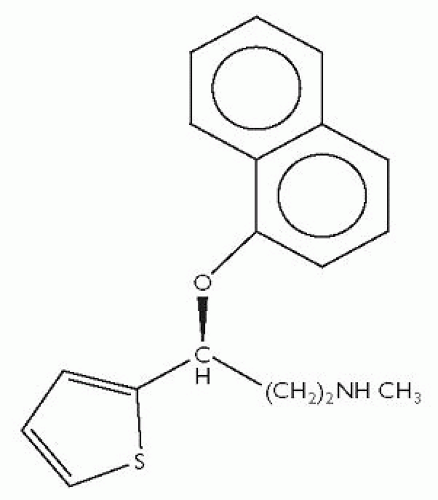
Other and Newer Antidepressants
Agomelatine
Agomelatine is a new antidepressant with MT1 and MT2 melatonergic agonist and 5-HT2C antagonist actions which has been shown to be effective in severe depression (see Mongomery and Kasper, 2007). These properties, together with its lack of major effects on the uptake of dopamine, serotonin, and noradrenaline, may account for its relative lack of adverse side-effects. As Sansone and Sansone (2011) have commented regarding agomelatine:
‘The melatonergic function appears to improve sleep patterns, whereas the serotonergic antagonism results in the release of norepinephrine [noradrenaline] and dopamine. Given the current information, the overall side-effect profile of agomelatine appears relatively mild. For example, agomelatine has no discontinuation syndrome, exhibits infrequent sexual dysfunction, and is generally weight neutral. The drug appears to be relatively safe in overdose.’
The initial adult (>18 years) oral antidepressant dose is 25mg nocte. This can be increased, according to clinical response, to 50mg nocte after 2 weeks. Liver function tests should be carried out prior to treatment and then at the 6-, 12-, and 24-week time-points, and then as appropriate. If the serum transaminase is higher than 3× the reference range upper limit, then treatment with agomelatine should be stopped.
The commonest side-effects are:
nausea
diarrhoea
constipation
abdominal pain
increased serum transaminases
headache
dizziness
drowsiness
insomnia
fatigue
anxiety
back pain
sweating.
Less common side-effects include:
paraesthesia
eczema
blurred vision.
Caution should be exercised in the following cases:
elderly patients
(hypo)mania
concomitant use of drugs associated with hepatic injury
excessive intake of alcohol.
Contraindications include:
dementia
hepatic impairment
breastfeeding.
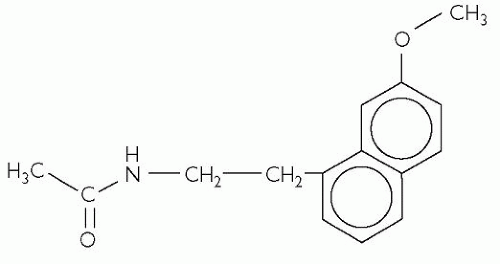
Duloxetine
This drug inhibits the central re-uptake of serotonin and noradrenaline (norepinephrine).
The adult (>18 years) oral antidepressant dose is 60mg once daily.
For the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder, the initial adult (>18 years) dose is 30mg daily, which may be increased as clinically appropriate to 60mg once daily. The maximum dose is 120mg daily.
The commonest side-effects are:
nausea
vomiting
dyspepsia
constipation
diarrhoea
abdominal pain
flatulence
dry mouth
hot flushes
decreased appetite
weight change
palpitations
abnormal dreams
paraesthesia
sweating
fatigue
increased sweating
anxiety
dizziness
headache
tremor
nervousness
anorexia
blurred vision
sexual dysfunction
thirst
lethargy
drowsiness
weakness
pruritus.
Less common side-effects include:
halitosis
bruxism
gastritis
hepatitis
tachycardia
hypertension
postural hypotension
syncope
vertigo
increased cholesterol
cold extremities
disturbance of taste sensation
impairment of temperature regulation
poor attention
movement disorders
musculoskeletal pain
twitching
stomatitis
thirst
photosensitivity
hypothyroidism
urinary disorders.
It may very rarely be associated with hyponatraemia.
Caution should be exercised in the following cases:
elderly patients
cardiac disease
hypertension
history of (hypo)mania
history of seizures
raised intraocular pressure
bleeding disorders
concomitant pharmacotherapy with agents which increase the bleeding time.
Contraindications include:
hepatic impairment
renal impairment (if estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <30mL/min/1.73 m2)
pregnancy
breastfeeding
narrow-angle glaucoma—duloxetine may be associated with increased mydriasis in patients with uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree