Fig. 20.1
Sagittal MRIs from a 62-year-old man with brucellar spondylodiscitis. (a) T1-weighted image showing irregularity and destruction of vertebral end plates and hypointensity at T11 to L2. (b) T2-weighted image showing increased signal intensity of the disk and loss of intervertebral disk height. (c) Sagittal STIR image shows hyperintense lesions vertebral contiguous. (d) Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted sagittal MRI shows involvement of intervertebral disk space between T11–L2 vertebral levels, vertebral bodies, and vertebral end plate
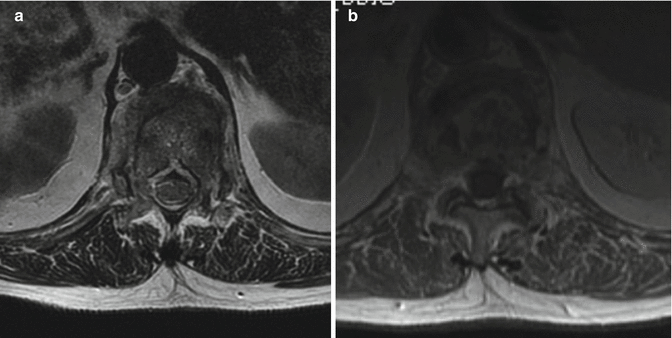
Fig. 20.2
(a) Axial T2-weighted MRI reveals a paravertebral abscess. (b) Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted axial image shows enhancement in affected vertebra and paravertebral soft tissue
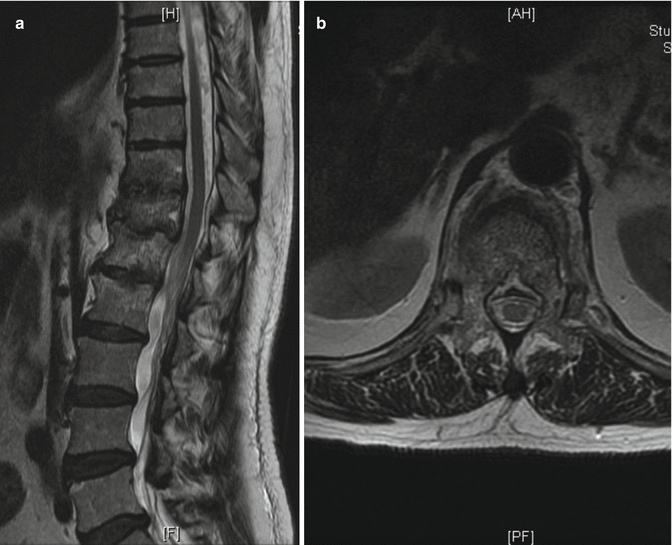
Fig. 20.3
(a) Sagittal and (b) axial MRIs after 1 year of diagnosis and treatment
The treatment should last not less than 3 months [9, 37]. Solera et al. [44] believe that aminoglycoside-containing regimens may be better than rifampicin-containing ones and suggest that the outcome of spondylitis may potentially be improved when such a streptomycin-containing regimen is used.
There is no recommendation for the use of oral antibiotics for the treatment of acute central nervous system (CNS) infections [13, 47]. The use of the oral antibiotic combination including rifampicin, doxycycline, and TMP/SMZ (co-trimoxazole) can be considered in poor countries. The use of streptomycin is not recommended for its doubtful ability to penetrate into the CSF and its potential neurotoxicity that can confuse the clinical presentation of the illness [35].
Erdem et al. [14] concluded in their study (multicenter retrospective study) in favor of 1 month of parenteral ceftriaxone in combination with doxycycline and rifampicin for the treatment of neurobrucellosis.
20.7 Conclusion
Neurobrucellosis should always be considered in the differential diagnosis of neurological and psychiatric cases in endemic areas of brucellosis. Patients with spondylitis or meningoencephalitis may need to be treated for a longer period of time [4, 5, 9, 37]. The treatment with the combination of ceftriaxone or TMP/SMZ (co-trimoxazole), doxycycline, and rifampicin is effective in neurobrucellosis cases that affect the CNS [8, 25]. Complications need long treatment courses and possibly surgical treatment [5].
References
1.
2.
Ariza J, Bosilkovski M, Cascio A, Colmenero JD, Corbel MJ, Falagas ME, Memish ZA, Roushan MR, Rubinstein E, Sipsas NV, Solera J, Young EJ, Pappas G (2007) Perspectives for the treatment of brucellosis in the 21st century: the Ioannina recommendations. PLoS Med 4, e317PubMedCentralPubMedCrossRef
3.
Ariza J, Gudiol F, Valverde J, Pallarés R, Fernández-Viladrich P, Rufí G, Espadaler L, Fernández-Nogues F (1985) Comparative trial of rifampin-doxycycline versus tetracycline-streptomycin in the therapy of human brucellosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 28:548–551PubMedCentralPubMedCrossRef
4.
Bordur H, Erbay A, Akinci E, Colpan A, Cevik MA, Balaban N (2003) Neurobrucellosis in an endemic area of brucellosis. Scand J Infect Dis 5:94–97CrossRef
5.
Bossi P, Tegnell A, Baka A, Van Loock F, Hendriks J, Werner A, Maidhof H, Gouvras G, Task Force on Biological and Chemical Agent Threats, Public Health Directorate, European Commission, Luxembourg (2004) Bichat guidelines for the clinical management of brucellosis and bioterrorism-related brucellosis. Euro Surveill 9:1–5
6.
Bouza E, García de la Torre M, Parras F, Guerrero A, Rodríguez-Créixems M, Gobernado J (1987) Brucellar menengitis. Rev Infect Dis 4:810–822CrossRef
7.
8.
9.
Colmenero JD, Reguera JM, Fernández-Nebro A, Cabrera-Franquelo F (1991) Osteoarticular complications of brucellosis. Ann Rheum Dis 50:23–26PubMedCentralPubMedCrossRef
10.
11.
Corbel MJ (2006) Brucellosis in humans and animals [WHO/CDS/ EPR/2006.7]. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 36–41
12.
13.
14.
Erdem H, Ulu-Kilic A, Kilic S, Karahocagil M, Shehata G, Eren-Tulek N, Yetkin F, Kemal M, Ceran N, Cem Gul H, Mert G, Tekin-Koruk S, Dizbay M, Seza Inal A, Nayman-Alpat S, Bosilkovski M, Inan D, Saltoglu N, Abdel-Baky L, Adeva-Bartolomé MT, Ceylan B, Sacar S, Turhan V, Yilmaz E, Elaldi N, Kocak-Tufan Z, Ugurlu K, Dokuzoguz B, Yilmaz H, Gundes S, Guner R, Ozgunes N, Ulcay A, Unal S, Dayan S, Gorenek L, Karakas A, Tasova Y, Usluer G, Bayindir Y, Kurtaran B, Resat O, Leblebicioglu H (2012) Efficacy and tolerability of antibiotic combinations in neurobrucellosis: results of the Istanbul study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:1523–1528PubMedCentralPubMedCrossRef
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







