Fig. 1
Overall research framework: three major experimental and simulation research levels (individual, group-wide and MAS simulation)
2.1 Individual Coherence Level
The main purpose of the proposed individual experimental EEG framework – to find out whether brain-wave patterns, i.e. EEG-recorded mind-fields, can demonstrate mutually correlated behavior that depends solely on the states of people’s minds. Hence, we tested few hypothesis (H0(1) and H0(2)), see Fig. 1. In short, our results also confirm, that temporally separated people doing the same mental activities demonstrate an increase of specific spectral coherence in their brain-wave patterns. Due to the space limitations in the current paper, plenty of obtained results can be provided in the extended version of this paper.
In short, benchmark EEG experimental results have shown partial confirmation of major OSIMAS assumptions concerning (a) oscillatory nature of the agent’s mental states and (b) some common principles of power spectra redistribution in different mental states. Based on these experimental findings, we made adjustments to the conceptual oscillating agent model (OAM).
In order to find further insights about oscillatory nature of human mental states, we have designed a simulation of human brain EEG signal dynamics using a refined Kuramoto model [11], i.e. coupled oscillator energy exchange model (COEEM), which simulates human brain single channel EEG signal dynamics (see Fig. 2), using fourth-order Runge-Kuta algorithms (RK4).
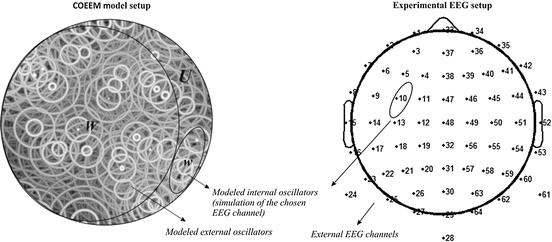

Fig. 2
The systems of the internal and external oscillators in the COEEM model
We have obtained unique prognostication results, suitable for relatively accurate prognoses of the human brain EEG signal dynamics for the chosen EEG channels, see http://vlab.vva.lt.
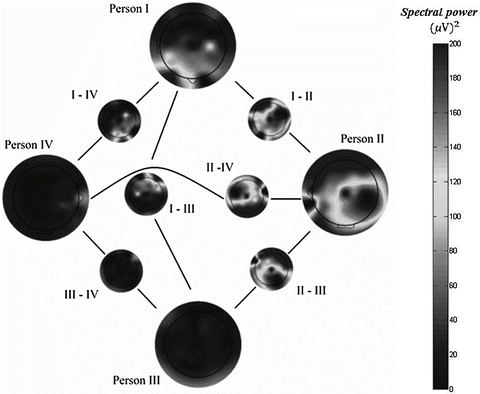
2.2 Group Coherence Level
Real-time group-wide EEG experiments (see Fig. 1) have also revealed spectral coherence and temporal synchronization patterns for the people in the same mental states (like concentration, contemplation, meditation, etc.). For analyses and visualization of group-wide neurodynamics we have designed GMIM method (URL: http://osimas-eeg.vva.lt), which shows simultaneous dynamics of the group-wide neurodynamic processes, see Fig. 3.