11
Movement Disorders
MELINDA TRIMBLE
NOTE: This chapter corresponds to Chapter 14 in Fundamentals of Sleep Technology, 2nd edition.
1. What seizure type emerges from an epileptic foci located in the mesial and orbital cortex and results in seizures occurring almost exclusively during sleep?
A. Nocturnal paroxysmal dystonia
B. Nocturnal frontal lobe epilepsy
C. Nocturnal nosology
D. Nocturnal epileptic nyquist
2. Nonepileptic seizures are more commonly seen in young ______________.
A. Women
B. Men
3. Nonepileptic seizures are not common during sleep. True or false?
4. ______________ is an autosomal dominant prion disease, characterized by difficulties in falling asleep and maintaining sleep.
A. Nocturnal dyskinesias
B. Fragmentary myoclonus
C. Fatal familial insomnia
D. Pseudoseizures
5. Hypnagogic foot tremor is a rhythmic movement of the feet or toes that occurs during the transition between wake and sleep. True or false?
6. Sleep-related events characterized by discrete periods of intense fear or discomfort upon awakening occur in relation to:
A. Posttraumatic stress disorder
B. Panic disorder
C. Diurnal movement disorders
D. Hypnic disorder
7. An anxiety disorder with which the patient experiences recurrent stereotypical anxiety dreams occurring in the aftermath of a traumatic event is called:
A. Posttraumatic stress disorder
B. Panic disorder
C. Diurnal movement disorders
D. Hypnic disorder
8. ______________ is a motor disorder characterized by resting tremor persisting in stages N1 and N2 sleep.
A. Alternating leg movement activation (ALMA)
B. Fatal familial insomnia (FFI)
C. Excessive fragmentary myoclonus (EFM)
D. Parkinson disease (PD)
9. Choreic movements seen in selected circumstances such as drug side effect or toxicity are most commonly seen in patients with:
A. Nocturnal dyskinesias
B. Fragmentary myoclonus
C. Fatal familial insomnia
D. Pseudoseizures
10. List the missing information in this table:
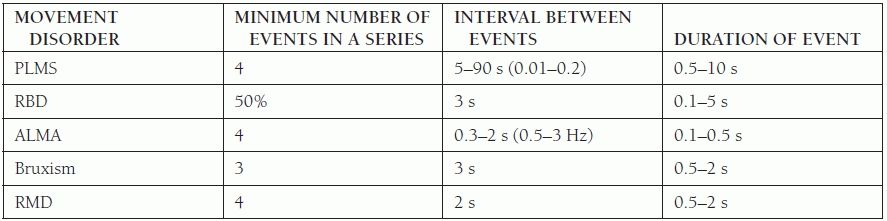
11. Another name for sleep starts is ______________.
12. OSA-induced arousals from NREM (or occasionally REM) sleep may trigger repeated episodes of sleep-related eating disorder. True or false?
13. When hooking up a patient, where would you place the leg leads and how many leads would you place on each leg in order to see alternating leg muscle activation (ALMA)?
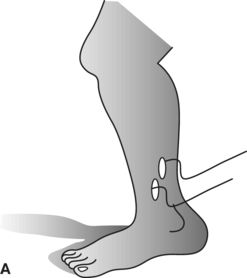
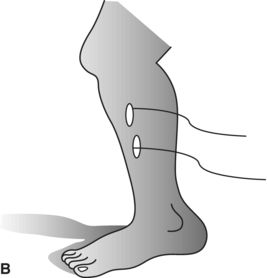
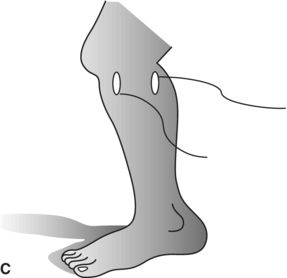
14. Which diagram shows the best placement for electrodes on the forearm extensors for evaluation of parasomnia during a sleep study?
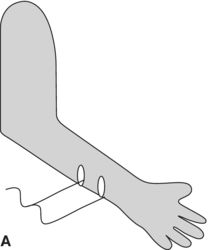
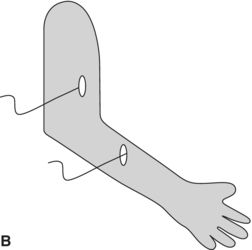
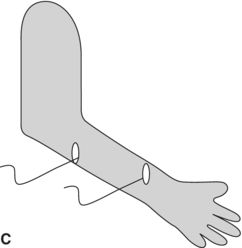
15. Attended video PSG (VPSG) is the accepted and preferred standard technique in the evaluation of patents with motor events in sleep. True or false?
16. Actigraphy can be used during:
A. Sleep only
B. Wake only
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




