Chapter 36 Health beliefs, motivation and behaviour
Health can be promoted through adoption of health-promoting behaviours and avoidance of health risk behaviours (see pp. 64–69) and the impact of illness can be minimized by seeking medical help and complying with treatment (see pp. 88–89 and pp. 94–95). So how can people be encouraged to adopt behaviours which promote health and minimize the impact of illness?
The Health Belief Model (HBM)
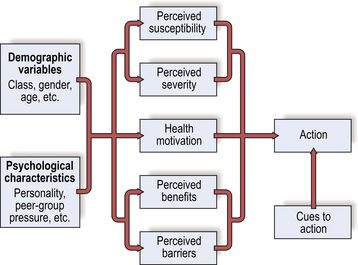
In the 1950s US public health researchers began to investigate which beliefs were associated with health behaviour. The resulting model focused on people’s beliefs about the threat of ill health and the costs and benefits of health behaviour (Fig. 1). Threat perception involved perceived susceptibility to illness or health breakdown (e.g. ‘How likely am I to suffer from breathing difficulties or contract lung cancer if I smoke?’) and the anticipated severity of the consequences of illness (e.g. ‘How bad would it be if I suffered from breathing difficulties or contracted lung cancer?’). The model also included beliefs concerning the benefits or effectiveness of a recommended health behaviour (e.g. ‘If I give up smoking, what will I gain?’) and the costs or barriers associated with the behaviour (e.g. ‘How difficult will it be to give up smoking and what will I lose?’). Two other factors were included: cues to action which trigger health behaviour when people are aware of a health threat and convinced of the effectiveness of action (e.g. advice from a doctor) and general health motivation (i.e. how highly a person values good health).
How useful is the Health Belief Model?
Reviews have also shown that perceived costs or barriers are especially important, suggesting that minimizing the degree to which health behaviours are thought to be painful, time-consuming, expensive or embarrassing will help promote them. Perceived severity has been shown to be less important in relation to prevention than responses to symptoms or medical advice. Thus stressing susceptibility to future health problems is likely to be more effective in promoting preventive health behaviour than emphasizing severity (see pp. 94–95).
Health-related intentions: the theory of planned behaviour
King (1982) extended the HBM in a study of hypertension screening. She designed a HBM-based questionnaire which included measures of intentions. Her model correctly predicted whether people did or did not attend later screening in 82% of cases. Measures of intention were found to be the most powerful predictors. A number of cognitive models have proposed that intentions are important indicators of whether or not people will take action. The most popular of these models is the ‘theory of planned behaviour’ (Ajzen, 1991; Fig. 2
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree