References
1. Stahl, S.M. (2006). Essential Psychopharmacology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
2. Simonato, M.(1996). The neurochemistry of morphine addiction in the neocortex. Trends in Pharmacological Science, 17, 410-15.
3. Strang, J., Griffiths, P., Gossop, M., et al. (1997). Heroin in the United Kingdom: different forms, different origins, and the relationship to different routes of administration. Drug and Alcohol Review,16, 329-37.
4. Strang, J., Griffiths, P., Powis, B., et al. (1999). Heroin chasers and heroin injectors: differences observed in a community sample in London. American Journal on Addictions, 8(2),148-60.
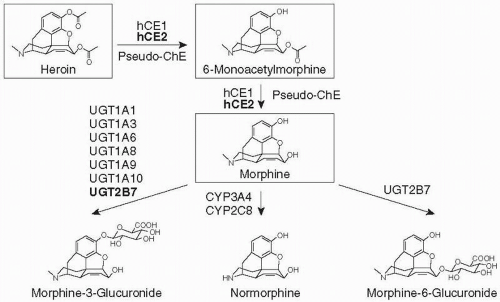
5. Maurer, H.H., Sauer, C., Theobald, D.S., et al. (2006) Toxicokinetics of drugs of abuse: current knowledge of the isoenzymes involved in the human metabolism of tetrahydrocannabinol, cocaine, heroin, morphine, and codeine. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring, 28(3), 447-53.
6. Annual report on the state of the drugs problem in the European Union 2000 European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). Accessed April 2007.
7. Gossop, M., Griffiths, P., Powis, B., et al. (1996). Frequency of non-fatal heroin overdose. British Medical Journal, 313, 402.
8. United Kingdom drug situation: annual report to the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) 2005.
9. Stimson, G.V. (1995). AIDS and injecting drug use in the UK, 1987-1993: the policy response and the prevention of the epidemic. Social Sciences and Medicine, 41, 699-716.
10. Fingerhood, M.I., Jasinski, D.R., Sullivan, J.T. et al.(1993). Prevalence of hepatitis C in a chemically dependent population. Archives of International Medicine, 153, 2025-30.
11. Verthein, U., Degkwitz, P., Haasen, C., et al.(2005). Significance of comorbidity for the long-term course of opiate dependence. European Addiction Resarch, 11(1),15-21.
12. Marsden, J., Gossop, M., Stewart, D., et al. (2000). Psychiatric symptoms among clients seeking treatment for drug dependence. Intake data from the National Treatment Outcome Research Study. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 176,285-9.
13. Lloyd, C.(1998). Risk factors for problem drug use: identifying vulnerable groups. Drugs: Education, Prevention and Policy, 5, 217-32.
14. Darke, S., Ross, J.(2002). Suicide among heroin users: rates, risk factors and methods. Addiction, 97(11),1383-94.
15. Havard, A., Teesson, M., Darke, S., et al. (2006). Depression among heroin users: 12-Month outcomes from the Australian Treatment Outcome Study (ATOS). Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 30(4), 355-62.
16. NICE technology appraisal guidance 114. (2007). Methadone and buprenorphine for the management of opioid dependence.
17. Mattick, R.P., Breen, C., Kimber, J., et al. (2003). Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Issue 2, Art. No.: CD002209. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002209.
18. Faggiano, F., Vigna-Taglianti, F., Versino, E., et al. (2003). Methadone maintenance at different dosages for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Issue 3, Art. No.: CD002208. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002208.
19. Caplehorn, J. and Drummer, O.H. (1999). Mortality associated with New South Wales methadone programs in 1994: lives lost and saved. Medical Journal of Australia, 170, 104-9.
20. Mattick, R.P., Kimber, J., Breen, C., et al. (2003). Buprenorphine maintenance versus placebo or methadone maintenance for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Issue 2, Art. No.: CD002207. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002207.pub2.
21. Ferri, M., Davoli, M., Perucci, C.A., et al. (2006). Heroin maintenance treatment for chronic heroin-dependent individuals: a Cochrane systematic review of effectiveness. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 30(1), 63-72.
22. Eder, H., Jagsch, R., Kraigher, D., et al. (2005) Comparative study of the effectiveness of slow-release morphine and methadone for opioid maintenance therapy. Addiction, 100(8), 1101-9.
23. Robertson, J.R., Raab, G., Bruce, M., et al. (2006). Addressing the efficacy of dihydrocodeine versus methadone as an alternative maintenance treatment for opiate dependence: a randomized controlled trial. Addiction, 101, 1752-9.
24. Gowing, L., Ali, R., White, J., et al. (2006). Buprenorphine for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Issue 2, Art. No.: CD002025. DOI: 10.1002/14651858. CD002025.pub3.
25. Amato, L., Davoli, M., Minozzi, S., et al. (2005). Methadone at tapered doses for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Issue 3, Art. No.: CD003409. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003409.pub3.
26. Gowing, L., Farrell, M., Ali, R., et al. (2004). Alpha2 adrenergic agonists for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Issue 4, Art. No.: CD002024. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002024.pub2.
27. NICE technology appraisal guidance 115 – January 2007. Naltrexone for the management of opioid dependence.
28. Marlatt, G.A., and Gordon, J.R. (ed.) (1985). Relapse prevention: maintenance strategies in the treatment of addictive behaviour. Guilford Press, New York.
29. Prochaska, J.O., and Di Clemente, C.C. (1986). Towards a comprehensive model of change. In Treating addictive behaviours: process of change (eds. W.R. Miller and N. Heather). Plenum Press, New York.
30. Miller, W., and Rollnick, S. (1991). Motivational interviewing. Guilford Press, New York.
31. Narcotics Anonymous webpage http://www.na.org/accessed April 2007
32. Mayet, S., Farrell, M., Ferri, M., et al. (2005), Psychosocial treatment for opiate abuse and dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 25(1).
33. Amato, L., Minozzi, S., Davoli, M., et al. (2004). Psychosocial and pharmacological treatments versus pharmacological treatments for opioid detoxification. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Issue 4, Art. No.: CD004147. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004147.pub2.
34. Department of Health. (1999). Drug misuse and dependence: guidelines on clinical management. HMSO, London.
35. Strang, J., Kelleher, M., Best, D., et al. (2006). Emergency naloxone for heroin overdose. British Medical Journal, 333(7569), 614-5.
36. Fischer, G. (2000). Treatment of opioid dependence in pregnant women. Addiction, 95(8), 1141-4.
37. Stover H. (2002). Drug and HIV/AIDS services in European Prisons Bibliotheks-und Unfomationssystems der Universitat Oldenurg BJS
38. Darke, S., Degenhardt, L., Mattick, R., et al. (2007). Mortality amongst illicit drug users: epidemiology, causes and intervention. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
39. McLellan, A.T., Lewis, D.C., O’Brien, C.P., et al. (2000). Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. Journal of the American Medical Association, 284(13), 1689-95.
40. McLellan, A.T., Alterman, A.I., Metzger, D., et al. (1994). Similarity of outcome predictors across opiate, cocaine and alcohol treatments: role of treatment services. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62, 1141-58
41. Hubbard, R.L., Craddock, S.G., Anderson, J., et al. (2003). Overview of 5-year follow up outcomes in the drug abuse treatment outcome studies (DATOS). Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 25(3), 125-34.
42. Gossop, M., Marsden, J., Stewart, D., et al. (2003) The National Treatment Outcome Research Study (NTORS): 4-5 year follow-up results. Addiction, 98(3), 291-303.
43. Darke, S., Ross, J., Teesson, M., et al. (2007). The Australian Treatment Outcome Study (ATOS): what have we learnt about treatment for heroin dependence? Drug and Alcohol Review, 26(1), 49-54.
44. Hser, Y.I., Hoffman, V., Grella, C.E., et al. (2001). A 33-year follow-up of narcotics addicts. Archives of General Psychiatry, 58(5), 503-8.
45. Smyth, B., Hoffman, V., Fan, J., et al. (2007). Years of potential life lost among heroin addicts 33 years after treatment. Preventive Medecine. 44(4), 369-74. Epub 2007, Feb 8.