Neuroradiology
 Contrast Agents in Neuroradiology
Contrast Agents in Neuroradiology
1. Characteristics of iodinated contrast agents |
| G7 p.122:60mm |
a. may delay excretion of_____. | metformin |
|
b. which is an_____ _____ agent | oral hypoglycemic |
|
c. used in_____ _____ _____ | diabtes type II |
|
d. It can produce |
|
|
i. l_____a_____ | lactic acidosis |
|
ii. and r_____f_____. | renal failure |
|
e. It should be held for_____ hours before and after administration of contrast agent. | 48 |
|
2. The primary approved agent for intrathecal use is_____, trade name_____. | iohexol, Omnipaque | G7 p.122:90mm |
3. Use Omnipaque cautiously in patients who have |
| G7 p.123:70mm |
a. s_____h_____ | seizure history |
|
b. c_____-v_____d_____ | cardio-vascular disease |
|
c. c_____a_____ | chronic alcoholism |
|
d. m_____s_____ | multiple sclerosis |
|
e. and stop_____medications | neuroleptic | G7 p.123:52mm |
f. at least_____hours before procedure | 48 |
|
4. Complete the following for an iodinated contrast allergy prep: |
| G7 p.124:85mm |
a. prednisone |
|
|
i. pretest timing in hours | 20 to 24 hours, 8 to 12 hours, 2 hours |
|
ii. dose in mg | 50 |
|
iii. route | PO |
|
b. Benadryl |
|
|
i. pretest timing in hours | 1 |
|
ii. dose in mg | 50 |
|
iii. route | IM |
|
c. cimetidine |
|
|
i. pretest timing in hours | 1 |
|
ii. dose in mg | 300 |
|
iii. route | PO or IV |
|
 Radiation Safety for Neurosurgeons
Radiation Safety for Neurosurgeons
5. Characterize radiation safety. |
| G7 p.126:165mm |
a. Rem is the absorbed dose in rads multiplied by_____. | Q |
|
b. Q “is the quality factor”; the Q of x-ray is_____. | 1 |
|
c. 1 rem causes_____cases of cancer in every 1 million people. | 300 |
|
d. Spine x-rays with obliques is_____rem. | 5 | G7 p.127:18mm |
e. Cerebral angiogram is_____rem. | 10 to 20 |
|
f. Cerebral embolization is rem. | 34 |
|
6. Complete the following regarding occupational radiation exposure: |
| G7 p.127:80mm |
a. It is advised to keep below_____rem per year, | 2 |
|
b. averaged over a_____year period. | 5 |
|
7. Provide the precautions advised. |
| G7 p.127:110mm |
Increase the_____from the radiation source. | distance |
|
b. Exposure is proportional to the_____ _____of the distance. | inverse square |
|
c. Stay at least_____feet away, preferably_____feet away, | 6, 10 |
|
d. Double the distance and get_____of the radiation. | 1/4 |
|
e. What is better: lead “doors” or lead aprons? | doors |
|
 CAT Scan
CAT Scan
8. For measurement on a CT scan |
| G7 p.128:46mm |
a. The eyeball is_____mm through its equator. | 25 |
|
b. Give Hounsfield units for |
|
|
i. air | -1000 |
|
ii. water | 0 |
|
iii. bone | +1000 |
|
iv. blood clot | 75-80 |
|
v. calcium | 100-300 |
|
vi. disc material | 55-70 |
|
vii. thecal sac | 20-30 |
|
c. Effect of anemia on an acute subdural hematoma (SDH) in a patient with less than 23% HCT will look_____. | isodense |
|
 Sylvian Point
Sylvian Point
9. True or False. The sylvian point is |
| G5 p.559:10mm |
a. the apex of the insula | true |
|
b. usually 5 to 10 mm from the inner table of the skull | false (30 to 43 mm from inner table) |
|
c. at or within 1 cm below the midpoint of a vertical line from the superior inner table to the orbital apex | true |
|
d. the point where the anterior choroidal artery enters the temporal horn of the lateral ventricle | false (That is called the plexal point.) |
|
 Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral Angiography
10. Answer the following concerning cerebral angiography: |
| G7 p.134:145mm |
a. What is the overall risk, in %, of a complication resulting in a permanent neurological deficit with angiography? | 0.1% |
|
b. What is the risk, in %, of neuropathy from femoral angiogram? | 0.2% |
|
11. Complete the following about angiography (cerebral): |
| G7 p.134:145mm |
a. The complication rate in |
|
|
i. uncomplicated angiography is approximately_____%. | 0.1% |
|
ii. asymptomatic carotid stenosis is_____%. | 1.2% |
|
b. The most common of the persistent carotid basilar anastomoses is_____ _____ _____ _____. | persistent primitive trigeminal artery |
|
c. This occurs in_____% of angiograms. | 0.6% |
|
d. The sylvian point marks the apex of the_____. | insula |
|
12. Characterize venous structures. |
| G7 p.134:160mm |
a. Deep lesions cause changes in_____ structures. | venous |
|
b. Superficial lesions cause changes in_____structures. | arterial |
|
c. Malignant lesion (i.e., GBM) show an early_____ _____. | draining vein |
|
d. Meningiomas show draining veins_____. | late |
|
e. Meningiomas come_____ and stay _____. | early, late | |
13. The recurrent artery of Heubner arises from the |
| G7 p.134:145mm |
a. _____ segment of the | A1 |
|
b. _____ _____ artery (80%) | anterior cerebral |
|
c. and supplies the: | (Controversial item: Rhoton’s Anatomy, page 119 column B 45 mm, recurrent branch most commonly arises from A2—78% A1—14% A1—A2 junction 8%) |
|
i. a_____ | anterior limb: internal capsule |
|
ii. p_____ | putamen |
|
iii. c_____ | caudate head |
|
14. What is the name of the artery that is the continuation of the anterior cerebral artery? | pericallosal artery | G7 p.101:15mm |
15. Complete the following statements about neuroradiology: |
| G7 p.101:70mm |
a. The_____ _____ artery enters | anterior choroidal |
|
b. the temporal horn via the_____fissure. | choroidal |
|
c. This is called the p_____p_____. | plexal point |
|
d. It is_____mm to_____mm from origin of that vessel. | 18 to 26 mm |
|
e. What is unique about this point on the angiogram? | It makes a distinct kink as seen on the lateral angiogram. |
|
16. True or False. From proximal to distal, the branches of the anterior cerebral artery are |
| G7 p.101:90mm |
a. medial orbitofrontal, frontopolar, callosomarginal, pericallosal | true |
|
b. frontopolar, callosomarginal, medial orbitofrontal, pericallosal | false |
|
c. frontopolar, medial orbitofrontal, pericallosal, callosomarginal | false |
|
d. medial orbitofrontal, frontopolar, pericallosal, callosomarginal | false |
|
17. True or False. The sylvian triangle on a lateral ICA angiogram is formed by |
| G5 p.560:135mm |
a. superior insular line, angular artery, line between MCA origin, and most anterior ascending branch | true |
|
b. superior insular line, line from bregma to torcula, line between posterior temporal branch, and lateral orbitofrontal branch | false |
|
c. superior insular line, clinoparietal line, limbus sphenoidale | false |
|
d. clinoparietal line, angular artery, line from bregma to torcula | false | |
18. True or False. The following are MCA branches: |
| G7 p.101:175mm |
a. lateral orbitofrontal | true |
|
b. ascending frontal | true |
|
c. medial orbitofrontal | false (The medical orbitofrontal is a branch of the anterior cerebral artery.) |
|
d. anterior temporal | true |
|
e. posterior parietal | true |
|
19. Complete the following about angiography (cerebral): |
| G7 p.105:86mm |
a. The foramen of Monro lies at the junction of what three veins? |
|
|
i. i_____c_____ | internal cerebral |
|
ii. t_____ | thalamostriate |
|
iii. s_____ | septal |
|
b. This site is known as the_____ _____. | venous angle |
|
20. True or False. The following veins will drain into the straight sinus in the normal venous anatomy: |
| G7 p.105:130mm |
a. vein of Galen | true |
|
b. basal cerebral vein of Rosenthal | true (via the vein of Galen) |
|
c. inferior sagittal sinus | true |
|
d. vein of Labbé | false | (It empties into the transverse sinus.) |
21. True or False. In the setting of a brain stem mass seen on a lateral vertebrobasilar angiogram, the displacement of the choroidal and colliculocentral points should be |
| G5 p.562:143mm |
a. both displaced anteriorly | false (They would both be displaced anteriorly by a cerebellar mass but posteriorly by a brain stem mass.) |
|
b. choroidal anteriorly, colliculocentral posteriorly | false (They outline the fourth ventricle and would move with it.) |
|
c. choroidal posteriorly, colliculocentral anteriorly | false (They outline the fourth ventricle and would move with it.) |
|
d. both displaced posteriorly | true (Both would be displaced posteriorly by a brain stem mass.) |
|
e. no displacement | false | |
22. Complete the following about cerebral angiography. |
| G5 p.562:135mm |
a. True or False. On a lateral vertebrobasilar angiogram, the most sensitive indicator of the anterior border of the pons is the |
|
|
i. pontomesencephalic vein | true |
|
ii. basilar artery | false (Basilar artery may be off to one side.) |
|
iii. choroidal point | false (junction of posterior medullary loop and supratonsillar loop) |
|
iv. copular point | false (on the inferior vermian vein) | G5 p.562:130mm |
b. Twinings line runs between |
|
|
i. t_____ | tuberculum |
|
ii. t_____ | torcula |
|
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
23. Matching. Match the best completion for each of the following: |
| G7 p.129:49mm |
|
|
|
a. T1-weighted MRI has: |
|
|
b. T2-weighted image has: |
|
|
24. Complete the following about magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): |
| G7 p.129:110mm |
a. List the three materials that appear white on T1-weighted imaging (T1WI) MRI. | fat, melanin, and subacute blood |
|
b. What color is pathology on T1WI? | low signal on T1 (dark) |
|
c. What color is pathology on T2WI? | high signal on T2 (white) |
|
25. Matching. Match the phrases with the appropriate signal. |
| G7 p.129:145mm |
|
|
|
a. Fat on T1 is_____ |
|
|
b. Fat on T2 is_____ |
|
|
c. 7-to 14-day-old blood on T2-weighted MRI is: |
|
|
d. 7-to 14-day-old blood on T1-weighted MRI is: |
On T1 both fat and 7-to 14-day-old blood are high signal (white). On T2 fat drops out (i.e., is dark); blood remains white. | |
26. Complete the following about MRI: |
| G7 p.129:170mm |
a. The best sequence for CVA is_____. | FLAIR |
|
b. which stands for_____-_____ _____ _____. | fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
|
c. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is_____. | black |
|
d. Most lesions appear_____in this sequence. | bright |
|
e. Most lesions are more_____. | conspicuous |
|
27. The best MRI sequence for |
|
|
a. SAH is_____ | FLAIR | G7 p.130:15mm |
b. blood is_____ _____ | gradient echo | G7 p.130:82mm |
28. Gradient echo |
| G7 p.130:60mm |
a. aka_____ _____ | T2 star |
|
b. aka_____ | grass white |
|
c. CSF and flowing blood appear_____ | white |
|
d. In cervical spine produces a_____effect | myelographic |
|
e. Improves delineation of_____ _____ | bone spurs |
|
f. Also shows small old_____ | hemorrhage |
|
g. It is the most sensitive MRI sequence for_____. | blood |
|
29. Complete the following about MRI: |
| G7 p.130:92mm |
a. True or False. An MRI sequence that summates T1 and T2 signals and causes fat to be suppressed is called the_____sequence. |
|
|
i. grass | false |
|
ii. stir | true |
|
iii. echo train | false |
|
iv. spin density | false |
|
b. STIR stands for_____ _____ _____ _____. | short tau inversion recovery (summates T1 and T2 images) |
|
c. Use it to_____. | see tissues that enhance in areas of fat |
|
30. If a MRI contrast is given to patients with severe renal failure, a rare condition called n_____s_____f_____may occur. | nephrogenic systemic fibrosis | |
31. Name two contraindications to MRI. |
| G7 p.131:20mm |
a. patients who contain_____or_____ | ferro metals or cobalt (i.e., cardiac pacemaker, implanted neurostimulators, cochlear implants, ferromagnetic aneurysm clips, foreign bodies with a large component of iron or cobalt, metallic fragments in the eye, placement of stent, coil, or filter within past 6 weeks) |
|
b. relative contraindication to MRI is_____ | claustrophobia |
|
32. Complete the following regarding programmable valves and MRI: |
| G7 p.131:80mm |
a. Can such patients have MRI studies? | yes |
|
b. You may need to check the_____ _____after the MRI. | pressure setting |
|
33. Hemorrhage on MRI. Related to time. T1 |
| G7 p.132:15mm |
Hint: George Washington Bridge |
|
|
a. acute g_____ | gray |
|
b. subacute w_____ | white |
|
c. chronic b_____ | black |
|
34. Hemorrhage on MRI. Related to time. T2 |
| G7 p.132:15mm |
Hint: layers of Oreo cookie |
|
|
a. acute b_____ | black |
|
b. subacute w_____ | white |
|
c. chronic b_____ | black |
|
35. Hemorrhage on MRI. Related to time. |
| G7 p.132:15mm |
Hint: i – baby, i – di, bi – di, ba – by, da – da |
|
|
a. hyper-acute |
|
|
i. T1: i_____ | isodense |
|
ii. T2: b_____ | bright |
|
b. acute |
|
|
i. T1: i_____ | isodense |
|
ii. T2: d_____ | dark |
|
c. subacute early |
|
|
i. T1: b_____ | bright |
|
ii. T2: d_____ | dark |
|
d. subacute late |
|
|
i. T1: b_____ | bright |
|
ii. T2: b_____ | bright |
|
e. chronic |
|
|
i. T1: d_____ | dark |
|
ii. T2: d_____ | dark | |
36. Age of hemorrhage |
| G7 p.132:15mm |
a. hyper acute_____ | <24 hours |
|
b. acute_____ | 1 to 3 days |
|
c. subacute early_____ | 3 to 7 days |
|
d. subacute late_____ | 7 to 14 days |
|
e. chronic_____ | >14days |
|
37. Complete the following regarding hemorrhage and the condition of hemoglobin: |
| G7 p.132:20mm |
a. hyperacute o_____ | oxy |
|
b. acute d_____ | deoxy |
|
c. subacute early m_____ | met |
|
d. subacute late m_____ | met |
|
e. chronic h_____ | hemosiderin |
|
38. a. Complete the following regarding hemorrhage and the location of hemoglobin: |
| G7 p.132:20mm Also see G7 p.1125:50mm |
a. hyperacute l_____ | intracellular |
|
b. acute l_____ | intracellular |
|
c. subacute early l_____ | intracellular |
|
d. subacute late E_____ | extracellular |
|
e. chronic l_____ | intracellular |
|
39. Complete the following regarding diffusion weighted images (DWI): |
| G7 p.132:103mm |
a. Its primary use is to detect |
|
|
i. i_____ | ischemia |
|
ii. and a_____p_____. | active plaques |
|
b. It first generates on_____map. | ADC |
|
c. On DWI freely diffusible water is_____. | dark |
|
d. Restricted diffusion is_____. | bright |
|
e. Which is abnormal? | restricted diffusion |
|
40. Characterize DWI. |
| G7 p.132:135mm |
a. Restricted perfusion usually indicates_____ _____. | cell death |
|
b. DWI abnormally will be present for_____. | 1 month |
|
c. DWI abnormalities can light up within_____of ischemia. | minutes |
|
41. The most sensitive study for ischemia of the brain is the_____. | PWI | G7 p.133:13mm |
42. DWI and PWI mismatch identifies penumbra. |
| G7 p.133:42mm |
Hint: DWI death PWI |
|
|
a. Which modality shows irreversible cell injury (death)? | DWI |
|
b. Which modality shows reversible cell injury (penumbra)? | PWI | |
43. The important peaks in MRS are |
| G7 p.133:105mm |
Hint: li-la-Na-crea-chol |
|
|
a. li_____ | lipid |
|
b. la_____ | lactate |
|
c. Na_____ | N acetyl aspartate |
|
d. crea_____ | creatine |
|
e. chol_____ | choline |
|
44. The significance of important peaks in MRS are |
| G7 p.133:105mm |
a. hypoxia | lactate |
|
b. a couplet peak | lactate |
|
c. nerve and axons | NAA |
|
d. a reference for choline | creatinine |
|
e. membrane synthesis | choline |
|
f. increased in tumor | choline |
|
g. increased in developing brain | choline |
|
h. reduced in CVA | choline |
|
45. The test that may help distinguish hemangiopericytom. |
| G7 p.134:20mm |
a. from meningioma is the_____; | MRS |
|
b. specifically the presence of a large_____peak. | inositol |
|
46. The test that may help a surgeon avoid critical white matter |
| G7 p.134:118mm |
a. tracts during brain surgery is_____. | DTI |
|
b. which stands for d_____t_____i_____. | difffusor tensor imaging |
|
 Plain Films
Plain Films
47. Complete the following about plain films. |
| G7 p.135:115mm |
a. The basion is at the tip of the_____. | clivus |
|
b. The opisthion is at the anterior lip of the_____ _____. | occipital bone | G7 p.135:118mm |
48. A lateral C-spine x-ray has four contour lines with two marking the borders of the spinal canal. |
| G7 p.135:160mm |
Hint: apsp |
|
|
a. front of vertebral body called_____ _____ _____ | anterior marginal line |
|
b. back of vertebral body called_____ _____ _____ | posterior marginal line (marks anterior border of spinal canal) |
|
c. posterior margin of spinal canal called_____ _____ | spinolaminar line |
|
d. posterior margin of spinous processes is called_____ _____ _____ | posterior spinous line | |
49. Complete the following about spine films: |
|
|
a. Cervical spine normal diameter is_____mm. | 17 ± 5 mm | G7 p.136:130mm |
b. Stenosis is present when the anteroposterior diameter is less than _____mm | 12 mm | G7 p.136:140mm |
50. Complete the following about normal prevertebral soft tissue: |
| G7 p.137:15mm |
a. Anterior to C1:_____mm | 10 |
|
b. Anterior to C2, 3,4:_____mm | 7 |
|
c. Anterior to C5-C6:_____mm | 22 |
|
51. Interspinous distances |
| G7 p.137:50mm |
a. are abnormal if it is_____times the adjacent levels on AP film | 1.5 |
|
b. if present it represents: true or false |
|
|
i. fracture | true |
|
ii. dislocation | true |
|
iii. ligament disruption | true |
|
c. this is called_____on lateral x-ray | fanning |
|
52. C1 has how many ossification centers? | 3 | G7 p.137:84mm |
53. C2 has how many ossification centers? | 4 | G7 p.137:140mm |
54. Matching. Match the following skull film findings with their characteristics: |
| G7 p.138:115mm |
|
|
|
a. craniopharyngioma |
|
|
b. pituitary adenoma |
|
|
c. optic glioma |
|
|
d. empty sella |
|
|
55. True or False. On a skull x-ray, erosion of the posterior clinoids would most often be seen in the setting of |
| G7 p.138:115mm |
a. craniopharyngioma | true |
|
b. empty sella syndrome | false |
|
c. pituitary adenoma | false |
|
d. Hurler syndrome | false |
|
e. optic glioma | false | |
56. Complete the following regarding lumbosacral spine films: |
| G7 p.138:25mm |
a. The disc space with the greatest heigh is at_____ | L45 |
|
b. AP view. Look for “owl eyes.” |
|
|
i. These correspond to the_____ | pedicles |
|
ii. Can be eroded in_____disease | metastatic |
|
c. Oblique views. Look for the neck of the scotty dog. |
|
|
i. It corresponds to the_____ _____ | pars interarticularis |
|
ii. Discontinuity occurs in a_____ | fracture |
|
57. True or False. The percentage of all patients over 20 years old who will have a calcified pineal gland visible on plain skull x-ray is |
| G5 p.570:55mm |
a. 0% | false |
|
b. 10% | false |
|
c. 20% | false |
|
d. 55% | true |
|
e. 90% | false |
|
58. True or False. The most common congenital anomaly of the craniocervical junction is |
| G7 p.139:140mm |
a. Chiari malformation | false |
|
b. basilar impression | true |
|
c. os odontoideum | false |
|
d. incomplete arch of C1 | false |
|
e. C1-C2 subluxation | false |
|
59. True or False. Basilar invagination is seen in |
| G7 p.139:166mm |
a. hypoparathyroidism | false |
|
b. Paget disease | true |
|
c. osteogenesis imperfecta | true |
|
d. osteomalacia | true |
|
e. hyperparathyroidism | true |
|
60. True or False. In the evaluation of basilar invagination, in the normal patient, no part of the odontoid should be above the McRae line. | true | G7 p.139:48mm |
61. True or False. A line used in the evaluation of the craniocervical junction is |
| G7 p.139:24mm |
a. McRae line | true |
|
b. Chamberlain line | true |
|
c. Wackenheim line | true |
|
d. Maginot line | false | G7 p.138:115mm |
e. Fischgold line | true | |
62. True or False. The most common nondisc spinal lesion is: |
| G6 p.142:150mm |
a. synovial cyst | false |
|
b. Tarlov cyst | false |
|
c. astrocytoma | false |
|
d. chordoma | false |
|
e. metastatic tumor | true |
|
 Myelography
Myelography
63. True or False. The risk of postlumbar puncture headache is higher with |
| G5 p.572:55mm |
a. water-soluble contrast | false |
|
b. non-water-soluble contrast | true |
|
64. Matching. Match each of the following two statements with answers 1,2,3, or 4. |
| G5 p.571:145mm |
|
|
|
a. In lumbar disc disease, what percentage of free fragments move inferiorly? |
|
|
b. In lumbar disc disease, what percentage of free fragments move superiorly? |
|
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


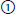 short TE, short TR;
short TE, short TR; 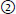 short TE, long TR;
short TE, long TR; 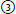 long TE, short TR;
long TE, short TR; 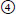 long TE, long TR
long TE, long TR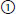
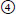
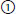 high signal (bright);
high signal (bright); 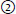 low signal (dark);
low signal (dark); 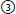 intermediate signal
intermediate signal
 enlarged sella;
enlarged sella;  J-shaped sella;
J-shaped sella;  symmetrical ballooning;
symmetrical ballooning;  erosion of posterior clinoids
erosion of posterior clinoids erosion of posterior clinoids
erosion of posterior clinoids enlarged sella
enlarged sella J-shaped sella
J-shaped sella symmetrical ballooning
symmetrical ballooning 10%;
10%;  35%;
35%;  65%;
65%;  90%
90%