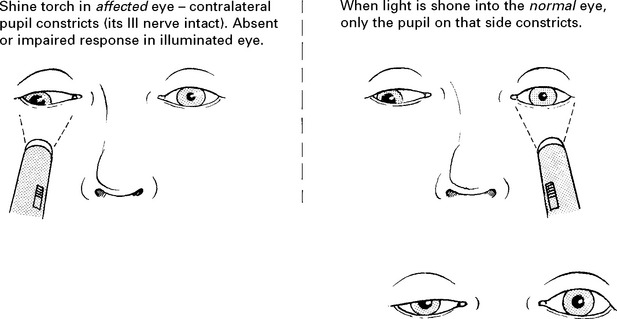
OPTIC NERVE (II)
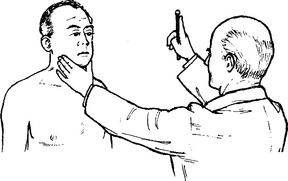
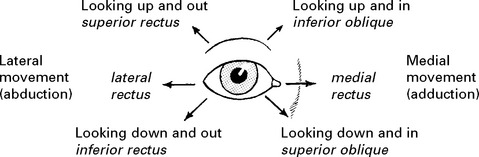
OCULOMOTOR (III), TROCHLEAR (IV) AND ABDUCENS (VI) NERVES
Pupil: The pupil dilates and becomes ‘fixed’ to light.
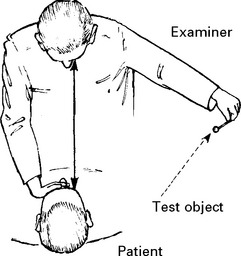
Ocular movement
Note any malalignment or limitation of range.
Question patient about diplopia; the patient is more likely to notice this before the examiner can detect impairment of eye movement. If present:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree