19
Pharmacopeia
Table 19.1. Approved indications of the antiepileptic drugs.
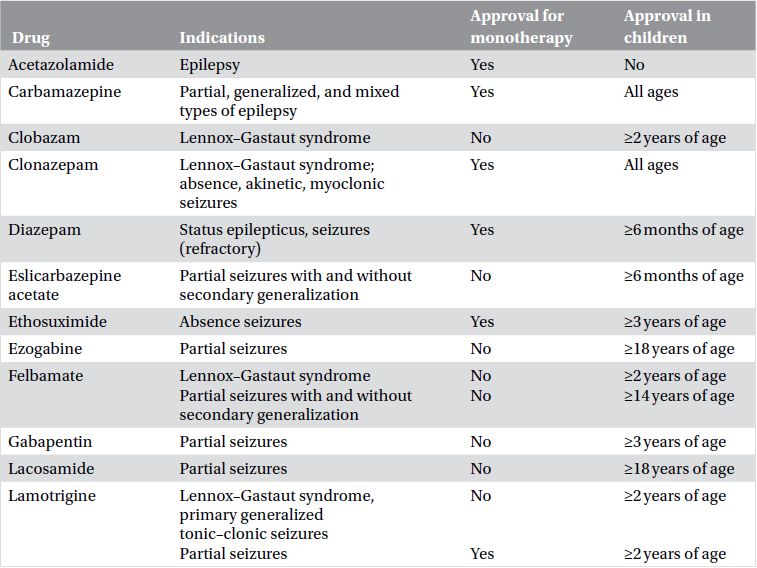
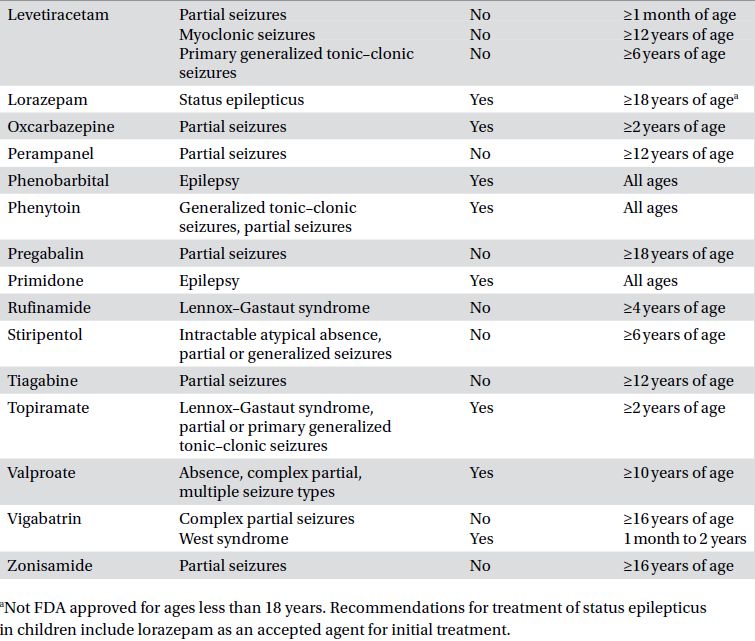
Table 19.2. Chemistry and pharmacology of the antiepileptic drugs.
| Drug | Chemical structure | Proposed mechanism of action |
| Acetazolamide | 5-Acetamido-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide | Inhibits carbonic anhydrase |
| Carbamazepine | 5-Carbamoil-5H-dibenz[b,f ]azepine | Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels Stabilizes neuronal membranes and limits sustained repetitive firing |
| Clobazam | 7-chloro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-1,5-benzodiazepine-2,4(3H,5H)dione | Enhances GABAA receptor-mediated chloride currents |
| Clonazepam | 5-(2-Chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-7-nitro-2H-1,4 benzodiazepin-2-one | Enhances GABAA receptor-mediated chloride currents |
| Diazepam | 7-Chloro-1,3-dihydro-1-methyl-5-phenyl-1,4 benzodiazepin-2(3H)-one | Enhances GABAA receptor-mediated chloride currents |
| Eslicarbazepine acetate | S-(−)-10-acetoxy-10,11-dihydro-5H-dibenzo[b,f]azepine-5-carboxamide | Voltage-gated sodium channel blocker |
| Ethosuximide | 2-Ethyl-2-methylsuccinimide | Attenuates voltage-sensitive calcium channels |
| Ezogabine | N-(2-amino-4-(4-fluorobenzyl-amino)-phenyl) carbamic acid ethyl ester | Opens/activates voltage-gated potassium channels (KCNQ2/3, KCNQ3/6) Potentiates GABA-evoked currents |
| Felbamate | 2-Phenyl-1,3-propanediol dicarbamate | Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels Inhibits calcium currents through NMDA receptors Enhances GABAA receptor-mediated chloride channels |
| Gabapentin | 1-Aminomethyl-cyclohexane acetic acid | Binds to α2δ subunit of the L-type calcium channel Increases GABA levels by increasing GABA turnover Inhibits monoamine neurotransmitter release Decreases sustained repetitive firing |
| Lacosamide | (R)-2-acetamido-N-benzyl-3-methoxypropionamide | Enhances slow inactivation of sodium channels |
| Lamotrigine | 3,5-Diamino-6-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,4-triazine | Inhibits sodium currents Inhibits high-threshold activated calcium channels |
| Levetiracetam | (S)-α-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide | Limits calcium influx through an N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel Binds to synaptic vesicle protein 2A |
| Lorazepam | 7-Chloro-5(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-3-dihydroxy-2H-1,4-benzoidazepin-2-one | Enhances GABAA receptor-mediated chloride currents |
| Oxcarbazepine | 10,11-Dihydro-10-oxo-carbamazepine | Active metabolite, 10-OH-carbazepine, inhibits sustained repetitive firing |
| Perampanel | Reduces neuronal excitation via the noncompetitive antagonism of the ionotropic AMPA-glutamate receptor on postsynaptic neurons | |
| Phenobarbital | 5-Ethyl-5-phenylbarbituric acid | Enhances GABAA receptor-mediated chloride currents |
| Phenytoin | 5,5-Diphenylhydantoin | Inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels Stabilizes neuronal membranes and limits sustained repetitive firing |
| Pregabalin | S-(+)-3-aminomethylhexanoic acid; Isobutyl-γ-aminobutyric acid | Selective inhibitor of L-type voltage-gated calcium channels containing the α2δ subunit |
| Primidone | 5-Ethyldihydro-5-phenyl-4,6 (1H,5H) pyrimidine-dione | Enhances GABAA receptor-mediated chloride currents |
| Rufinamide | 1-(2,6-Difluorophenyl)methyl-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carboxamide | Sodium channel blocker |
| Stiripentol | 4,4-Dimethyl-1-[(3,4 methylenedioxy) phenyl]-1-penten-3-ol | Enhances GABAergic neurotransmission by increasing the release of GABA and the duration of the activation of GABAA receptors |
| Tiagabine | (−)-R-1-[4,4-bis(3-methyl-2-thienyl)-3-butenyl]-3-piperidinecarboxylic acid | Selective blocker of neuronal and glial GABA transporters resulting in increased brain GABA levels |
| Topiramate | 2,3:4,5-bis-O-(1-methylethylidene)-β–D-fructopyranose sulfamate | Blocks sustained repetitive firing and inhibits sodium currents Decreases glutamate-mediated excitation via the AMPA/kainate receptor Enhances GABAA currents Potentiates hyperpolarizing potassium currents Inhibits high-threshold activated calcium channels Inhibits carbonic anhydrase |
| Valproate | 2-Propylpentanoic acid | Attenuates voltage-sensitive calcium channels, inhibits sodium channels, and stabilizes neuronal membranes Enhances GABAergic-mediated inhibition |
| Vigabatrin | 4-Amino-5-hexenoic acid; γ-vinyl GABA | Irreversibly inhibits GABA transaminase, resulting in increased brain GABA levels |
| Zonisamide | 1,2-Benzisoxazole-3-methane sulfonamide | Blocks sustained repetitive firing through an effect on voltage-sensitive sodium channels Reduces T-type calcium currents Alters ligand binding to GABAA receptor Inhibits carbonic anhydrase |
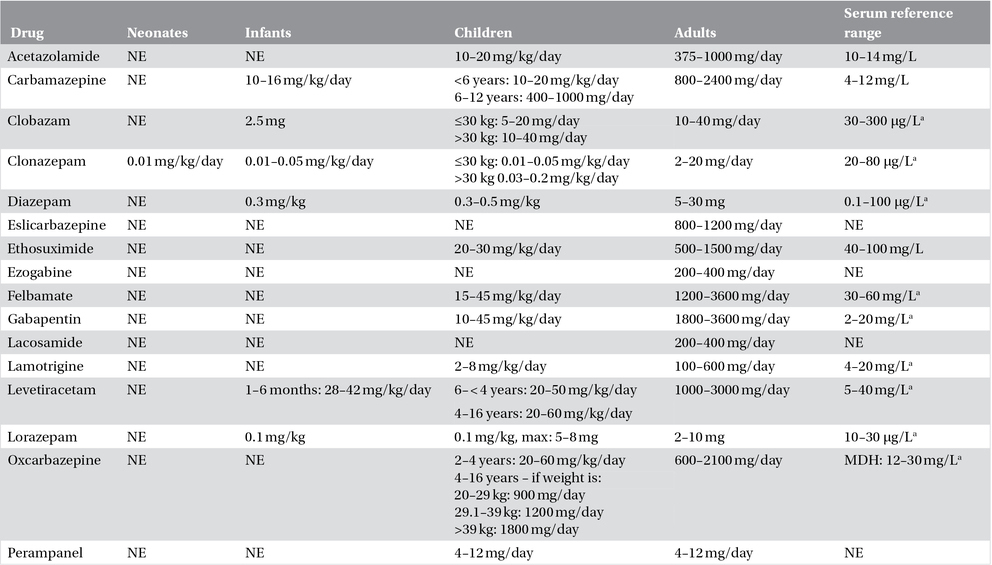
Table 19.3. Average daily doses of the antiepileptic drugs (monotherapy).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


