Chapter 116 Occult Spinal Dysraphism and the Tethered Spinal Cord
Tethered Cord Syndrome
Pathology
The term tethered cord syndrome, as used in this chapter, signifies a pathologic fixation of the spinal cord in an abnormally low position so that the spinal cord, with activities and growth, undergoes mechanical stretching, distortion, and ischemia.1 Many conditions can cause tethering of the spinal cord, including tight filum terminale, split cord malformations, lipoma, dermal sinus, and meningomyelocele. The remainder of this section addresses the care and treatment of these conditions, excluding meningomyelocele.
Presentation
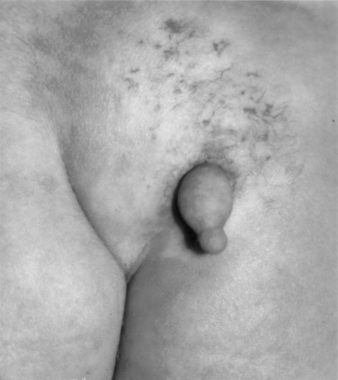
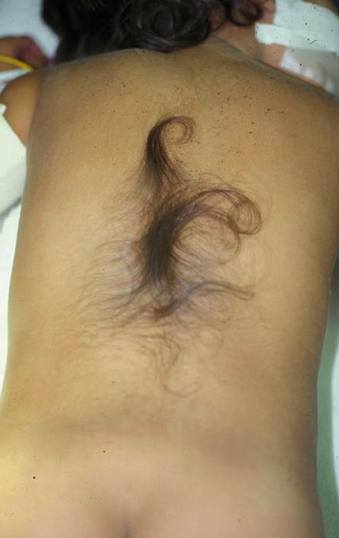
The patient with a tethered cord may be either symptomatic or asymptomatic. Both groups often, but not invariably, have a midline cutaneous dorsal abnormality such as a dimple, a hairy patch or faun’s patch, a hemangioma, a lipoma, or a skin tag (Figs. 116-1 and 116-2). If there is no external manifestation, the problem usually goes unrecognized until symptoms begin to develop.
Symptoms, when present, can be grouped into three general areas: sensorimotor, sphincteric, and orthopaedic. Sensorimotor symptoms can include pain, delayed walking, sensory loss (usually in the dermatomes of the lumbosacral roots), and motor weakness of the distal leg or foot (the most common symptom, presenting in 76% of cases).2 Sphincteric symptoms usually are insidious, with frequent urinary tract infections secondary to incomplete emptying, hydronephrosis with renal involvement secondary to reflux, and fecal incontinence. In addition, these patients may develop urinary incontinence or become impotent. The orthopaedic problems are related to gait disturbance and abnormalities of the foot or scoliosis. Adult patients with tethered cords also may present with back pain that may radiate to the legs, urinary difficulties, and lower extremity weakness.3 Patients may present either as asymptomatic in childhood and symptomatic in adulthood or as having a progression of symptoms once they reach adulthood, perhaps due to repeated microtrauma to the cord.4 In adults, the disease may have an insidious onset or may have a predisposing factor such as exercise, lifting heavy loads, or even birth trauma.3,5
Diagnostic Aids
Any infant or child with a midline cutaneous lesion such as a dimple, hair patch, or hemangioma or symptoms mentioned earlier may be suspected of having a tethered cord.6 The intention of the workup is to determine the anatomy of the anomaly.
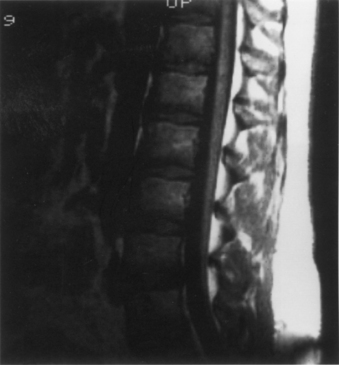
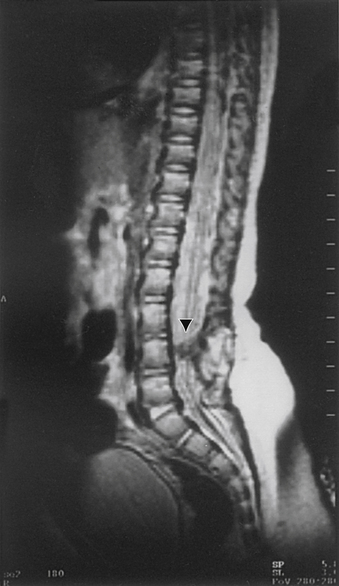
A careful neurologic examination with attention paid to evaluation of motor and sensory function as well as sphincter tone is imperative. If the history indicates possible bladder involvement, a urologic evaluation is indicated. Plain radiographs, which may be obtained as a screening procedure, may show a widened interpedicular distance and defects at one or more levels. The procedure of choice is MRI (Fig. 116-3). Often, this is the only necessary imaging study, and treatment can be planned on the basis of MRI alone. It is prudent to image the entire spinal cord at least once to rule out other associated anomalies, such as a syrinx or a type I Chiari malformation. If there are any remaining concerns or issues, a myelogram with subsequent CT may be helpful.
Treatment
Once the problem is identified, the treatment of the tethered cord is surgical. Although controversy existed in the past (over the concept of prophylactic surgery of asymptomatic patients), most surgeons now believe that the risk of waiting for deterioration to begin is not justified, because the deficit often is not reversible. Therefore, surgery is recommended, even in the asymptomatic patient,7 although a recent study8 suggests that careful follow-up and monitoring for upper motor neuron signs using urodynamic assessments, in order to time surgical intervention to coincide with the appearance of upper motor neuron signs, may be possible. In adults, patients with back pain and lower extremity pain seem to benefit more than those with sphincter problems.3
Outcome
The shorter the duration of symptoms, the better the prognosis.5 A study by Archibeck et al.9 demonstrated a 50% revision rate by 5 years after initial revision and a 57% revision rate by 2 years after the second release. In addition, 50% of patients required at least one orthopaedic procedure after tethered cord release.9 In a study by Cornette et al.8 of 12 patients operated on for tethered cord, none required a second operation. However, the series is small, although the follow-up period was reasonable (58 months). In terms of urologic outcome, improvement in symptoms as well as urologic dynamic parameters is expected in most patients, although few if any will return to normal.10 Improvements may be noted in detrusor function, EMG recordings, and pressures.11
Split Cord Malformations
Embryology and Pathology
The term split cord malformation (SCM) was introduced by Pang et al.12 in 1992 to describe diastematomyelia based on the dural tube and the nature of the septum. Two types of SCM exist: type I, diastematomyelia with septum, and type II, diastematomyelia without septum. Type II is more common.
By the end of the second week of gestation, the human embryo normally consists of a bilaminar structure: (1) an epiblast, or layer of cells next to the amnion, and (2) a hypoblast, or layer of cells next to the yolk sac. From there, the cells divide to form the primitive streak. During gastrulation, the embryo becomes trilaminar as adjacent epiblastic cells migrate medially toward the primitive streak to become mesoderm. The primitive streak begins to regress by day 16,12 and the notochordal process begins. As the notochord elongates, it canalizes, initially forming a connection through the embryo to join the amnion and yolk sac. This connection is then lost as the open notochord separates from the endoderm and again forms a blind tube.12
In the split cord malformations, an adhesion forms between the ectoderm and endoderm, leading to the formation of an “accessory neurenteric canal around which condenses an endomesenchymal tract that bisects the developing notochord and causes formation of two hemineural plates.”12 Whether a type I or type II SCM is formed depends on what happens to the endomesenchymal tract. If it develops toward bone and cartilage, the result will be two dural sacs and a type I SCM. If the tract regresses or leaves a fibrous septum, a type II SCM will develop.13
The spinal cord above and below the split is normal. The two hemicords themselves usually are the same size, but in 10% of patients, they are grossly asymmetrical. When this occurs, the spinal cord itself, above and below the bifurcation, is asymmetrical, being smaller on the side of the smaller hemicord.
The anterior spinal artery and the central canal bifurcate to accompany each hemicord,14 so that each has its own blood supply. The two hemicords give rise to the spinal nerve roots on their respective sides. Although splitting of the spinal cord at more than one site and cases of incomplete splitting of the spinal cord with a resultant partial cleft cord have been reported, most cases involve a single, complete cleft through the spinal cord and meninges. In cases in which there are two hemicords without an intervening septum, a single dural sac surrounds both. In such cases, symptoms may result from tethering of the cord by fibrous bands or a thickened filum terminale.
In cases in which the meninges themselves also are bifurcated, there almost always is an intervening septum. Its position is at the caudal end of the split; therefore, ascent of the neural elements is prohibited. The septum, or spur, usually is attached to both the dorsal elements and the dorsal aspect of the vertebral body. Because of the incidence of spina bifida, the spur may continue dorsally between unfused laminae. These spurs may present anywhere along the spine, but in 70% of cases they are between L1 and L5. They are less likely to occur in the thoracic spine and have only a 1% incidence in the cervical spine.15,16 The spur initially is cartilaginous and may mature to calcified bone with time.
Pathophysiology
The clinical symptoms most likely evolve from traction of the spinal cord against the restricting septum or bony spur.1,17 As with other forms of tethered spinal cord, ascent of the cord within the dural sac and spinal canal is prohibited. The average age of presentation is 6½ years, with neurologic symptoms first becoming evident with the onset of walking.16 With the onset of walking, however, increased traction of the distal spinal cord against the restricting septum results in new symptoms. To support this finding, Yamada et al.18 have studied the oxidative metabolism of the distal spinal cord and have found a decrease when the cord is under axial tension.
Presentation
Boxes 116-1 and 116-2 include some of the presenting symptoms and physical signs of patients with split cord malformations.19 In general, signs and symptoms fall into three categories: (1) cutaneous abnormalities, (2) pain, and (3) neurologic deficits (from spinal cord traction).
BOX 116-1 Split Cord Malformation: Common Presenting Complaints
Data from Mathern GW, Peacock WJ: Diastematomyelia. In Park TS, editor: Spinal dysraphism, Boston, 1992, Blackwell Scientific, p 91.
BOX 116-2 Split Cord Malformation: Common Physical Signs
Data from Mathern GW, Peacock WJ: Diastematomyelia. In Park TS editor: Spinal dysraphism, Boston, 1992, Blackwell Scientific, p 91.
In newborns and infants in whom neurologic deficits may not yet have developed, cutaneous lesions bring the child to the attention of the neurosurgeon. Most commonly, a patch of hair or hypertrichosis is noted in the thoracic or lumbosacral midline dorsally. This hair, usually coarse and long, is sometimes referred to as faun’s tail. The surrounding skin is associated with an intradermal angiomatous malformation, giving the skin a pinkish blue color. In addition, a dermal sinus, lipoma, abnormally protuberant spinous process, or meningocele may be associated with the spur.
If the patient with split cord malformation has successfully progressed through development with few or none of the aforementioned symptoms, the most common complaint, particularly in older children and adults, is back or leg pain.20 This pain may be due to subtle concomitant scoliosis or to the spinal bony deformity itself. The presence of unilateral symptoms is a key difference in the presentation of split cord malformation versus tethered cord syndrome.
Diagnostic Aids
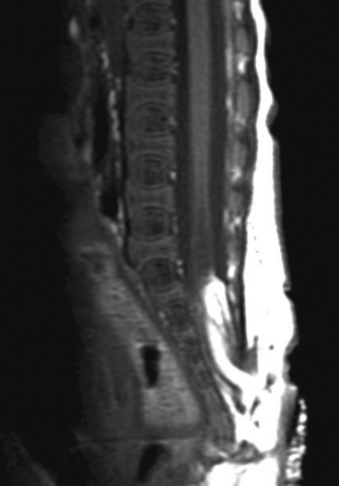
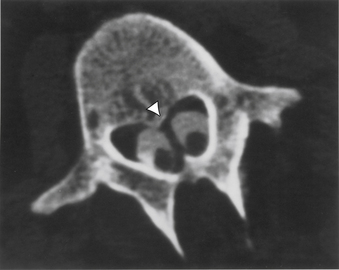
Aids that confirm the diagnosis of split cord malformation usually are radiologic. Although plain radiographs or unenhanced CT scans of the spine may reveal the bony spur, a widened interpedicular distance, spina bifida occulta, or other segmental vertebral anomalies, MRI in all three axes can be more revealing and is the preferred procedure (Figs. 116-4 to 116-7). Associated lipomas, hydromyelia, and other intraspinal and intradural defects also may be observed incidentally, allowing for a more focused treatment approach. If there are any questions or further clarification is required, myelography and postmyelographic CT best delineate the hemicords, the dural sac, and the presence and extent of the intervening bony septum (Fig. 116-8).21 Plain and CT myelography may reveal aberrant nerve roots, intradural bands, a thickened filum terminale, or a concomitant intradural lipoma. In addition, a recent study22 reported an incidence of abnormal urologic dynamic studies as high as 75% in patients with SCM, despite a lack of symptoms. Therefore, obtaining preoperative and postoperative urologic dynamic studies may be of some benefit. Again, as in the tethered cord syndrome, the entire spinal cord should be imaged.
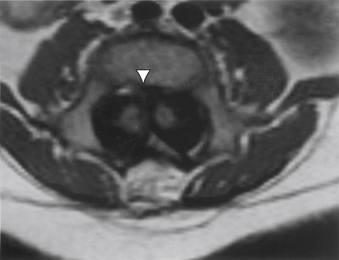
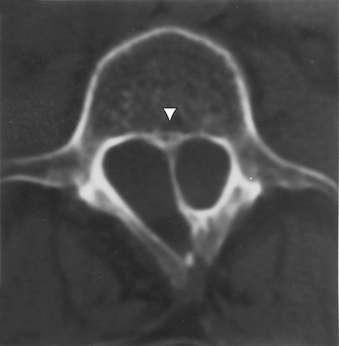
FIGURE 116-7 Axial T1-weighted MRI revealing the septum (arrowhead) and hemicords of split cord malformation.
Treatment
Before making a standard midline incision to the lumbosacral fascia, the spine should be palpated. Occasionally, a protruding spinous process or bony spur may be felt, allowing for a more localized incision. In addition, a localizing plain radiograph with a skin marker is used and correlated with the preoperative MRI. If a cutaneous lesion, such as a patch of hair, is present, it may be beneficial to create an elliptical incision circumferentially around the defect. Because the underlying bony and soft tissue defect may not be clear, it is helpful to incise the fascia and perform a subperiosteal reflection of the paraspinous musculature at the levels above and below the level of the lesion, understanding that midline fusion defects may also exist here. The monopolar electrocautery should be used cautiously in retracting the muscles, because areas of expected protective bone may be missing. After the laminae above and below the lesion are exposed, their spinous processes are removed using a rongeur. A partial laminectomy is then performed at the caudal aspect of the lamina above the septum and the rostral aspect of the lamina below the septum. After careful curettage of the underside of both these laminae, the ligamentum flavum, if still intact, is elevated laterally with Penfield forceps and incised longitudinally through its outer layer. A blunt instrument is then gently inserted through the remaining ligament, and a small cottonoid patty is placed between the dura mater and the ligamentum flavum for protection. A small, angled Kerrison punch is then used to remove the ligamentum flavum until the dura mater is completely exposed laterally. With a no. 4 Penfield dissector, the septum is then felt over the dura from above and from below. A small-mouthed rongeur or angled Kerrison punch or high-speed drill is used to remove the lamina and overhanging bone of the involved level until only the spur is left. Because of the substantial epidural venous plexus associated in and around the bony spur and deep to the two hemicords, control of bleeding and cauterization of these vessels should be performed prior to and during the removal of the spur (Fig. 116-9). After decompression, with movement of the hemicords, it may be very difficult to maintain hemostasis. Any extruding segment of spur is removed using a rongeur, and a small dissector is used to probe and dissect the dural sheath away from the bony spicule down to the level of the dorsal vertebral body. A high-speed diamond-bit drill is then used to carefully thin down the spicule as far as possible.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree