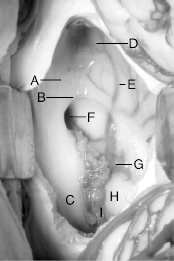
Chapter 1 Neurosurgery For questions 1 to 9, identify the following structures.The figure illustrates a right transcallosal approach to the third ventricle 1. caudate nucleus 2. choroid plexus 3. foramen of Monro 4. columns of the fornix 5. septum pellucidum 7. thalamus 8. body of the fornix 9. anterior caudate vein 10. Surgical procedures utilized in the treatment of spasmodic torticollis include I. upper cervical ventral rhizotomies and spinal accessory neurectomy II. stereotactic thalamotomy III. microvascular decompression of the spinal accessory nerve IV. Myotomy A. I, II, III B. I, III C. II, IV D. IV E. all of the above 11. Which surgical approach for thoracic disk herniations is associated with the highest rate of neurologic injury? A. costotransversectomy B. lateral extracavitary C. midline laminectomy D. transpedicular E. transthoracic 12. Most patients with intrinsic brainstem gliomas initially present with A. cranial neuropathies B. headache C. hydrocephalus D. nausea and vomiting E. papilledema 13. Each of the following is characteristic of complex regional pain syndrome II (causalgia) except A. atrophic changes in the limb B. hypesthesia C. increased sweating D. lack of major motor deficit E. good relief with sympathetic block For questions 14 to 18, match the description with the structure. A. dermoid cyst B. epidermoid cyst C. both D. neither 14. bacterial meningitis 16. associated congenital malformations 17. most often midline 18. responsive to radiation therapy 19. Ventricular enlargement from choroid plexus papillomas can be secondary to I. entrapment of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) II. decreased absorption of CSF from hemorrhage-induced arachnoiditis III. tumor growth IV. excessive production of CSF A. I, II, III B. I, III C. II, IV D. IV E. all of the above 20. Which approach is favored for a patient with an 8 mm acoustic neuroma in which hearing preservation is a goal? A. middle fossa B. suboccipital C. translabyrinthine 21. Uncinate seizures typically produce A. auditory hallucinations B. gustatory hallucinations C. olfactory hallucinations D. vertiginous sensations E. visual seizures For questions 22 to 25, match the description with the structure. A. calcarine sulcus B. lateral mesencephalic sulcus C. posterior communicating artery D. tectal plate 22. separates the P1 and P2A segments of the posterior cerebral artery 23. separates the P2A and P2P segments of the posterior cerebral artery 24. separates the P2P and P3 segments of the posterior cerebral artery 25. separates the P3 and P4 segments of the posterior cerebral artery 26. The radial nerve or one of its branches innervates each of the following except the A. abductor pollicis longus B. adductor pollicis C. brachioradialis D. extensor pollicis brevis E. supinator 27. Each of the following is true of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) in the newborn except A. Periventricular hemorrhagic infarction is one sequela. B. Posthemorrhagic hydrocephalus can result in persistent bradycardia and apneic spells. C. The capillary bed of the germinal matrix is composed of large irregular vessels. D. The germinal matrix is the most common site of IVH in the full-term neonate. E. The risk of IVH is greater in the preterm than in the term infant. 28. The ossification centers of the odontoid consist of A. one primary and two secondary centers B. one secondary and three primary centers C. three secondary and one primary center D. two primary centers E. two primary and one secondary center 29. The most common single-suture synostosis is A. coronal B. lambdoid C. metopic D. sagittal E. sphenozygomatic 30. The most sensitive method for detecting carpal tunnel syndrome is A. needle examination of the abductor pollicis brevis B. needle examination of the first and second lumbricals C. motor amplitude of the median nerve D. motor distal latency of the median nerve E. palmar sensory conduction time of the median nerve 31. Coup contusions most commonly occur at the A. cerebral convexities B. frontal and temporal poles C. orbital surface of the frontal lobes D. posterior fossa E. ventral surface of the temporal lobe A. anterior communicating artery aneurysm B. intracavernous carotid aneurysm C. middle cerebral artery aneurysm D. ophthalmic artery aneurysm E. posterior communicating artery aneurysm 32. pupil-involving third nerve palsy 33. seizures 34. diabetes insipidus 35. inferior nasal quadrantanopia 36. exophthalmos 37. The essential difference between a syringomyelic and a hydromyelic cavity is that the cavity in A. hydromyelia is lined with ependymal cells, and in syringomyelia is not B. hydromyelia is lined with choroid plexus, and in syringomyelia is not C. syringomyelia contains CSF, and in hydromyelia contains serum D. syringomyelia is focal, and in hydromyelia is more extensive E. syringomyelia is an enlargement of the central canal, and in hydromyelia is an enlargement of the anterior median septum For questions 38 to 45, identify the following structures.The figure illustrates the structures exposed through the right opticocarotid triangle. 38. basilar artery 40. right oculomotor nerve 41. right posterior cerebral artery 42. internal carotid artery 43. left duplicated superior cerebellar artery 44. right superior cerebellar artery 45. right A1 artery 46. Each of the following is true of basilar impression except A. Cerebellar and vestibular complaints typically overshadow motor and sensory complaints. B. McGregor’s line is helpful in routine screening. C. McRae’s line is helpful in clinical assessment. D. Short necks and torticollis are common. E. Vertebral artery anomalies are common. 47. Which of the following fractures has the poorest prognosis for healing without surgical intervention? A. hangman’s B. Jefferson’s fracture with 4 mm displacement of lateral masses C. type I odontoid D. type II odontoid E. type III odontoid 48. Sprengel’s deformity refers to a(n) A. congenital elevation of the scapula B. congenital fusion of the upper cervical vertebrae C. intravertebral disk herniation D. postlaminectomy kyphosis E. scoliosis resulting from tethering of the spinal cord For questions 49 to 55, match the fracture type with the mechanism.Each response may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
| Force | Neck Posture | |
| A. | flexing | flexed |
| B. | compressing | flexed |
| C. | compressing | neutral |
| D. | distracting | extended |
| E. | flexing | axially rotated |
| F. | compressing | laterally bent |
49. hangman’s fracture
51. unilateral facet dislocation
52. teardrop fracture
53. bilateral facet dislocation
54. horizontal facet fracture
55. Jefferson’s fracture
56. Lateral recess stenosis in spondylosis is most commonly caused by
A. disk herniation
B. hypertrophied pedicles
C. inferior articular facet hypertrophy
D. ligamentum flavum hypertrophy
E. superior articular facet hypertrophy
57. In the treatment of chronic pain, the undesirable effect(s) that is/are more common in stimulation of the periaqueductal gray than the periventricular gray region is/are
I. diplopia
II. oscillopsia
III. reduction of upgaze
IV. sense of impending doom
A. I, II, III
B. I, III
C. II, IV
D. IV
E. all of the above
58. “Trilateral retinoblastoma” describes bilateral ocular retinoblastomas and a(n)
A. astrocytoma
B. medulloblastoma
C. neurofibroma
D. optic nerve sheath tumor
E. pineoblastoma
59. Carotid artery ligation is absolutely contraindicated in patients with (a)
A. bilateral intracavernous carotid aneurysms
B. giant ophthalmic artery aneurym and evidence of vasospasm on arteriogram
C. giant ophthalmic artery aneurysm and extracranial atherosclerotic disease
D. intracavernous carotid artery aneurysm and sudden loss of extraocular motility
E. traumatic dissecting aneurysm of the petrous carotid artery
A. clivus
B. falx
C. foramen magnum
D. olfactory groove
E. tuberculum sella
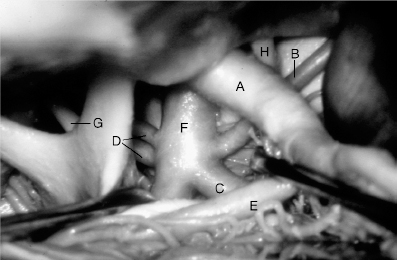
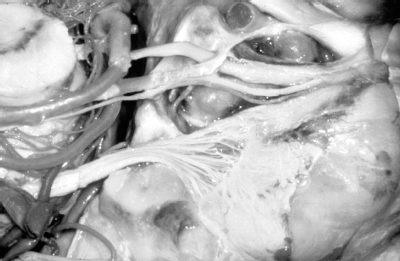
For questions 61 to 70, the figure illustrates a lateral view of the left cavernous sinus.Match the following triangles with the descriptions/structures.Each response may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
A. clinoidal
B. oculomotor
C. supratrochlear
D. infratrochlear or Parkinson’s
E. anteromedial
F. anterolateral
G. posterolateral or Glasscock’s
H. posteromedial or Kawase’s
61. clinoidal segment of the internal carotid artery
62. intracavernous carotid artery
63. intrapetrous carotid artery
64. meningohypophyseal trunk origin
65. optic strut
66. sphenoid sinus and lower margin of V1
67. Two margins of this triangle are formed by the anterior and posterior petroclinoidal dural folds.
68. located between V2 and V3
69. contains the foramen spinosum
70. contains the cochlea
71. Adherence of a posterior communicating artery aneurysm to the temporal lobe is most likely in a patient presenting with
A. loss of consciousness
B. no third nerve palsy
C. projection of the aneurysm medial to the carotid on the anteroposterior (AP) angiogram
D. third nerve involvement
E. seizures
72. Weakness of the deltoid muscle is caused by injury to the
A. axillary nerve
B. dorsal scapular nerve
C. musculocutaneous nerve
D. suprascapular nerve
E. thoracodorsal nerve
73. Subdural empyema resulting after meningitis in an infant most commonly develops with
A. Escherichia coli
B. Haemophilus influenzae
C. Listeria
D. Neisseria
E. Staphylococcus
74. Sudeck’s atrophy, associated with causalgia, refers to atrophic changes occurring in each of the following structures except
A. bone
B. joints
C. muscle
D. nerve
E. skin
A. 13
B. 17
C. 22
D. 24
E. 26
75. closure of the caudal neuropore
76. closure of the cranial neuropore
77. formation of the notochord
78. formation of the primitive streak
79. fusion of the neural folds to form the neural tube
80. Factors that predispose to the subclavian steal syndrome include
I. occlusion of the left subclavian artery before the origin of the left vertebral artery
II. occlusion of the left subclavian artery after the origin of the left vertebral artery
III. active use of the left arm
IV. occlusion of the left vertebral artery
A. I, II, III
B. I, III
C. II, IV
D. IV
E. all of the above
81. The articular facet joint in the upper thoracic region is oriented
A. axially
B. coronally
C. obliquely
D. sagittally
82. The most common presenting symptom of a thoracic herniated disk is
A. back pain
B. leg numbness
C. leg weakness
D. thoracic numbness
E. urinary incontinence
I. drowsiness
II. hemiparesis
III. mutism
IV. seizures
A. I, II, III
B. I, III
C. II, IV
D. IV
E. all of the above
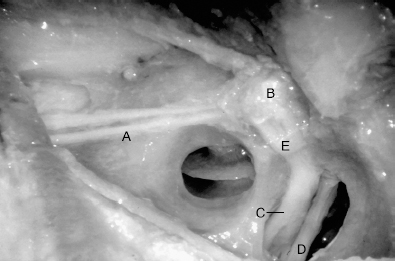
For questions 84 to 88, the figure illustrates the right internal auditory canal through a middle fossa approach.Identify the following nerves.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



