♦ Preoperative
- Medical therapy based on immune status of patient (i.e., AIDS, lymphoma, chronic steroids)
- Most intracranial abscesses require surgical intervention, though some may have initial medical management attempted (better for smaller lesions ≤ 2.5 to 3 cm and early in disease course, when abscess is not yet encapsulated).
- Abscess formed secondary to penetrating injury often requires open débridement
- Previously treated abscesses may be sterile at time of operative culture
- Timing surgical intervention before treatment will increase chances for positive culture results
- Approach based on location of lesion(s) (Fig. 74.1)
- Superficial: open treatment preferred
- Deep: stereotactic aspiration preferred
- Ventricular: may require aspiration along with intrathecal antimicrobial therapy
- Superficial: open treatment preferred
Anesthetic Issues
- Valsalva may increase yield of stereotactic aspiration
- Start antibiotics after cultures obtained when possible
♦ Intraoperative
Stereotactic Aspiration
- Typically performed on a symptomatic deeper mass lesion
- Abscesses in late capsule stage may resist or deflect needle penetration
- Endoscopic aspiration
- May be fewer epileptic complications with stereotactic aspiration rather than open excision
< div class='tao-gold-member'>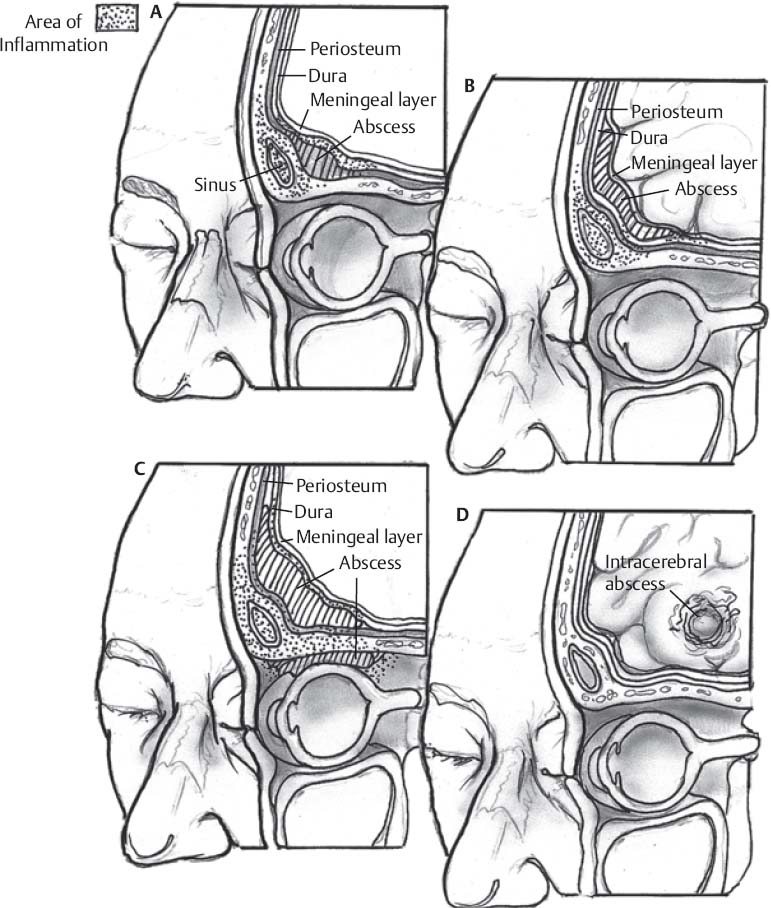 Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






