Neurotology
 Dizziness and Vertigo
Dizziness and Vertigo
1. What is the definition of vertigo? |
| G7 p.840:78mm |
a. sensation of_____ | movement (usually spinning) |
|
b. from |
|
|
i. i_____ e_____ d_____ or | inner ear dysfunction or |
|
ii. v_____ n_____ d_____ | vestibular nerve dysfunction |
|
2. True or False. Inner ear dysfunction presenting with vertigo includes the following: |
| G7 p.840:82mm |
a. labyrinthitis | true |
|
b. trauma, i.e., e_______ l_______ | true (i.e., endolymphatic leak) |
|
c. drugs, i.e., a_____ | true (i.e., aminoglycosides) |
|
d. acoustic neuroma | false (Acoustic neuroma does not cause inner ear dysfunction but may cause vertigo from compression of the vestibular nerve.) |
|
e. vertebrobasilar insufficiency | true (Other causes of vertigo include inner ear causes: Meniere disease, benign/paroxysmal positional vertigo, syphilis.) |
|
3. Complete the following regarding cupulolithiasis: |
| G7 p.840:90mm |
a. What is cupulolithiasis? c_____ c_____ in s_____ c_____ | calcium concretions in semicircular canal |
|
b. It is also known as b_____ p_____ v_____. | benign (paroxysmal) positional vertigo |
|
c. Symptoms are made manifest by_____ _____. | head turning |
|
d. Patient is usually in_____. | bed |
|
e. Is it self-limiting? | yes |
|
f. For how long? | usually not for > 1 year |
|
g. Is hearing affected? | no hearing loss | |
4. Describe indications and complications of selective vestibular neurectomy (SVN). |
| G7 p.841:40mm |
a. Indications |
|
|
i. M_____ d_____ | Meniere disease |
|
ii. p_____ v_____ i_____ | partial vestibular injury |
|
b. Rationale? | In disabling cases of vertigo, refractory to medical/nondestructive surgical treatment. SVN preserves hearing; is 90% (Meniere disease) and 80% (vertiginous spells) effective. |
|
c. Complications |
|
|
i. h_____ l_____ | hearing loss (unusual) |
|
ii. o_____ | oscillopsia (Dandy syndrome) |
|
iii. l_____ of b_____ in the d_____ | loss of balance in the dark with bilateral SVN |
|
5. Answer the following about the vestibular nerve: |
| G7 p.841:117mm |
a. In which half of the eighth nerve complex? | superior |
|
b. What color relative to the cochlear nerve? | more gray |
|
c. To preserve hearing what vessel must be preserved? | artery of the auditory canal |
|
6. True or False. CN VII can be differentiated from CN VIII at the internal auditory canal (IAC) by all of the following: |
| G7 p.841:122mm |
a. direct stimulation/recording | true |
|
b. lies anterior/superior to VIII | true |
|
c. transverse crest and Bill bar | true |
|
d. darker color c/w CN VIII | false (CN VII is paler/whiter than CN VIII) |
|
e. electromyographic (EMG) monitoring of CN VII during manipulation | true |
|
 Meniere Disease
Meniere Disease
7. What is the clinical triad of Meniere disease? |
| G7 p.842:33mm |
a. v_____ v_____ a_____ | violent vertigo attacks |
|
b. t_____ | tinnitus “escaping steam” |
|
c. h_____ l_____ | fluctuating low-frequency hearing loss |
|
8. Meniere disease is also known as e_____ h_____. | endolymphatic hydrops | |
9. True or False. Treatment of Meniere disease includes |
| G7 p.843:23mm |
a. middle ear perfusion with gentamicin | true |
|
b. bilateral vestibular neurectomy | false (Bilateral ablative procedure is to be avoided.) |
|
c. salt restriction | true |
|
d. vestibular suppressants (e.g., Valium) | true |
|
e. endolymphatic shunting | true |
|
 Facial Nerve Palsy
Facial Nerve Palsy
10. Segments of the facial nerve include |
| G7 p.844:30mm |
Hint: see my little tin man |
|
|
a. c_____ | cisternal |
|
b. m_____ | meatal |
|
c. l_____ | labyrinthine |
|
d. t_____ | tympanic |
|
e. m_____ | mastoid |
|
11. Answer the following about supranuclear facial palsy: |
| G7 p.844:55mm |
a. Which part of the face is involved? | lower only |
|
b. Emotional facial expression is _____. | intact |
|
c. The lesion is in the lowest part of the _____ _____. | precentral gyrus |
|
d. Part of the face is spared paralysis because the _____ _____ has _____ _____. | upper face; bilateral representation |
|
12. True or False. The following is correct regarding central facial palsy (supranuclear facial palsy): |
| G7 p.844:55mm |
a. confined to lower face | true |
|
b. spares emotional facial expression | true |
|
c. lesion in most inferior opercular portion of precentral gyrus | true |
|
d. upper face has bilateral representation | true |
|
13. Complete the following regarding nuclear facial palsy: |
| G7 p.844:80mm |
a. It causes paralysis of all _____ _____ _____ muscles. | ipsilateral CN VII innervated |
|
b. It plus sixth nerve palsy constitutes the _____-_____ syndrome. | Millard-Gubler |
