Fig. 1
(a) Distribution of small ischemic lesions in brain detected by MRI in examinees of a brain dock. White matter lesion (red) and infarction (blue). (b) A cortical infarction (blue arrow) incidentally found in an examinee of a brain dock. (c) A cerebral white matter lesion (red arrow) located in the centrum semiovale
Animal Study
Histological examination revealed that a round infarct with thrombosed parenchymal vessels surrounded by a layer of selective neuronal death formed around the tip of the optic fiber both in caudate and cortical infarct animals (Fig. 2) The lesion volume 1 day after photothrombosis was 7.04 ± 1.18 mm3 (mean ± SD) in rats with 10 min light exposure with an optic fiber 0.75 mm in diameter. The volume was 4.2 ± 1.24 mm3 and 1.2 ± 0.25 mm3 using a 0.5 mm diameter optic fiber with 10 and 5 min exposure, respectively. Ischemic lesions turned into cystic cavities (lacune) over 6 weeks.
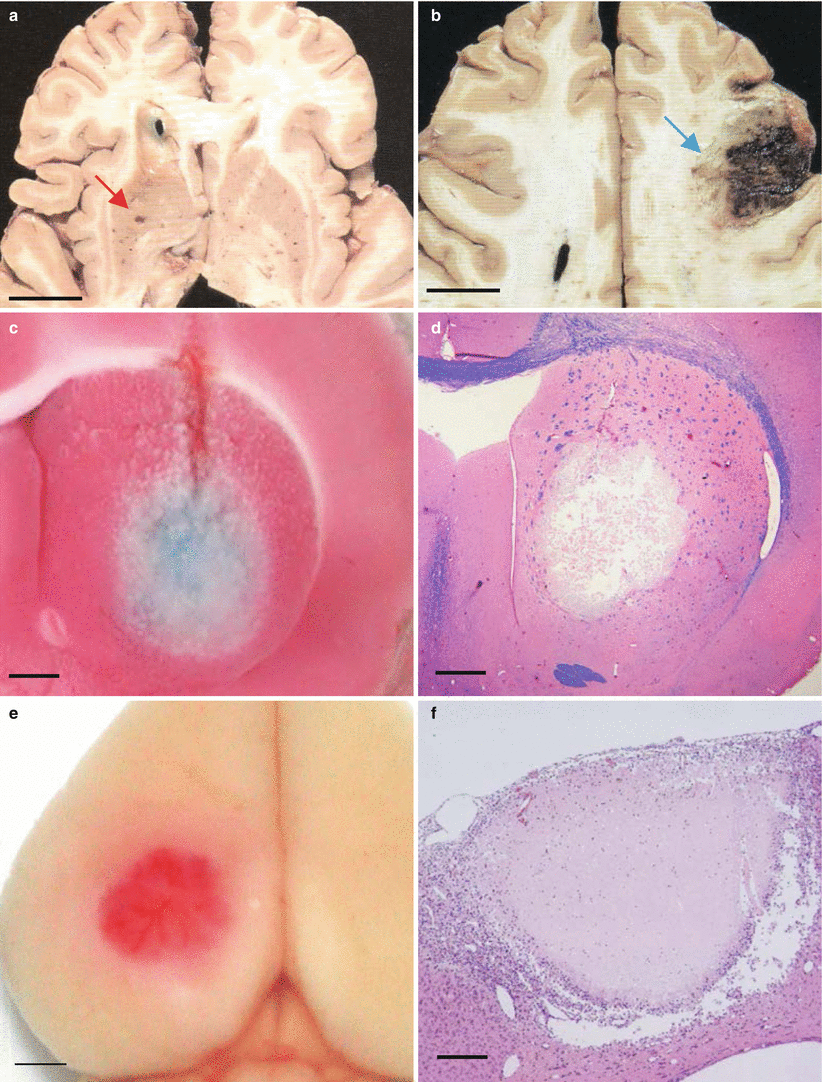

Fig. 2
(a) A lacunar infarct in the striatum in a clinical case (red arrow). (b) A hemorrhagic infarct in the frontal cortex in a clinical case (blue arrow). (c) A round infarction was induced by photothrombosis in the caudate nucleus in gerbil. The brain was stained with TTC (triphenyl tetrazolium chloride) solution. (d) Hematoxylin eosin staining of the caudate photothrombotic infarction. (e) A cortical ischemic lesion induced by photothrombosis in gerbil. (f) Hematoxylin eosin staining of the cortical photothrombotic infarction. Bar = 2 cm in figs (a, b), Bar = 5 mm in figs (c–f)
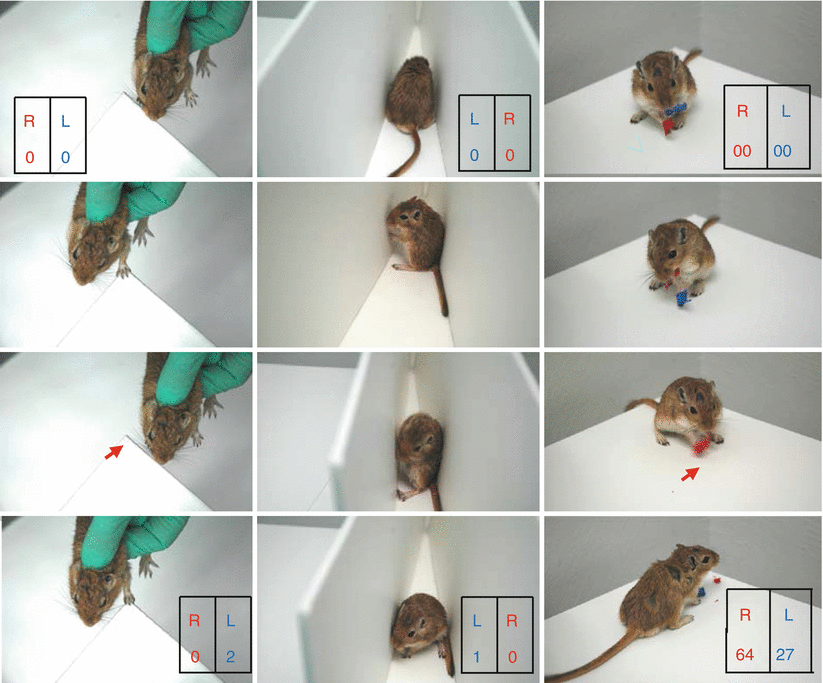
Lesioned animals showed reduced right forelimb placing compared with the left forelimb (Fig. 3 left) Thus, successful placing of the right forelimb 1 day after a caudate photothrombotic lesion was 45 ± 21 % compared with 95 ± 8.5 % in sham-operated animals. In the corner turn test, 1 day after lesioning (10 min exposure with 0.5 mm optic fiber) right turns were 6.7 ± 8.3 % compared with 53.3 ± 10.5 % in sham-operated animals (Fig. 3 middle). Deficits were observed for 6 weeks in animals with large lesion volumes (7.0 ± 1.2 mm3), but only for 3 days with small lesion volumes (1.2 ± 0.3 mm3). In the adhesive tape removal test, lesioned animals took longer to remove adhesive tape from the right forepaw compared with the left. Recording of locomotion in gerbil after photothrombosis revealed a different pattern and distribution between caudate and cortical lesions. Animals before photothrombosis moved evenly in both the center and the periphery of the open field. Tracking showed circling after caudate photothrombosis. After cortical photothrombosis, animals developed linear locomotion, mainly in the periphery of the open field.