♦ Preoperative
- Work-up should include serum markers including alpha-fetoprotein (alpha-FP), beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG), carcinoembryonic antigen, acid phosphatase
- Total imaging of the central nervous system is recommended if there is a suspicion for drop metastasis
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) markers as above should be sent if CSF is easily accessible
Operative Planning
- Review imaging (magnetic resonance imaging with or without contrast, computed tomography)
- Spinal imaging to review for possible drop metastasis along spinal axis
- Confirm CSF and serum for tumor markers (beta-hCG, alpha-FP)
- Preoperative steroids for significant vasogenic edema
- Treat hydrocephalus if present and symptomatic
- Wide diversity in pathology of pineal region tumors, tissue diagnosis is critical for diagnosis and to guide therapy
Hydrocephalus Treatment
External Ventricular Drain
- Advantages
- Temporary and may be weaned postoperatively
- Can be placed emergently at bedside
- Can be utilized to increase drainage and decrease intracranial pressure
- May help clear blood and debris postoperatively with drainage
- Temporary and may be weaned postoperatively
- Disadvantages
- May need to convert to shunt if unable to tolerate weaning in 5 to 7 days
- Increase risk of infections
- Bleeding risk during placement of external ventricular drain
- May need to convert to shunt if unable to tolerate weaning in 5 to 7 days
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt
- Advantages
- Definitive treatment
- Disadvantages
- May not be needed postresection
- Risk of shunt obstruction, malfunction, and infection
- May not be needed postresection
Third Ventriculostomy
- Advantages
- Avoids permanent hardware
- Decreased long-term risk of infection as compared with shunting procedures
- May be able to endoscopically biopsy some pineal region lesions after third ventriculostomy in the same surgical session
- Decreased risk of subdural hematoma (as compared with ventriculoperitoneal shunt) because of less drastic ventricular size reduction
- Avoids permanent hardware
- Disadvantages
- Not possible in all case (e.g., tumor filling third ventricle, anatomy not favorable)
- Difficult to assess patency because ventricle may not change in size
- There is potential for ventriculostomy closure or failure
- Not possible in all case (e.g., tumor filling third ventricle, anatomy not favorable)
- We prefer stereotactic endoscopic third ventriculostomy over CSF diversion by ventriculoperitoneal shunt when possible
Operative Options
Stereotactic Biopsy
- Several approaches possible: we prefer the precoronal, lateral trajectory
- Advantages
- May avoid morbidity associated with an open procedure
- Reduced hospital stay compared with open surgery
- May avoid morbidity associated with an open procedure
- Disadvantages
- Higher risk than traditional supratentorial stereotactic biopsy
- Sampling error
- No debulking or resection
- Heterogeneity of pathology (i.e., mixed germ cell tumor) may preclude definitive diagnosis
- Higher risk than traditional supratentorial stereotactic biopsy
- Open biopsy or resection
- Can be achieved through three main approaches and a combination of the three:
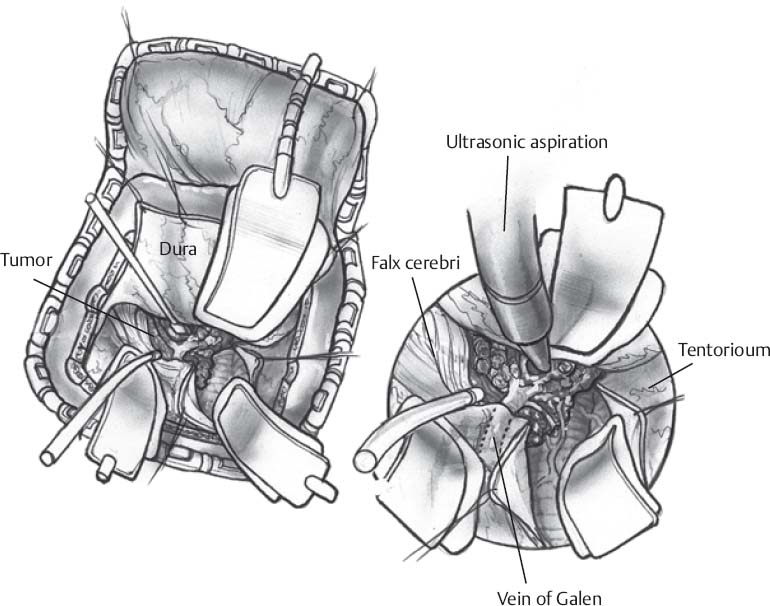
- Supracerebellar infratentorial (Fig. 51.1)
- Suboccipital transtentorial
- Posterior interhemispheric transcallosal
- Combination of approaches
- Supracerebellar infratentorial (Fig. 51.1)
- Can be achieved through three main approaches and a combination of the three:
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue