Intracerebral Hemorrhage
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Adults
Intracerebral Hemorrhage in Adults
1. Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) accounts for _____ to _____% of strokes. | 15 to 30% | G7 p.1118:73mm |
2. Complete the following regarding incidence of intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: |
| G7 p.1118:130mm |
a. In 100,000 people incidence is _____ to _____ cases per year. | 12 to 15 |
|
b. Relative to subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) it is _____ times as frequent. | 2 |
|
c. More cases occur in which sex? | males |
|
3. True or False. The following are risk factors for ICH: |
| G7 p.1118:140mm |
a. age | true |
|
b. gender | true (M > F) |
|
c. race | true (black > white) |
|
d. recent ETOH | true |
|
e. chronic ETOH | true |
|
f. cigarettes | false |
|
4. True or False. The following increases the incidence of cerebral hemorrhage: |
| G7 p.1118:141mm |
a. alcohol, amyloid angiopathy, age | true |
|
b. birefringence | true |
|
c. Charcot-Bouchard aneurysms | true |
|
d. carotid disease | true |
|
e. central nervous system (CNS) infection | true |
|
f. cerebrovascular accident (CVA) previously | true |
|
g. street drugs | true |
|
h. male gender | true |
|
i. liver disease | true |
|
j. race | true |
|
k. smoking | false | |
5. For hypertensive hemorrhage sites of predilection are |
| G7 p.1119:40mm |
a. s_____;_____% | striate body (basal ganglia); 50% (putamen, lenticular nucleus, internal capsule, globus pallidus) |
|
b. t_____;_____% | thalamus; 15% |
|
c. p_____;_____% | pons; 10% |
|
d. c_____;_____% | cerebellum; 10% |
|
e. c_____w_____m_____;_____% | cerebral white matter; 10% |
|
f. b_____s_____;_____% | brain stem; 5% |
|
6. Complete the following regarding intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: |
| G7 p.1119:41mm |
a. The number one location for deep ICH is_____ | putamen |
|
b. from rupture of_____ _____. | lenticulostriate arteries |
|
7. Complete the following regarding intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: |
| G7 p.1119:78mm |
a. Incidence of lobar hemorrhages is_____to_____%. | 10 to 30% |
|
b. Is lobar or deep more fatal? | deep |
|
c. Which is more related to alcohol? | lobar |
|
8. Complete the following regarding lobar hemorrhage: |
| G7 p.1119:80mm |
a. Incidence per 100,000 is_____to_____. | 2 to 10(10to30% of the 15 to 30% of hemorrhagic CVAs) |
|
b. Compared with deep hemorrhages, lobar hemorrhages have a_____prognosis. | better |
|
c. Hemorrhagic transformation may occur in |
|
|
i._____% of CVAs | 43% |
|
ii. in time from_____to_____. | 1 day to 1 month |
|
9. List the causes of lobar hemorrhage. |
| G7 p.1119:95mm |
Hint: teach it |
|
|
a. t_____ | tumor |
|
b. e_____ | extension of deep ICH |
|
c. a_____ | amyloid angiopathy |
|
d. c_____ | cerebrovascular malformation or aneurysm |
|
e. h_____ | hemorrhagic conversion of ischemic stroke |
|
f. i_____ | idiopathic |
|
g. t_____ | trauma |
|
10. Hemorrhagic transformation of an ischemic infarct |
| G7 p.1120:69mm |
a. is estimated to occur in_____% | 43% |
|
b. within the first_____ | month |
|
c. and may occur within_____hours. | 24 | |
11. True or False. The incidence of symptomatic ICH within 36 hours of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) treatment for acute ischemic CVA is approximately |
| G7 p.1120:178mm |
a. < 1% | false |
|
b. 6% | true(The incidence is 6.4% versus 0.6% for placebo.) |
|
c. 15% | false |
|
d. 30% | false |
|
12. What types of infection predispose to cerebral hemorrhage? |
| G7 p.1121:67mm |
a. f_____ | fungal |
|
b. g_____ | granulomas |
|
c. h_____s_____ | herpes simplex |
|
13. True or False. Cocaine/amphetamine can cause |
| G7 p.1121:95mm |
a. ischemic CVA | true |
|
b. ICH | true |
|
14. Complete the following regarding intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: |
| G7 p.1122:73mm |
a. Hypertension is a risk factor for hemorrhage in which locations? |
|
|
i. p_____ | pontine ICH |
|
ii. c_____ | cerebellar ICH |
|
iii. b_____g_____h_____ | basal ganglia hemorrhages (65%) |
|
b. Not a risk factor for_____% | 35% of basal ganglia hemorrhages |
|
15. Complete the following regarding intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: |
| G7 p.1122:100mm |
a. Lobar hemorrhages are associated with_____ _____ | amyloid angiopathy |
|
i. also known as_____ _____ | congophilic angiopathy |
|
ii. deposit of_____ _____ | beta amyloid |
|
iii. appears on polarized light as_____ | birefringent—apple green color |
|
b. Responsible for_____% of cases of ICH | 10% |
|
c. Any genetic factors? | yes |
|
d. If so, what? Apoli protein E e4 allele |
| G7 p.1123:33mm |
e. How does this affect patients clinically? those with APOE have hemorrhage 5 years earlier |
| |
16. True or False. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy is associated with systemic amyloidosis. | false (It does not require systemic amyloidosis.) | G7 p.1122:110mm |
17. Recurrent lobar hemorrhages should suggest a diagnosis of c_____a_____a_____. | cerebral amyloid angiopathy | |
18. Malignant tumors associated with ICH include |
| G7 p.1123:60mm |
a. primary (name two) |
|
|
i. g_____m_____ | glioblastoma multiforme |
|
ii. l_____ | lymphoma |
|
b. metastatic (name four) |
|
|
i. l_____ | lung (Only approximately 9% hemorrhage but is so much more common than the others that it is seen the most.) |
|
ii. ch_____ | choriocarcinoma (approximately 60% bleed) |
|
iii. m_____ | melanoma (approximately 40% bleed) |
|
iv. r_____ | renal cell carcinoma |
|
19. Complete the following regarding anticoagulation preceding ICH: |
| G7 p.1123:125mm |
a. Incidence of bleeding complications in patients on anticoagulation is_____% per year. | 10% |
|
b. Incidence of ICH is_____. | 0.3 to 1.8% per year; 3 to 18/1000 |
|
c. Mortality in the ICH group is_____. | 65%; 2 to 12/1000 die each year |
|
20. True or False. Transient ischemic attack (TIA)— like symptoms precede lobar ICH in patients with amyloid angiopathy ~50% of the time. | true(But these have Jacksonian-March-style numbness, weakness, or tingling.) | G7 p.1124:15mm |
21. What is the most common site for intracerebral hemorrhage? | putamen | G7 p.1124:45mm |
22. Complete the following regarding ICH with thalamic hemorrhage: |
| G7 p.1124:60mm |
a. Clinically usually found to have_____loss. | hemisensory loss(contralaterally) |
|
b. Any motor function loss? | yes(hemiparesis if internal capsule compressed) |
|
c. Any eye signs such as anisocoria or miosis? | yes(with upper brain stem extension) |
|
d. Beyond what size has high mortality? | 3.3 cm in diameter(i.e., 18 cc) | G7 p.1124:78mm |
23. True or False. Cerebellar hematomas |
| G7 p.1124:106mm |
a. produce hemiparesis before coma | false |
|
b. produce coma before hemiparesis | true(because of compression of the brain stem) |
|
c. do not produce coma or hemiparesis | false | |
24. Answer the following about rebleeding after intracerebral hematoma: |
| G7 p.1124:160mm |
a. True or False. It occurs more frequently in basal ganglia hemorrhages than lobar. | true |
|
b. True or False. It occurs most frequently on the second day. | false(most commonly within the first hour) |
|
c. True or False. Incidence increases with time. | false (decreases with time) |
|
d. True or False. It is more common with small hemorrhages. | false (more common with large hemorrhages) |
|
e. True or False. It is more likely if there is a coagulopathy. | true |
|
f. Early rebleeding can occur in_____%. | 33 to 38%(in 1 to 3 hours) |
|
g. Late rebleeding can occur in_____%. | 1.8 to 5.3% |
|
25. The component that is released by clot and presumed to be the most likely cause of surrounding delayed edema and deterioration is_____. | thrombin | G7 p.1125:45mm |
26. What is the formula for volume of a hematoma? |
| G7 p.1125:105mm |
a. sphere V =_____ | V = π D3 ÷ 6 for a sphere |
|
b. ellipse V =_____ | V = π (h × w × d) ÷ 6 for ellipse |
|
c. modified V =_____ | V = h × w × d ÷ 2 modified |
|
27. What equation can be used to estimate the volume of an ICH? | (A × B × C) ÷ 2 modified ellipsoid volume where A, B, and C are the diameters of the clot in each of the three dimensions | G7 p.1125:106mm |
28. Complete the following regarding intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: |
| G7 p.1125:113mm |
a. An average size of a clot decreases at the rate of_____ mm/day. | 0.75 |
|
b. The density decreases by_____Hounsfield units (HU) per day. | 2 |
|
c. There is_____change for the first | little |
|
d._____weeks. | 2 |
|
29. List the sequence of hemoglobin evolution after intracerebral hemorrhage. |
| G7 p.1125:125mm |
Hint: On days my mom’s home |
|
|
a. o_____ 0 to 1 day | oxyhemoglobin |
|
b. d_____ 1 to 3 | deoxyhemoglobin |
|
c. m_____ 3 to 7 | methemoglobin |
|
d. m_____ 7 to 14 | methemoglobin |
|
e. h_____ 14-plus | hemosiderin | |
30. Give the ICH scores for the following: |
| G7 p.1126:35mm |
a. Glasgow coma scale (GCS) |
|
|
i. finding 3 to 4 points_____ | 2 |
|
ii. finding 5 to 12 points_____ | 1 |
|
iii. finding 13 to 15 points_____ | 0 |
|
b. location |
|
|
i. finding infratentorial points_____ | 1 |
|
ii. finding supratentorial points_____ | 0 |
|
c. age |
|
|
i. finding > 80 years points_____ | 1 |
|
ii. finding < 80 years points_____ | 0 |
|
d. volume |
|
|
i. finding > 30 cc points_____ | 1 |
|
ii. finding < 30 cc points_____ | 0 |
|
e. intraventricular |
|
|
i. finding yes points_____ | 1 |
|
ii. finding no points_____ | 0 |
|
31. ICH score vs mortality |
| G7 p.1126:35mm |
a. points 0 mortality in 30 days_____rounded out_____ | points 0, mortality in 30 days 0%, rounded out 0 |
|
b. points 1 mortality in 30 days_____rounded out_____ | points 1, mortality in 30 days 13%, rounded out 10 |
|
c. points 2 mortality in 30 days_____rounded out_____ | points 2, mortality in 30 days 26%, rounded out 30 |
|
d. points 3 mortality in 30 days_____rounded out_____ | points 3, mortality in 30 days 72%, rounded out 70 |
|
e. points 4 mortality in 30 days_____rounded out_____ | points 4, mortality in 30 days 97%, rounded out 90 |
|
f. points 5 mortality in 30 days_____rounded out_____ | points 5, mortality in 30 days 100%, rounded out 100 |
|
g. points 6 mortality in 30 days_____rounded out_____ | points 6, mortality in 30 days rounded out 100 |
|
32. Complete the following about management of ICH: |
| G7 p.1126:118mm |
a. Blood pressure (BP) permissible to reduce mean arterial pressure (MAP) by_____%. | 20% |
|
b. Target level BP is_____and diastolic_____. | 140 and diastolic; 90 |
|
33. Matching. Match the percent yield for finding AVM or aneurysm on angiogram in the following patients: |
| G7 p.1127:88mm |
|
| |
a. patient > 45 years old + hypertension (HTN)lobar ICH |
|
|
b. patient > 45 years old + HTN thalamic putamen ICH cerebellar/pons |
|
|
c. patient with intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) without parenchymal hemorrhage |
| |
34. When is it appropriate to restart anticoagulation after cerebral hemorrhage? |
| G7 p.1128:45mm |
a. If there is a strong indication restart in_____days. | 5 |
|
b. If Coumadin is stopped for 10 days the chance of stroke within 30 days in a patient with |
|
|
i. prosthetic heart value is_____% | 2.5% |
|
ii. atrial fibrillation is_____% | 2.6% |
|
iii. cardioembolic stroke is_____% | 4.8% |
|
c. The basic recommendation is to stay off blood thinners for_____. | 2 weeks |
|
d. If the patient needs dialysis, use h_____-f_____ d_____. | heparin-free dialysis |
|
35. True or False. The volume of hematoma on which it is usually most appropriate to operate is |
| G7 p.1129:125mm |
a. < 10 cc | false (< 10 cc too small; no major mass effect) |
|
b. 10 to 30 cc | true |
|
c. > 30 cc | false(usually a poor outcome) |
|
d. > 85 cc | false (no survivors) |
|
36. True or False. Surgical treatment for cerebellar ICH is recommended for |
| G7 p.1130:35mm |
a. GCS 14, hematoma 3 cm diameter | false(may treat conservatively 14 cc) |
|
b. GCS 13, hematoma 4 cm diameter | true(Surgical treatment is recommended for GCS ≤ 13 or hematoma ≤ 4 cm diameter = 32 cc.) |
|
c. GCS 3 | false(not in the face of complete neurologic destruction where the outcome will be poor [i.e., flaccid, no brain stem reflex]) |
|
d. hematoma plus hydrocephalus | true |
|
37. With cerebral hemorrhage, the possible mortality in 30 days for the following conditions is |
| G7 p.1131:44mm |
a. SAH_____% | 46% |
|
b. ICH-basal ganglia thalamus_____% | 44% |
|
c. ICH-lobar_____% | 11% |
|
 ICH in Young People
ICH in Young People
38. Name the top five causes of nontraumatic ICH in patients 15 to 45 years old(other than “undetermined,” which is ˜ 1/4). |
| G7 p.1131:70mm |
Hint: AHadt |
|
|
a. A_____ | AVM (˜30%) |
|
b. H_____ | HTN (˜15%) |
|
c. a_____ | aneurysm (˜10%) |
|
d. d_____ | drugs (˜7%) |
|
e. t_____ | tumor (˜4%) |
|
 Intracerebral Hemorrhage in the Newborn
Intracerebral Hemorrhage in the Newborn
39. Synonyms are |
| G7 p.1131:143mm |
a. SEH_____ | subependymal hemorrhage |
|
b. GMH_____ | germinal matrix hemorrhage |
|
c. IVH_____ | intraventricular hemorrhage |
|
40. True or False. The germinal matrix normally involutes around |
| G7 p.1131:170mm |
a. 26 to 28 weeks gestation | false |
|
b. 28 to 30 weeks gestation | false |
|
c. 30 to 32 weeks gestation | false |
|
d. 32 to 36 weeks gestation | true |
|
41. Complete the following about intracerebral hemorrhage in the newborn: |
| G7 p.1131:180mm |
a. True or False. Extremely early(< 28 weeks gestation) germinal matrix hemorrhage is most likely to occur at the |
|
|
i. head of caudate | false |
|
ii. body of caudate | true(Most hemorrhages, however, occur at the head of the caudate at a later age of gestation.) |
