Liaison psychiatry
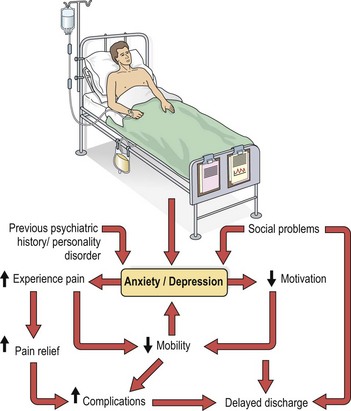
Very few disorders can be considered to wholly affect the body but not the mind, and vice versa. The majority of psychiatric disorders have some impact upon the patient’s physical wellbeing. For example, depression can result in weight loss, constipation and tiredness, in addition to having an impact on the individual’s ability to cope with any existing physical illness. Pain from arthritis is often worse during a depressive episode. Similarly, physical disorders will often affect the emotional state of the patient. Feelings of anxiety, depressed mood, anger and frustration are common accompaniments to physical illness. They will impact upon the recovery process (Fig. 1), and mental illness may be precipitated.
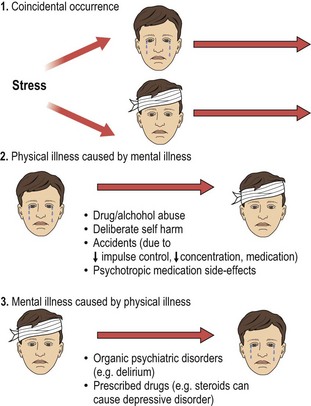
High rates of mental illness have been found in general hospitals, even when those patients being treated for overdose and other forms of deliberate self harm are excluded from the figures. Up to 60% of medical inpatients have a mental disorder, and up to half of all medical outpatients. A quarter of male medical inpatients have problems associated with alcohol abuse. The reasons for these high rates are illustrated in Figure 2.
Liaison psychiatry
 consultation, in which patients are assessed by members of the liaison psychiatrist at the request of the physician or surgeon caring for them
consultation, in which patients are assessed by members of the liaison psychiatrist at the request of the physician or surgeon caring for them liaison, in which members of the liaison psychiatry team have a broader role and become integrated into the work of their general hospital colleagues. They may attend ward rounds or take part in assessment or follow-up of patients attending outpatient clinics. This approach is time-consuming but improves joint working between general hospital and mental health staff. It also reduces the stigma of a psychiatric referral, which can be a problem with the consultation model, particularly for patients with conditions such as somatisation disorder, in which psychological explanations for symptoms are actively resisted.
liaison, in which members of the liaison psychiatry team have a broader role and become integrated into the work of their general hospital colleagues. They may attend ward rounds or take part in assessment or follow-up of patients attending outpatient clinics. This approach is time-consuming but improves joint working between general hospital and mental health staff. It also reduces the stigma of a psychiatric referral, which can be a problem with the consultation model, particularly for patients with conditions such as somatisation disorder, in which psychological explanations for symptoms are actively resisted.Psychological causes of physical illness
 Depressive disorder may present with biological symptoms including sleep disturbance, loss of energy and lethargy, sexual dysfunction, loss of appetite and weight loss and loss of concentration with apparent memory loss resulting in a misdiagnosis of dementia (known as pseudodementia).
Depressive disorder may present with biological symptoms including sleep disturbance, loss of energy and lethargy, sexual dysfunction, loss of appetite and weight loss and loss of concentration with apparent memory loss resulting in a misdiagnosis of dementia (known as pseudodementia).Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree