Outcome
Tier 1 (0.625 g/kg)
Tier 2 (1.25 g/kg)
Tier 3 (1.875 g/kg)
All groups
TCD vasospasm
15/20 (75 %)
11/20 (55 %)
2/7 (28.6 %)
28/47 (59.6 %)
DCI
4/20 (20 %)
3/20 (15 %)
1/7 (14.3 %)
8/47 (17 %)
Cerebral infarction
5/11 (45 %)
3/18 (16 %)
1/4 (25 %)
9/33 (27 %)
New
3/11 (27 %)
3/18 (16 %)
0
6/33 (18 %)
Old
2/11 (18 %)
0
1/4 (25 %)
3/33 (9 %)
Vascular territory
All MCA
1 MCA, 2 ACA
MCA
7 MCA, 2 ACA
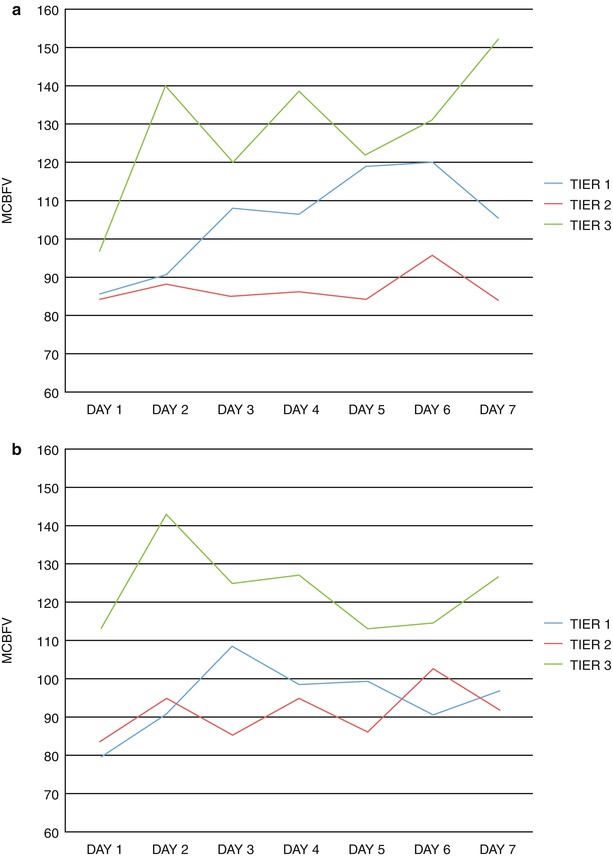
Fig. 1
Distribution of MCBFV by treatment tier. (a) Left MCA. (b) Right MCA. MCA middle cerebral artery, MCBFV mean cerebral blood flow velocity
Discussion
ALB has been shown to be neuroprotective in animal models of cerebral ischemia [1, 2]. In addition, there is some preliminary data indicating improved clinical outcome in patients with ischemic stroke [5]. We have shown that ALB dosages up to 1.25 g/kg/day × 7 days are well tolerated and may improve outcome in SAH patients [7]. This finding extends the applicability of ALB to clinical entities other than ischemic stroke.
The mechanisms by which ALB accomplish its salutatory effects on the brain are still under investigation but may include several actions [5, 7]. ALB administration can produce an increase in the serum oncotic pressure, which draws interstitial fluid and ameliorates organ perfusion. Moreover, ALB has significant antioxidant properties and can improve microcirculatory blood flow while decreasing leukocyte adherence with resultant anti-inflammatory effects.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