|
iii. tail of caudate | false |
|
iv. choroid plexus | false |
|
b. Sequence the preceding responses according to the following ages: |
| |
i. Premature under 28 weeks gestation bleed in_____ | body of caudate |
|
ii. Infants 32 to 34 weeks gestation bleed in_____ | head of caudate |
|
iii. Mature infants bleed from the_____ | choroid plexus | |
42. True or False. The following is most important for risk of developing a germinal matrix hemorrhage: |
| G7 p.1132:70mm |
a. ↑ CO2 | true |
|
b. ↑ cerebral blood flow (CBF) | true |
|
c. ↑ temperature | false |
|
d. ↑ cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) | true (The most common denominators for all risk factors for germinal matrix hemorrhage are increased cerebral blood flow and increased cerebral perfusion pressure. Specific risk factors include asphyxia, hypervolemia, seizures, pneumothorax, cyanotic heart disease, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [ECMO] ventilation, and maternal cocaine abuse.) |
|
43. List the risk factors for germinal matrix (subependymal) hemorrhage. |
| G7 p.1132:85mm |
Hint: vespacc |
|
|
a. v_____ | volume expansion |
|
b. e_____ | extracorporeal membrane oxygenation(ECMO) |
|
c. s_____ | seizures |
|
d. p_____ | pneumothorax |
|
e. a_____ | asphyxia |
|
f. c_____ | cyanotic heart disease |
|
g. c_____ | cocaine abuse(maternal) |
|
44. Complete the following regarding intracerebral hemorrhage in the newborn: |
| G7 p.1133:150mm |
a. What% of babies with germinal matrix hemorrhage (GMH) will develop hydrocephalus? | 20 to 50% |
|
b. Grading system of_____ | Papile |
|
c. List the criteria for the four grades. |
|
|
i. grade I | subependymal hemorrhage(SE) |
|
ii. grade II | intraventricular hemorrhage without ventricular enlargement(IVH without VE) |
|
iii. grade III | IVH + ventricular enlargement (IVH with VE) |
|
iv. grade IV | IVH + parenchymal hemorrhage (IVH with PH) | |
d. Hydrocephalus occurs in_____to_____%. | 20 to 50% | G7 p.1134:70mm |
e. Hydrocephalus usually occurs_____to_____weeks after the subependymal hemorrhage(SEH). | 1 to 3 | G7 p.1134:82mm |
45. True or False. A germinal matrix hemorrhage that extends into the ventricle but does not cause ventricular dilation is the following grade, according to the Papile grading system: |
| G7 p.1133:150mm |
a. grade I | false |
|
b. grade II | true |
|
c. grade III | false |
|
d. grade IV | false |
|
46. Complete the following regarding intracerebral hemorrhage in the newborn: |
| G7 p.1136:163mm |
a. CSF protein above_____mg/cc will prevent spontaneous reabsorption. | 100 |
|
b. Additional concerns regarding high protein include |
|
|
i. m_____by the p_____ | malabsorption by the peritoneum |
|
ii. i_____ | ileus |
|
iii. o_____of s_____t_____ | occulsion of shunt tubing |
|
47. Indications for converting an Ommaya to a VP shunt are |
| G7 p.1137:35mm |
a. CSF protein below_____ | 100 mg/cc |
|
b. Weight of the child is at least_____ | 2500 g |
|
48. Give the germinal matrix hemorrhages outcome. |
| G7 p.1137:70mm |
a. mortality_____% | 5 to 65% |
|
b. hydrocephalus_____% | 15 to 100% |
|
c. IQ_____ | 75% (normal) |
|
d. ambulatory_____% | 100% (all survivors ambulatory) |
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


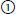 0%;
0%; 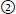 10%;
10%; 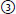 65%
65%