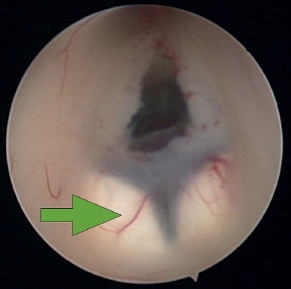
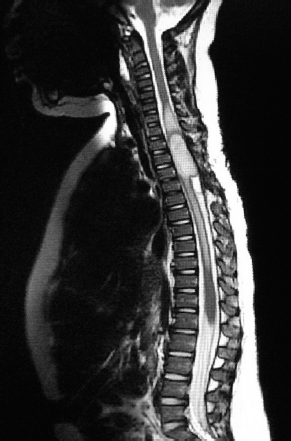
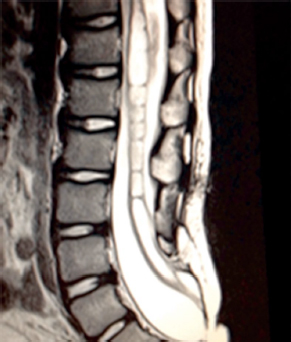
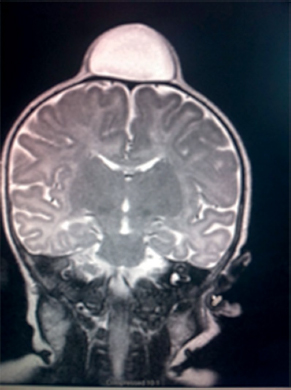
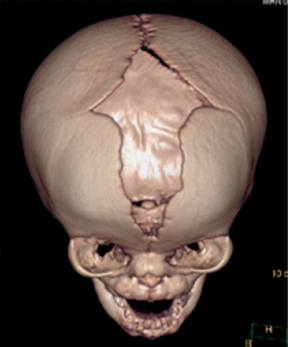
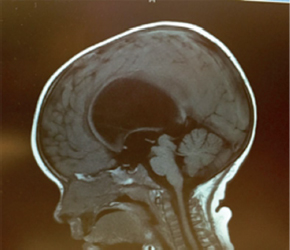
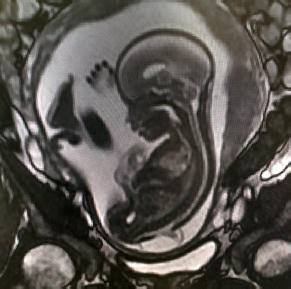
4Pediatric Neurosurgery What structure is indicated by the arrow in this image from an endoscopic third ventriculostomy? A. Optic chiasm B. Pituitary stalk C. Tip of basilar artery D. Fornix E. Mammillary bodies During an infratentorial supracerebellar approach to a pineal tumor, what vein in the galenic draining group may be sacrificed safely without negative sequelae? A. Basal vein of Rosenthal B. Posterior mesencephalic vein C. Straight sinus D. Precentral cerebellar vein E. Internal cerebral vein A premature neonate’s head ultrasound demonstrates intraventricular hemorrhage. The ventricles are dilated mildly. What is the infant’s subependymal hemorrhage grade? A. Grade 1 B. Grade 2 C. Grade 3 D. Grade 4 A 3-year-old boy presents with a history of spinal cord de-tethering and excision of a thoracic dermal sinus tract during infancy. What is the most likely spinal cord lesion seen on the current T2 MRI shown in this image? A. Syrinx B. Ependymoma C. Astrocytoma D. Dermoid tumor E. Epidermoid tumor What component is necessary to classify a Chiari malformation as type 3? A. Cervical cord syrinx B. Occipital encephalocele C. Lumbar myelomeningocele D. Cerebellar vermian agenesis E. Platybasia A 2-year-old boy presents with gait imbalance and progressive headaches. MRI suggests a posterior fossa tumor. Gross total resection and pathological analysis reveal an average risk medulloblastoma. The next adjuvant therapy step is: A. Chemotherapy alone B. Radiation therapy alone C. Concomitant chemotherapy and radiation D. No need for further adjuvant therapy An 8-year-old child with a history of myelomeningocele repair after birth presents with progressive leg weakness and a neurogenic bladder. An MRI of lumbar spine, shown in this image, suggests: A. Syringomyelia secondary to a tethered spinal cord B. Idiopathic syringomyelia C. Spinal lipoma D. Dermoid tumor E. Thickened filum terminale A 2-month-old baby has a slowly growing midline mass over the anterior fontanelle, as shown in the MRI in this image. The most likely diagnosis is: A. Dermoid cyst B. Eosinophilic granuloma C. Epidermoid cyst D. Fibrous dysplasia E. Hemangioma A 3-month-old baby has an abnormal head shape. Based on the 3D reconstruction imaging of the skull, shown in this image, what syndrome is suspected? A. Pierre Robin syndrome B. Treacher Collins syndrome C. Pfeiffer syndrome D. Goldenhar syndrome E. Moebius syndrome The normal level of conus medullaris in infants and children is at the level of: A. L1-L2 B. L3-L4 C. L4-L5 D. L5-S1 E. T12-L1 The most common postoperative complication encountered after selective dorsal rhizotomy for spasticity is: A. Cerebrospinal fluid leak B. Paraplegia C. Bladder incontinence D. Bowel incontinence E. Lower extremity hyperesthesia The most life-threatening complication during endoscopic third ventriculostomy for obstructive hydrocephalus is secondary to: A. Forniceal injury B. Thalamic injury C. Injury to the basilar artery bifurcation D. Meningitis E. Oculomotor nerve injury The most common location of atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors during infancy and childhood is in the: A. Suprasellar region B. Spinal cord C. Posterior fossa D. Frontal lobe E. Temporal lobe What surgical procedure should be considered as a treatment option in pediatric patients with disabling drop attacks and generalized seizures? A. Anatomic hemispherectomy B. Functional hemispherectomy C. Mesial temporal lobectomy D. Amygdalohippocampectomy E. Corpus callosotomy The most common symptomatic intracranial vascular anomaly in children is a(n): A. Arteriovenous malformation (AVM) B. Cavernoma C. Venous angioma D. Berry aneurysm E. Mycotic aneurysm What particular spinal feature is associated with achondroplasia? A. Scalloping of the vertebrae B. Hemivertebrae C. Foramen magnum stenosis D. Os odontoideum E. Dermal sinus tract An 11-month-old boy presents with macrocrania and failure to thrive. An MRI of the brain, shown in this image, confirms what likely type of hydrocephalus? A. Communicating hydrocephalus B. Obstructive hydrocephalus secondary to a Dandy-Walker malformation C. Obstructive hydrocephalus secondary to aqueductal stenosis D. Obstructive hydrocephalus secondary to a posterior fossa tumor E. Obstructive hydrocephalus secondary to a vein of Galen aneurysm A 10-year-old boy presents with progressive weakness of his bilateral wrist and finger extensors (wrist drop). He also has abdominal pain. What is the most likely source of his chemical poisoning? A. Lead B. Arsenic C. Mercury D. Copper E. Iron What molecular subgroup of medulloblastoma is associated with the best 5-year overall survival rate? A. Wnt subgroup B. SHH subgroup C. Group 3 D. Group 4 Trilateral retinoblastoma describes bilateral ocular retinoblastomas and a(n): A. Astrocytoma B. Medulloblastoma C. Neurofibroma D. Optic nerve sheath tumor E. Pineoblastoma A pregnant woman presents after a pelvic MRI, shown in this image, evaluated a fetal spina bifida lesion detected by ultrasound. She is being considered for a fetal in-utero repair. What are the gestational age limits (minimum and maximum) for consideration of fetal repair per the MOMs trial criteria?
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree