Diltiazem
Nicardipine
Number of patients
67
52
Male/Female
23/44
15/37
n.s.
Age
59 ± 12
62 ± 12
n.s.
Blood pressure(on admission)
Systolic
164 ± 30
167 ± 24
n.s.
Diastolic
87 ± 18
87 ± 16
n.s.
Time after onset
4.6 ± 4.6
4.7 ± 5.7
n.s.
Hunt & Kosnic grade
2.8 ± 1.0
2.7 ± 1.0
n.s.
Fisher scale (1+2/3+4)
5/62
4/48
n.s.
Immediately after the onset of SAH, markedly high levels of AD were seen, which then rapidly decreased to the normal range within 6 h. There were no significant differences between the two groups at any time point (Fig. 1a). Patients receiving diltiazem exhibited lower plasma concentrations of NA and DP than those receiving nicardipine at 3 and 6 h. The difference was not significant for NA levels (p = 0.021, P = 0.368, respectively) (Fig. 1b), but a significant difference was observed in DP levels at 3 h (p = 0.002, p = 0.029, respectively) (Fig. 1c).
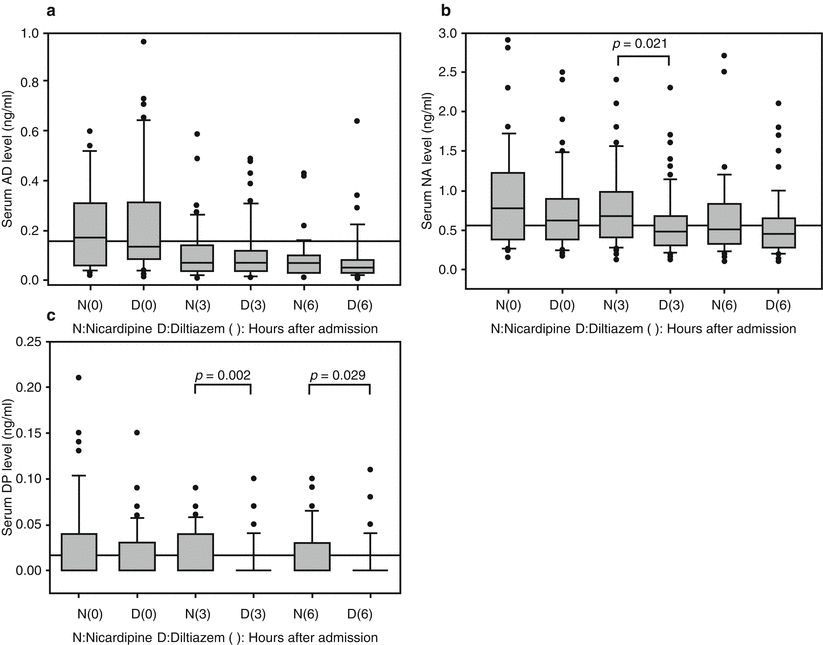

Fig. 1
Time course of the changes in AD (a), NA (b), and DP (c) concentration between the two treated groups. Concentrations below the detection limit (0.02 ng/ml) were assigned a value of zero. The horizontal line represents the upper limit of normal
Discussion
The present study demonstrated that diltiazem may be more repressive than nicardipine against the acute surge of NA and DP in patients with SAH. NA and DP are mainly derived from sympathetic nerve endings [5] and our findings support the notion that diltiazem exerted inhibitory effects on the sympathetic nervous system. The primary action of Ca2+ channel blockers is to inhibit the Ca2+ influx through voltage-dependent calcium channels in the plasma membrane that leads to relaxation and vasodilation of vascular smooth muscle [1]. Previous studies have shown that the inhibition of Ca2+ channels can decrease catecholamine release by inhibiting neurotransmitter release at adrenergic nerve terminals [6, 11]. Several authors reported that diltiazem might have an inhibitory effect on sympathetic transmission through some extra actions in addition to the inhibition of Ca2+ influx into the adrenergic nerve endings [8, 16], although the mechanism remains to be elucidated.
We have demonstrated previously that AD concentrations were markedly high immediately after SAH onset and decreased rapidly, whereas NA and DP concentrations had a significant time delay until their peak occurred compared with AD [17, 19]. The discrepancy of response to diltiazem among catecholamines may arise from the difference in the time course of when diltiazem affects the activated sympathetic nervous system. Further controlled clinical trials are needed to establish the beneficial effect of diltiazem in patients with aneurysmal SAH.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






