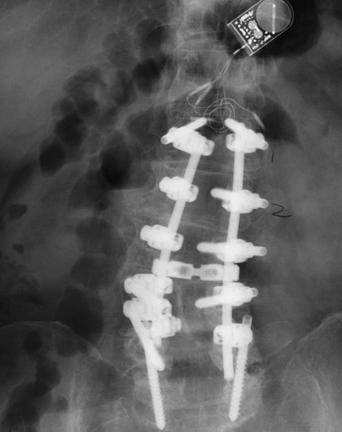
51 A 58-year-old man complained of progressive mechanical low back pain, radiating down his right lower extremity. He has antalgic weakness of the proximal lower extremities and decreased lumbar flexion. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of his lumbar spine demonstrated degenerative scoliosis with multilevel stenosis with spondylolisthesis. Anteroposterior (AP) x-ray of the lumbar spine shows an L1-S1 rod and screw construct with a bone stimulator (Fig. 51-1). Degenerative scoliosis An L1-L5 decompression was completed with L1-S1 bilateral pedicle screw fusion with arthrodesis and reduction of scoliosis. Scoliosis has been classified into two types: structural or nonstructural (postural, inflammatory, compensatory, etc.). The latest classification by the Scoliosis Research Society includes idiopathic, neuromuscular, congenital, neurofibromatosis, mesenchymal, rheumatoid, traumatic, osteochondral dystrophies, infectious, metabolic, degenerative, or tumorous types of scoliosis. Adult scoliosis is a type of deformity that has its onset in adulthood, secondary to progressive multilevel disc degeneration leading to asymmetric loss of disc height along with facet degeneration and osteopenia. This contributes to progressive deformity of the spinal segment, which can be measured with Cobb angles. The typical presentation is that of spinal stenosis and asymmetric radiculopathies secondary to foraminal stenosis. Axial pain is more frequent on the convex side due to muscle fatigue, and the radicular pain usually stems from the concave side.
Lumbar Scoliosis
Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Treatment
Discussion
Lumbar Scoliosis
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








