Peripheral neuropathies I
Clinical approach and investigations
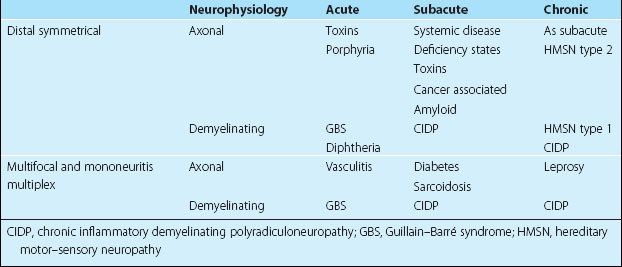
Peripheral neuropathies are very variable, both in their clinical manifestations and in their aetiology (Table 1). These three sections give an overview of peripheral nerve disease, with the third concentrating on the common isolated peripheral nerve lesions.
Pathology
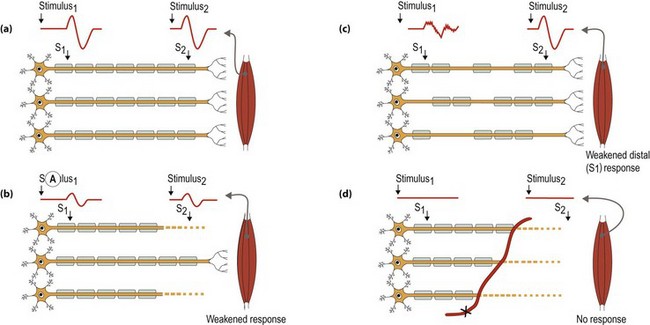
Peripheral nerves can be affected in three ways (Fig. 1). These mechanisms of injury are not mutually exclusive and in some conditions there are contributions from all three mechanisms:
Clinical features
There are four patterns of clinical presentation of peripheral nerve disease (Fig. 2):
1. Distal symmetrical neuropathy. This is the most common presentation of axonal neuropathies. There is distal sensory and motor dysfunction, affecting the legs more than the arms; sensory changes in the hands are noted when sensory changes in the legs get to the knees.
2. Multifocal neuropathies. There is an asymmetrical involvement, without involving specifically named nerves. This is usually the presentation of demyelinating or vasculitic neuropathies.
3. Mononeuropathies. The involvement of an individual named nerve. The most commonly affected nerves are described on page 106.