Fig. 1
Developmental milestone, measured by negative geotropism (seconds), 72 h after collagenase infusion; (asterisk) <0.05 compared with sham; (cross) <0.05 compared with GMH (vehicle); SEM standard error of the mean; n = 6/group
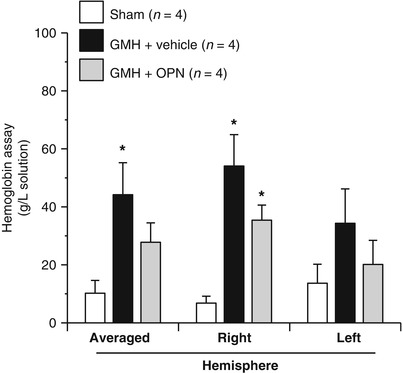
Fig. 2
Hemoglobin assay, measured by spectrophotometer, 72 h after collagenase infusion; (asterisk) <0.05 compared with sham; SEM standard error of the mean; n = 4/group
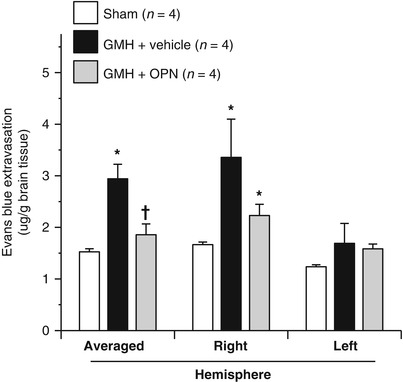
Fig. 3
Evans blue, measured by spectrophotometer, 72 h after collagenase infusion; (asterisk) <0.05 compared with sham; (cross) <0.05 compared with GMH (vehicle); SEM standard error of the mean; n = 4/group
Conclusion
OPN may play an important role in enhancing neuroprotective brain signaling following GMH. Translational stroke studies, including animal modeling, are greatly needed to safely integrate basic preclinical scientific principles ahead of clinical application [24–28]. Intranasal OPN improved outcomes after GMH by attenuation of brain swelling, BBB function, re-bleeding, and neurological outcomes. These observed effects may offer novel possibilities for eventual therapy in this patient population. Further study is needed to evaluate the mechanisms of this neuroprotection.
Acknowledgment
This study was partially supported by the National Institutes of Health grant RO1 NS078755 (Dr. Zhang) and American Heart Association CRP 17380009 (Dr. Lekic).
Disclosures
None
References
1.
Ballabh P (2010) Intraventricular hemorrhage in premature infants: mechanism of disease. Pediatr Res 67:1–8PubMedCentralCrossRefPubMed
2.
3.
Chen Q, Zhang J, Guo J, Tang J, Tao Y, Li L, Feng H, Chen Z (2014) Chronic hydrocephalus and perihematomal tissue injury developed in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage with ventricular extension. Transl Stroke Res. doi:10.1007/s12975-014-0367-5
4.
Zhao J, Chen Z, Xi G, Keep RF, Hua Y (2014) Deferoxamine attenuates acute hydrocephalus after traumatic brain injury in rats. Transl Stroke Res 5:586–594PubMedCentralCrossRefPubMed
5.
6.
Uria-Avellanal C, Robertson NJ (2014) Na(+)/H(+) exchangers and intracellular pH in perinatal brain injury. Transl Stroke Res 5:79–98PubMedCentralCrossRefPubMed
7.
Whitelaw A (2001) Intraventricular haemorrhage and posthaemorrhagic hydrocephalus: pathogenesis, prevention and future interventions. Semin Neonatol 6:135–146CrossRefPubMed
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