|
c. It can be caused by a particular tumor called _____ | medulloblastoma |
|
d. especially when it _____ the _____ of the _____ _____. | invades the floor of the fourth ventricular |
|
e. True or False. Nuclear facial palsy is due to damage to the motor nucleus at the pontomedullary junction. | true | |
14. True or False. Regarding CN VII anatomy: |
| G7 p.844:100mm |
a. enters superior-anterior portion of IAC | true |
|
b. external genu is geniculate ganglion | true |
|
c. GSPN first branch after the ganglion | true |
|
d. exits at stylomastoid foramen | true |
|
15. Complete the following about the seventh nerve: |
| G7 p.844:100mm |
a. It exits the brain stem at the _____ _____. | pontomedullary junction |
|
b. It enters the internal auditory canal at the _____ _____. | superoanterior portion |
|
c. The geniculate ganglion is located in the _____ bone. | temporal |
|
d. The first branch is the _____ _____ _____ _____ | greater superficial petrosal nerve |
|
e. which goes to the _____ _____ | pterygopalatine ganglion |
|
f. and innervates the _____ _____. lacrimal gland—dry eye and nasal mucosa if injured |
| |
g. The next branch goes to the _____. | stapedius muscle—to ear—hyperacusis |
|
h. The next branch is the _____ _____. | chorda tympani—taste |
|
i. It then exits the s_____ f_____ | stylomastoid foramen |
|
j. and sends branches to the _____. | face |
|
16. Name the facial nerve branches within the temporal bone and their function. |
| G7 p.844:115mm |
a. g_____ | greater superficial petrosal nerve (GSPN) to pterygopalatine ganglion, innervates nasal and palatine mucosa and lacrimal gland |
|
b. s_____ | branch to stapedius muscle, volume regulation |
|
c. c_____ | chorda tympani, taste sensation from anterior two thirds of tongue |
|
d. fibers to s_____ g_____ | salivary glands, submandibular, sublingual |
|
e. The nerve travels on to _____ _____. | facial muscles |
|
17. Name the facial nerve branches to the facial muscles cranial to caudal. |
| G7 p.844:135mm |
a. t_____ | temporal |
|
b. z_____ | zygomatic |
|
c. b_____ | buccal |
|
d. m_____ | mandibular |
|
e. c_____ | cervical | |
18. Name the three most common causes of facial nerve palsy. |
| G7 p.844:155mm |
a. B_____ | Bell palsy |
|
b. h_____ | herpes zoster oticus |
|
c. t_____ | trauma/basal skull fracture |
|
19. Study Chart. Provide the differential diagnosis for facial nerve palsy. | facial nerve palsy acoustic tumor Bell—birth congenital diabetes fracture Guillain-Barré herpes zoster Klippel-FeilLyme disease meningioma neoplasm otitis media parotid surgery sarcoid trauma | G7 p.844:155mm |
20. Describe seventh nerve palsy. |
| G7 p.845:80mm |
a. The most common cause of facial palsy is _____ _____. | Bell palsy |
|
b. Etiology: _____ | unknown |
|
c. Probable etiology: v_____ i_____ d_____ p_____ | viral inflammatory demyelinating polyneuritis |
|
d. It is caused by the _____ _____ virus. | herpes simplex |
|
e. It progresses _____ _____ _____. | distally to proximally |
|
f. Meaning |
|
|
i. first | facial movements weak |
|
ii. then | loss of taste and salivation |
|
iii. and then | hyperacusis |
|
iv. and then | decreased tearing |
|
g. Percent that recover completely is _____%; partially _____%. | 75 to 80%; 10% |
|
h. Manage with _____ and _____. | EMG and steroids |
|
21. Answer the following regarding Bell palsy: |
| G7 p.845115mm |
a. What often precedes Bell palsy? | a viral syndrome |
|
b. What is the usual sequence of clinical findings? List in order: #x2460; decreased tearing; |
|
|
c. What treatment is recommended? | steroids | |
22. What are the considerations for facial nerve injury surgical repair? |
| G7 p.846:180mm |
a. if known to be interrupted _____ | reanastomose early |
|
b. if known to be in continuity _____ | several months of observation |
|
c. role of electrical testing _____ | serial electrical testing after 1 week |
|
 Hearing Loss
Hearing Loss
23. Describe the following about hearing loss: |
| G7 p.848:40mm |
a. conductive |
|
|
i. speech | normal or low volume |
|
ii. Rinne | air less than bone = negative (i.e., abnormal) |
|
iii. Weber lateralizes to _____ _____ side | poor hearing |
|
b. sensorineural |
|
|
i. speech | loud |
|
ii. Rinne | air more than bone = positive (i.e., normal) |
|
iii. Weber lateralizes to _____ _____ side | good hearing |
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


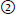 hyperacusis;
hyperacusis; 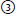 facial muscle weakness;
facial muscle weakness; 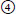 loss of taste
loss of taste ,
,  ,
,  ,
,