Neurocritical Care
 Fluids and Electrolytes
Fluids and Electrolytes
1. The diagnosis is hyponatremia if the serum sodium is less than_____mEq/l. | 135 | G7 p.7:107mm |
2. The syndrome is SIADH |
| G7 p.7:107mm |
a. if the serum osmolality is less than_____mOsm/l | 275 |
|
b. and the urine osmolality is more than_____mOsm/l. | 100 |
|
3. The syndrome is CSW if the urinary sodium is greater than_____mEq/l. | 20 | G7 p.7:123mm |
4. Severe hyponatremia is considered a sodium lower than_____mEq/l. | 125 | G7 p.7:142mm |
5. Hyponatremia is considered |
| G7 p.7:145mm |
a. mild if sodium is_____mEq/l | 135 |
|
b. moderate if sodium is_____mEq/l | 130 |
|
c. severe if sodium is_____mEq/l | 125 |
|
6. Matching. For Na metabolism, match the conditions with their characteristics and treatment. |
| G7 p.7:145mm |
Characteristics and treatment: |
|
|
Conditions: |
|
|
a. inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (ADH) |
|
|
b. cerebral salt wasting |
|
|
7. Complete the equation to calculate serum osmolality. |
| G7 p.8:175mm |
a. Effective serum osmolality = measured osmolality − | BUN | |
8. Matching. Match symptoms with severity of hyponatremia. |
| G7 p.9:150mm |
Hyponatremia: |
|
|
Symptoms: |
|
|
a. headache |
|
|
b. cerebral edema |
|
|
c. anorexia |
|
|
d. nausea vomiting |
|
|
e. muscle weakness |
|
|
f. muscle twitching |
|
|
g. seizures |
|
|
h. respiratory arrest |
|
|
i. difficulty concentrating |
|
|
9. List the symptoms of hyponatremia. |
| G7 p.9:158mm |
Hint: c6natremia |
|
|
a. cep_____ | cephalgia |
|
b. cer_____e_____ | cerebral edema |
|
c. com_____ | coma |
|
d. con_____ | confusion |
|
e. conv_____ | convulsions |
|
f. c_____ | cramps |
|
g. n_____ | nausea |
|
h. a_____ | anorexia |
|
i. t_____ | twitching |
|
j. r_____ a_____ | respiratory arrest |
|
k. e_____ | excitability |
|
l. m_____ w_____ | muscle weakness |
|
m. i_____ | irritability |
|
a |
|
|
10. SIADH criteria are |
| G7 p.10:115mm |
a. NA is_____ | low |
|
b. Urine osmolality is_____ | high |
|
c. Volemia is_____ | high |
|
d. Due to release of_____ | ADH |
|
i. without_____stimuli | osmotic |
|
ii. creates_____hyponatremia | dilutional |
|
e. The release of ADH without a stimulus is what makes the release_____ | inappropriate |
|
11. One of the major effects of antidiuretic hormone is to |
| G7 p.11:155mm |
a. _____the permeability of the | increase |
|
b. _____renal tubule. This results in | distal |
|
c. _____ _____ of water. | increased reabsorption |
|
d. Its effects on the circulating blood? | dilutes it |
|
e. Its effect on urine volume? | reduces urine volume |
|
f. Its effect on urine concentration? | increases urine concentration | |
12. True or False. SIADH stands for syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone. | true | G7 p.10:115mm |
13. SIADH can also stand for s_____i_____a_____d_____h_____. | sodium is abnormal dilutionally hyponatremic | G7 p.10:115mm |
14. Complete the following regarding the treatment of hyponatremia: |
| G7 p.10:140mm |
a. Avoid_____correction. | rapid |
|
b. Avoid_____correction. | over |
|
c. Do not exceed_____mEq/l per hour. | 1 |
|
d. Do not exceed_____mEq/l per 24 hours. | 8 |
|
e. Do not exceed_____mEq/l per 48 hours. | 18 |
|
15. Matching. Diagnosis of SIADH depends on three diagnostic criteria. Match the laboratory value with the appropriate test. |
| G7 p. 11:28mm |
Test: |
|
|
|
|
|
a. low |
|
|
b. high |
|
|
c. normal |
|
|
16. Give the expected result for each test in the diagnosis of SIADH. |
| G7 p.11:35mm |
a. serum Na_____ _____ _____ | low—below 134 mEq/l |
|
b. serum osmol _____ _____ _____ | low—below 280 mOsm/L |
|
c. urinary Na _____ _____ _____ | high—above 18 mEq/l |
|
d. urinary Na may be as high as _____ | 50 to 150 mEq/l |
|
e. serum BUN below_____ | 10 |
|
f. serum creatinine_____ | normal |
|
17. Na at what level is always symptomatic? | 120 to 125 mEq/l | G7 p.11:95mm |
18. Characterize the symptoms of SIADH. |
| G7 p11:95mm |
a. Symptoms are almost always present at a Na of_____to_____ | 120 to 125mEq/l |
|
b. May treat if asymptomatic with_____restriction | fluid |
|
c. Avoid too rapid_____ | correction | |
19. Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) is |
| G7 p.11:150mm |
a. aka o_____ d _____syndrome | osmotic demyelination |
|
b. due to r_____ c_____ of hyponatremia | rapid correction |
|
c. a disorder of p_____ w_____ m_____ | pontine white matter |
|
d. Its symptoms are |
|
|
i. f_____ q_____ | flaccid quadriplegia |
|
ii. m_____s_____changes | mental status |
|
iii. c_____ n_____ abnormalitie | cranial nerve |
|
iv. p_____ p_____ appearance | pseudobulbar palsy |
|
20. Features common to patients who develop CPM are |
| G7 p.11:178mm |
Hint: rodi |
|
|
a. r_____c_____ | rapid correction |
|
b. o_____c_____ | over correction |
|
c. d_____ in d_____ for more than_____hours | delay in diagnosis, 48 |
|
d. increase in NA by more than_____mEq/l within_____hours | 25; 48 |
|
21. To treat mild SIADH you could modify the following by: |
| G7 p.13:100mm |
a. H2O_____ _____ | restrict fluid |
|
b. Salt_____ _____ | use 3% NaCl (to increase Na) |
|
22. To treat cerebral salt wasting (CSW) you could modify the following by: |
| G7 p.14:65mm |
a. H2O_____ _____ | give fluid |
|
b. Salt_____ _____ | give salt (Hint: CSW—cure with salt and water.) |
|
23. What is the treatment of severe hyponatremia? |
| G7 p.12:140mm |
a. Correct hyponatremia that is below_____mEq/l. | 125 |
|
b. Start with a _____% correction. | 10% |
|
24. Do not exceed a correction of |
| G7 p.13:15mm |
a. more than_____mEq/l/hr | 1.3 |
|
b. more than _____ mEq/l/24/hrs | 10 |
|
c. use _____% NaCl | 3% |
|
d. this has_____Eq/NaCl | 513 |
|
e. start with_____cc/hr | 25 |
|
f. simultaneously administer _____ | furosemide |
|
25. List the expected patient laboratory result when comparing SIADH with CSW. |
| G7 p.14:20mm |
a. water: in SIADH _____, in CSW_____ | SIADH: hypervolemic, CSW: hypovolemic |
|
b. Na (serum): in SIADH_____, in CSW_____ | SIADH: low, CSW: low |
|
c. osmol (serum): in SIADH_____, in CSW_____ | SIADH: low, CSW: high | |
d. osmol (urine): in SIADH _____, in CSW_____ | SIADH: high, CSW: high |
|
e. Na (urine): in SIADH _____, in CSW_____ | SIADH: high, CSW: high |
|
f. Hct: in SIADH_____, in CSW_____ | SIADH: low, CSW: high |
|
26. What is the treatment of CSW? |
| G7 p.14:70mm |
a. Hydrate |
|
|
i. with _____%_____ saline | 0.9%, normal |
|
ii. at_____cc/hr | 100 to 125 |
|
b. Use furosemide (yes or no?) | no |
|
c. Avoid_____correction | rapid |
|
27. In neurosurgical patients hyponatremia is seen in |
| G7 p.14:140mm |
a. c_____ s_____ w_____ | cerebral salt wasting |
|
b. and S_____. | SIADH |
|
28. In neurological patients hypernatremia is seen in |
| G7 p.14:144mm |
a. d_____i_____. | diabetes insipidus |
|
b. Define hypernatremia. | Na above 150mEq/l |
|
29. Characterize diabetes insipidus. |
| G7 p.15:40mm |
a. Due to low level of_____. | ADH |
|
b. Urine output is >_____ cc/hr. | 200 |
|
c. Specific gravity of urine is <_____. | 1.003 |
|
d. Serum osmolarity is normal or_____. | high |
|
e. Serum sodium is_____. | high |
|
30. In diabetes insipidus is the following low or high? |
| G7 p.15:40mm |
a. ADH is_____. | low |
|
b. Urine specific gravity is_____. | low |
|
c. Urine output is_____. | high |
|
d. Serum osmolality is_____. | high |
|
e. Serum sodium is_____. | high |
|
31. Diabetes insipidus features: |
| G7 p.15:40mm |
a. Urine output is_____. | high |
|
b. Urine mOsm/l is below_____. | 200 |
|
c. Specific gravity is below_____. | 1.003 |
|
d. Serum osmol is_____. | high or normal |
|
e. Normal serum osmol is between _____ and _____ mOsm/l. | 282 and 295 mOsm/l |
|
32. Diabetes insipidus etiology: |
| G7 p.15:80mm |
a. neu_____ | neurogenic |
|
b. nep_____ | nephrogenic |
|
33. Diagnosis of diabetes insipidus occurs when |
| G7 p.16:110mm |
a. urine output is above_____. | 250 cc/hr |
|
b. urine osmol is below_____. | 200 mOsm/l |
|
c. specific gravity is below_____. | 1.003 | |
34. Characterize serum osmolality. |
| G7 p.19:30mm |
a. Normal range is between _____ to _____ mOsm/l | 282 to 295 |
|
b. Dangerous if below_____ mOsm/l | 240 |
|
c. Dangerous if above_____mOsm/l | 320 |
|
d. Risk of renal failure if above_____ mOsm/l | 320 |
|
e. Seizures can occur if above_____ mOsm/l | 400 |
|
 Blood Pressure Management
Blood Pressure Management
35. List the effects of labetalol on the following: |
| G7 p.20:50mm |
a. ICP | no change |
|
b. pulse | no change |
|
c. cardiac output | no change |
|
d. coronary ischemia | no change |
|
e. renal failure | no change |
|
36. List the plasma expanders that are useful cardiovascular agents for treating shock. |
| G7 p.22:50mm |
a. cr_____ | crystalloids |
|
b. co_____ | colloids |
|
c. bl_____p_____ | blood products |
|
37. Describe the method of dosage for an intravenous (IV) drip of labetalol. |
| G7 p.20:70mm |
a. add_____ml (200 mg) | 40 |
|
b. to_____ml volume to create a volume | 160 |
|
c. of_____ml and infuse | 200 |
|
d. at_____ml/min until | 2 |
|
e. _____mg is given or the desired blood pressure (BP) is achieved. | 300 |
|
38. For the listed pressors complete the following statements to describe the cautions required. |
|
|
a. Neo-Synephrine: avoid in s_____c_____i_____ | spinal cord injuries | G7 p.22:170mm |
b. Dopamine: may cause h_____ | hyperglycemia | G7 p.22:100mm |
c. Dobutamine: may cause dysfunction of p_____ | platelets | G7 p.22:127mm |
 Sedatives and Paralytics
Sedatives and Paralytics
39. The Richmond Scale: Rass quantitates _____and_____ levels. | agitation and sedation | |
40. True or False. Indicate whether the following statements are true or false: |
| G7 p.24:25mm |
a. Methohexital (Brevital) is more potent and shorter acting than thiopental. | true |
|
b. Fentanyl causes dose-dependent respiratory depression. | true (also causes chest wall rigidity if given rapidly) |
|
c. Propofol has better neuroprotection than barbiturates (during aneurysm surgery). | false (barbiturates are better) |
|
d. Haldol can cause neuroleptic malignant syndrome. | true |
|
41. True or False. The following sedatives may induce seizures: |
| G7 p.24:30mm |
a. thiopental | false |
|
b. methohexital | true |
|
c. fentanyl | false |
|
d. propofol | false |
|
e. haloperidol | false |
|
42. True or False. The drug that can produce a neuroleptic malignant syndrome as a secondary effect is |
| G7 p.24:47mm |
a. propofol | false |
|
b. benzodiazepines | false |
|
c. fentanyl | false |
|
d. haloperidol | true |
|
e. thiopental | false |
|
43. Complete the following statements about the neuroleptic malignant syndrome: |
| G7 p.24:47mm |
a. Characterized by Hint: neuroleptic |
|
|
i. n_____ | motor, mutism |
|
ii. e_____ | elevation of temperature |
|
iii. u_____ | unconsciousness |
|
iv. r_____ | rigid muscles, rapid heart rate, respiratory failure |
|
v. o_____ | opisthotonus |
|
vi. l_____ | lethargy, leucocytosis |
|
vii. e_____ | elevated CPK |
|
viii. p_____ | potentially lethal |
|
ix. t_____ | trembling |
|
x. i_____ | imbalance of autonomic system |
|
xi. c_____ | coma | |
44. True or False. Regarding thiopental: |
| G7 p.24:86mm |
a. It’s a long-acting barbiturate. | false (Thiopental is a short-acting barbiturate with consciousness returning after 20 to 30 minutes.) |
|
b. It causes dose-related respiratory depression. | true |
|
c. It causes myocardial depression. | true |
|
d. It is an antianalgesic. | true |
|
e. It causes hypotension in hypovolemic patients. | true |
|
45. True or False. The following sedative causes necrosis when injected intraarterially: |
| G7 p.24:94mm |
a. thiopental | true |
|
b. fentanyl | false |
|
c. propofol | false |
|
46. True or False. Choose the correct order from long-acting to short-acting for the following neuromuscular blocking agents: |
| G7 p.24:120mm |
a. succinylcholine, vecuronium, pancuronium, nocuronium | false |
|
b. vecuronium, pancuronium, succinylcholine, rocuronium | false |
|
c. pancuronium, vecuronium, rocuronium, succinylcholine | true—pancuronium (Pavulon)—60 to 180 minutes vecuronium (Norcuron)—40 to 60 minutes rocuronium (Zemuron)—40 to 60 minutes (but shorter onset) succinylcholine (Anectine)—20 minutes |
|
d. rocuronium, succinylcholine, pancuronium, vecuronium | false |
|
e. vecuronium, pancuronium, rocuronium, succinylcholine | false |
|
47. True or False. The following is always required in a conscious patient simultaneously with a paralytic agent and as ventilation is being established: |
| G7 p.25:100mm |
a. arterial line | false |
|
b. Swan-Ganz catheter | false |
|
c. sedation | true |
|
d. intracranial pressure (ICP) monitor | false |
|
e. all of the above | false | |
48. True or False. |
| G7 p.25:165mm |
a. Pancuronium is a long-acting agent. | true |
|
b. Rocuronium is a short-acting agent. | true |
|
c. Succinylcholine is a competitive blocker and is short acting. | noncompetitive blocker and false (Succinylcholine is a is considered the only depolarizing ganglionic blocker. It has been linked to malignant hyperthermia.) |
|
d. Sedation is required for conscious patients. | true |
|
49. True or False. The only depolarizing ganglionic blocker among the following paralytics is |
| G7 p.26:25mm |
a. succinylcholine | true |
|
b. rapacuronium | false |
|
c. mivacurium | false |
|
d. rocuronium | false |
|
50. True or False. Possible side effects of succinylcholine include |
| G7 p.26:53mm |
a. elevated serum K+ | true (Succinylcholine can cause elevated K+, especially in patients with neuronal [spinal cord injury, hemiparesis] or muscular pathology, causing hyperkalemia.) |
|
b. cardiac arrest in adolescents and children | true (Adolescents and children with undiagnosed cardiac myopathies may arrest.) |
|
c. sinus bradycardia | true (It causes dysrhythmia, mainly sinus bradycardia.) |
|
d. malignant hyperthermia | true (It has been linked to malignant hyperthermia.) |
|
51. True or False. The following paralytic is contraindicated in the acute phase of injury because of the risk of hyperkalemia: |
| G7 p.26:60mm |
a. succinylcholine | true |
|
b. metocurine | false |
|
c. doxacurium | false |
|
d. pancuronium | false |
|
e. vecuronium | false |
|
52. True or False. The shortest-acting nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent (NMBA) is |
| G7 p.26:162mm |
a. mivacurium | false |
|
b. rocuronium | false |
|
c. vecuronium | true |
|
d. metocurine | false |
|
e. doxacurium | false | |
53. True or False. The nondepolarizing paralytic that does not affect ICP or CPP is |
| G7 p.26:168mm |
a. vecuronium | true |
|
b. pancuronium | false |
|
c. succinylcholine | false |
|
d. rapacuronium | false |
|
e. rocuronium | false |
|
54. True or False. The main difference between cisatracrium and its isomer atracurium is |
| G7 p.27:40mm |
a. cost | false |
|
b. onset of action | false |
|
c. duration | false |
|
d. cisatracrium does not release histamine | true |
|
e. none of the above | false |
|
55. The complete reversal of Pavulon’s effect takes _____ minutes. | 20 | G7 p.27:55mm |
56. True or False. It is true about pancuronium that |
| G7 p.27:55mm |
a. it is not reversible | false (It is reversible with anticholinesterases.) |
|
b. it is not a competitive paralytic | false (It is a competitive paralytic.) |
|
c. it increases cardiac output, pulse rate, and ICP | true |
|
d. it is eliminated through the liver | false (It is eliminated through the kidneys.) |
|
57. True or False. Regarding atracurium: |
| G7 p.27:60mm |
a. It is a nondepolarizing (competitive) blocker. | true |
|
b. It can produce hypotension. | true |
|
c. It is reversible with neostigmine. | true |
|
d. It is metabolized in the kidneys and liver. | false |
|
 Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema
Neurogenic Pulmonary Edema
58. True or False. Which of the following statements about neurogenic pulmonary edema are true and which are false? |
| G7 p.28:30mm |
a. relatively common condition in the neurosurgical patient | false |
|
b. caused by intracranial pathologies such as subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), seizure (Sz), head injury | true |
|
c. mechanism caused in part by slow increase in intracranial pressure (ICP) | false |
|
d. surge of catecholamine disrupts capillary endothelium with increase in alveolar permeability | true |
|
59. True or False. For treatment of neurogenic pulmonary edema, you should use high levels of positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) to keep alveoli distended. | false—low levels of PEEP | G7 p.28:55mm |
60. True or False. For neurogenic pulmonary edema, dobutamine does not reduce cerebral perfusion. | true—and therefore is better than á or â blockers to treat neurogenic pulmonary edema | G7 p.28:67mm |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


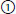 hyponatremia;
hyponatremia;  increased intravascular volume;
increased intravascular volume;  treat with volume restriction;
treat with volume restriction;  volume depletion;
volume depletion;  treat with Na + volume replacement;
treat with Na + volume replacement;  symptoms made worse by fluid restriction
symptoms made worse by fluid restriction ,
,  ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
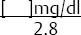
 mild hyponatremia is less than 130 mEq/l,
mild hyponatremia is less than 130 mEq/l,  severe hyponatremia is less than 125 mEq/l
severe hyponatremia is less than 125 mEq/l
 serum Na;
serum Na;  serum K;
serum K;  serum osmolality;
serum osmolality;  urinary osmolality;
urinary osmolality;  urinary Na;
urinary Na;  urinary K;
urinary K;  blood urea nitrogen (BUN) creatinine Laboratory value:
blood urea nitrogen (BUN) creatinine Laboratory value: