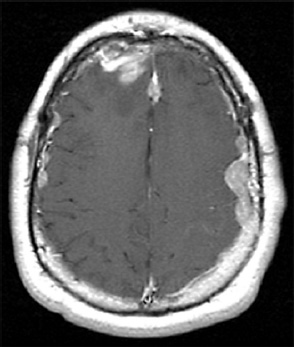
1. Regarding the pathophysiology of myasthenia gravis, what is/are the possible mechanisms by which acetylcholine receptor antibodies interfere with neuromuscular transmission? A. binding to the acetylcholine receptor and blocking the binding of acetylcholine B. cross-linking acetylcholine receptors, thereby increasing their rate of internalization C. binding of complement resulting in destruction of the muscle end plate D. all of the above E. none of the above 2. All of the following statements are correct regarding the medial lemniscus EXCEPT: A. Near the sensory decussation, its blood supply comes from the anterior spinal artery. B. The medial lemniscus can be found in close proximity to the anterolateral tract in the medulla. C. Its somatotopy in the pons is such that leg fibers are lateral to arm fibers. D. The fibers of the medial lemniscus arise from the cuneate and gracile nuclei. E. Brainstem lesions involving medial lemniscus fibers usually include adjacent structures, resulting in motor and sensory losses. A. 10% formalin B. 12% glutaraldehyde C. UV irradiation D. autoclaving at 121°C E. sodium hydroxide (2N) 4. Which of the following lines at the craniocervical junction extends from the basion to the opisthion? A. McRae’s line B. McGregor’s line C. Chamberlain’s line D. Wackenheim’s line E. Anterior marginal line 5. The somatotopic arrangement in the ventral horn is such that A. the flexors are dorsal to extensors and limbs are medial to trunk. B. the extensors are dorsal to flexors and limbs are medial to trunk. C. the flexors are dorsal to extensors and limbs are lateral to trunk. D. the extensors are dorsal to flexors and limbs are lateral to trunk. E. none of the above 6. The oxygen extraction ratio is increased when blood flow decreases in all of the following organs EXCEPT: A. brain B. kidney C. liver D. heart E. lungs A. pathology reveals pleomorphic short and wide septate hyphae B. treated with Cancidas, Voriconazole, and AmBisome C. causes hemorrhagic necrosis and ischemic strokes D. organism originates in the soil E. may be seen in an immunocompromised patient 8. Somatic motor efferents to the urethral sphincter are located A. in intermediolateral cell columns of the sacral cord. B. in Onuf’s nucleus. C. in Barrington’s nucleus. D. all of the above E. none of the above 9. Cerebral ischemia begins when cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) falls below A. 100 mm Hg. B. 75 mm Hg. C. 50 mm Hg. D. 23 mm Hg. E. 8 mm Hg. 10. Regarding the anatomy near the cavernous sinus, the borders of the clinoidal triangle are cranial nerves A. I and II. B. II and III. C. III and IV. D. IV and V. E. none of the above 11. Which of the following is FALSE regarding myasthenia gravis? A. The first presentation is usually weakness of the extraocular muscles. B. Weakness that fluctuates and fatigues over the course of the day. C. Speech may be hypernasal or hoarse in some patients. D. It may present with a head drop. E. Dysphagia is worst at breakfast and improves during the course of the day. 12. All of the following are true of polymyositis EXCEPT: A. It involves a symmetric weakness of proximal limb and trunk muscles. B. Its onset is insidious. C. Ocular muscles are usually spared. D. Muscles are not tender to palpation. E. Skin changes typically occur before muscle abnormalities. 13. Protein 14–3-3 is elevated in the CSF in which of the following conditions? A. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease B. demyelinating disease C. head trauma D. meningoencephalitis E. all of the above 14. Which of the following statements is most accurate regarding the nerve supplying the teres minor muscle? A. It has a contribution from the lateral cord. B. It is an extension of the posterior cord. C. Ventral rami C8 and T1 are major contributors to this nerve. D. It is derived from the same cord as the musculocutaneous nerve. E. None of the above 15. The pterion is formed by the junction of the all of the following EXCEPT: A. frontal bone B. sphenoid bone C. zygomatic bone D. temporal bone E. parietal bone 16. Which of the following increase dead space? A. PE (pulmonary embolus) B. PEEP (positive end expiratory pressure) C. emphysema D. all of the above E. none of the above 17. Regarding infection in a trauma patient with the following x-ray, the most common pathogen is A. S. aureus. B. Pseudomonas. C. Proteus. D. S. pneumoniae. E. E. coli. 18. Patients with interstitial cystitis A. are rarely incontinent. B. have an overwhelming desire to urinate. C. have activation of a sensory pathway subserving cortical sensation of the bladder without activation of the afferent reflex pathway. D. all of the above E. none of the above 19. Which of the following factors increase ICP? A. movement B. pain C. fever D. Valsalva E. all of the above 20. The posterior loop of the internal carotid artery and the origin of the meningo-hypophyseal trunk are exposed in the floor of which triangle? A. lateral triangle B. anterior lateral triangle C. Parkinson’s triangle D. anterior medial triangle E. none of the above A. as synchronous muscle fiber activation between fibers of different motor units. B. as the difference in timing of muscle fiber activation between two fibers in a single motor unit. C. as the difference in timing of muscle fiber activation between two fibers of different motor units. D. as the complete failure of neuromuscular transmission at one muscle fiber in a pair. E. none of the above 22. Ataxia may be seen in all of the following syndromes EXCEPT: A. Claude’s syndrome B. Benedikt’s syndrome C. Nothnagel’s syndrome D. Basilar artery syndrome E. Weber’s syndrome 23. Which one of the following findings is seen with subacute combined degeneration? A. ataxic gait B. antalgic gait C. myopathic gait D. apraxia gait E. calcaneus gait 24. A lesion of which of the following structures would MOST significantly impair memory? A. amygdala B. fornix C. dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus D. mamillary body E. area 44 25. Which of the following is NOT associated with the findings on this x-ray? A. weakness of hand B. Horner’s syndrome C. Raynaud’s syndrome D. traction meningocele E. ulnar paresthesias 26. Which of the following are true of PEEP (postive end expiratory pressure)? A. it decreases work of breathing B. it increases cerebral perfusion pressure C. it decreases physiologic dead space D. all of the above E. none of the above 27. Which of the following can decrease the infection rate of venous catheters? A. changing the line periodically over a guide-wire B. occlusive dressings C. masks and gowns D. all of the above E. none of the above 28. Which of the following neurotransmitters promotes penile erection? A. serotonin B. dopamine C. noradrenaline D. all of the above E. none of the above 29. The peak reduction in ICP after administration of mannitol occurs A. in about 4 hours. B. in about 2 hours. C. in about 1 hour. D. in about 30 minutes. E. in about 15 minutes. 30. The borders of Parkinson’s triangle are cranial nerves A. I and II. B. II and III. C. III and IV. D. IV and V1 E. none of the above 31. The Tensilon test A. is not sensitive but very specific for myasthenia gravis (MG). B. is not particularly useful in ocular MG. C. when negative, rules out the diagnosis of MG. D. shows no correlation with subsequent response to pyridostigmine. E. is not affected by the quantity of acetylcholine receptors. 32. In posterior interosseous syndrome, there is a fingerdrop but no wristdrop because of sparing A. of the extensor carpi radialis longus. B. of the extensor carpi radialis brevis. C. of the extensor digitorum. D. of the extensor carpi ulnaris. E. of the brachioradialis. 33. What is the name of the following equation? E = (RT/zF) ln Q A. Nernst equation B. Goldman equation C. Poiseuille’s equation D. Henderson-Hasselbalch equation E. none of the above 34. Interruption of the inferior geniculocalcarine fibers results A. in an ipsilateral superior quadrantanopsia. B. in a contralateral superior quadrantanopsia. C. in an ipsilateral inferior quadrantanopsia. D. in a contralateral inferior quadrantanopsia. E. none of the above 35. Which of the following may be seen with ocular myoclonus? A. vertical oscillation of the eyes occurring with movements of the palate B. hypertrophy of the inferior olivary nucleus C. prior lesions of the central tegmental tract D. all of the above E. none of the above 36. All of the following characterize adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) EXCEPT: A. late hypoxemia B. diffuse infiltrate C. leaky capillaries D. association with sepsis and trauma E. protein content of fluid greater than with pulmonary edema 37. In a healing wound, maximum collagen deposition occurs A. at 2 weeks. B. at 4 weeks. C. at 6 weeks. D. at 8 weeks. E. at 10 weeks. 38. All of the following are true regarding the condition depicted by the following histopathology EXCEPT: A. It is histologically characterized by a biphasic pattern. B. Rosenthal fibers are a prerequisite for this diagnosis. C. It may mimic oligodendroglioma. D. It is a CNS neoplasm seen with neurofibromatosis type 1. E. Recurrence is usually a reformation of the cyst rather than the solid tumor. 39. Barbiturates presumably act by which of the following mechanisms? A. inverse steal phenomenon B. decreased CMR (cerebral metabolic rate) C. decreased oxygen consumption D. scavenger free radicals E. all of the above 40. The anterolateral middle fossa triangle is defined by cranial nerves A. II and III. B. III and IV. C. IV and V1. D. V1 and V2. E. V2 and V3. 41. Which of the following is true of myasthenia gravis? A. The majority of acetylcholine receptor antibodies are of the M subtype. B. Cyclosporine is used as a first-line treatment. C. Corticosteroids may reduce the risk of secondary generalization in the ocular form. D. Pathologic abnormalities of the thymus are found in less than 5% of patients. E. Weakness confined to the ocular muscles beyond 3 years is associated with poor prognosis. 42. The border of the foramen lacerum is formed A. by the sphenoid bone. B. by the temporal bone. C. by the sphenoid and temporal bones. D. by the sphenoid, temporal, and occipital bones. E. by the occipital bone. 43. Absence of inflammation is typical of the following diseases EXCEPT: A. neuropathy from diphtheria B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease C. paraneoplastic necrotizing myelopathy D. central pontine myelinolysis E. Tolosa-Hunt syndrome 44. Wernicke’s area is BEST described as including A. area 39. B. the supramarginal, area 40, and posterior one third of the superior temporal gyri. C. the angular and posterior one third of the superior temporal gyri. D. areas 39 and 40. E. the supramarginal and posterior one third of the superior temporal gyri. A. in opsoclonus. B. in square wave jerks. C. in downbeat nystagmus. D. in upbeat nystagmus. E. none of the above 46. The origin of axons that mediate the swallowing reflex A. is the solitary nucleus. B. is the dorsal motor nucleus of X. C. is the nucleus ambiguus. D. all of the above E. none of the above For the MRI findings in questions 47 to 51, please choose the answer option that is correct. A. scan 1 B. scan 2 C. both scans 1 and 2 D. neither scan 1 nor scan 2 47. Hypertension 48. Early facial nerve involvement 49. Hypotension and bronchoconstriction during resection 50. Diarrhea 51. Early hearing loss and tinnitus A. increased fibrinogen level B. prolonged PT C. prolonged PTT D. thrombocytopenia E. fragmented RBCs 53. The mastoid air cells are innervated A. by V1. B. by V2. C. by V3. D. by IX. E. by X. 54. Which of the following statements is most accurate regarding the band of Gennari? A. It divides the third layer of the cortex of areas 17 and 18. B. It divides the third layer of the cortex of area 17. C. It divides the fourth layer of the cortex of areas 17 and 18. D. It divides the fourth layer of the cortex of area 17. E. It divides the fourth layer of the cortex of areas 17, 18, and 19. 55. The following are prenuclear structures for vertical gaze EXCEPT: A. nucleus of Darkshevich B. posterior commissure C. interstitial nucleus of Cajal D. rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) E. nucleus prepositus hypoglossi 56. Which of the following neurons or nerve cell processes is/are particularly involved with new, novel movements? A. mossy fibers B. Betz cell C. climbing fibers D. all of the above E. none of the above 57. Which of the following disease states is characterized by high trophic hormone and low target hormone? A. Cushing’s disease B. Graves’ disease C. Adrenal tumors D. Addison’s disease E. None of the above 58. Which of the following intrinsic muscles of the thumb does NOT insert on the proximal phalanx? A. adductor pollicis B. abductor pollicis brevis C. flexor pollicis brevis D. opponens pollicis E. extensor pollicis brevis 59. Resolution of brain edema occurs primarily A. through bulk flow. B. through vascular clearance. C. through unknown mechanisms at the blood–brain barrier. D. all of the above E. none of the above For the brachial plexus structures in questions 60 to 64, choose the appropriate letter in the diagram below: 60. Medial brachial cutaneous nerve 61. Long thoracic nerve 62. Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve 63. Suprascapular nerve 64. Median pectoral nerve 65. The MLF is responsible for the binocular coordination of the following eye movements EXCEPT: A. lateral B. vertical C. vergence D. oblique E. horizontal 66. Which of the following is a distinguishing factor between Apert’s and Crouzon’s syndrome? A. pattern of inheritance B. association with bilateral coronal synostosis C. severity of mental retardation D. all of the above E. none of the above 67. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is a secretagogue A. for prolactin. B. for adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). C. for growth hormone (GH). D. for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). E. all of the above 68. Which of the following pairs of nerves is responsible for movement of the ring finger? A. radial only B. radial and median C. radial, median, and ulnar D. radial, median, and axillary E. musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar 69. Which of the following types of edema is a feature of hydrocephalus? A. Vasogenic edema B. Cytotoxic edema C. Interstitial edema D. All of the above E. None of the above A. lateral triangle B. paramedial triangle C. Glasscock’s triangle D. Kawase’s triangle E. Parkinson’s triangle 71. Which is FALSE regarding the hormone prolactin (PRL)? A. Its releasing hormone is located in the arcuate nucleus. B. Normal levels are 5 to 25 ng per mL. C. Levels may be increased after syncope. D. Levels are increased after tonic clonic seizure activity. E. Levels are increased after nonepileptic seizures. 72. Which of the following circumventricular organs is a central receptor site for angiotensin II? A. organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis B. median eminence of the tuber cinereum C. subcommissural organ D. subfornical organ E. area postrema 73. All of the following are true of the sinuvertebral nerve EXCEPT: A. It is a branch from the posterior division of the spinal nerve proximal to the dorsal root ganglion. B. It may enter the intervertebral foramen. C. It supplies most of the innervation to the posterior aspect of the disk. D. It may have a proprioceptive and/or nociceptive function. E. It has been shown to consist of two roots at cervical levels. 74. All of the following are true of conduction aphasia EXCEPT: A. It is caused by a lesion of the arcuate fasciculus. B. There is fluent paraphasic speech with intact repetition. C. It may be caused by occlusion of an MCA posterior temporal branch. D. Patients may mimic Wernicke’s, but are able to understand. E. Patients are aware of the problem. 75. Which statement is true about the following aneurysm? A. It arises from the cavernous internal carotid artery. B. It measures about 6 to 8 mm. C. It usually presents with pituitary dysfunction. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above are true. 76. During surgery for craniosynostosis, the MOST common event associated with poor outcome is A. poor sterile technique and infection. B. excessive blood loss and hypothermia. C. inexperienced surgeon and need for reoperation. D. all of the above are equally associated with poor outcome. E. none of the above 77. Which of the following disorders is due to a defect in neural cell adhesion molecules (N-CAM) that guide the migration of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons? A. Laron-type dwarfism B. Kallmann’s syndrome C. Letterer-Siwe disease D. Wolfram’s syndrome E. none of the above 78. Cell bodies of nerve fibers in the medial brachial cutaneous nerve are found A. in the dorsal root ganglia only. B. in the anterior horn only. C. in the sympathetic chain ganglia and dorsal root ganglia. D. in the lateral horn and sympathetic chain ganglia. E. none of the above 79. The perforant path is the main A. inhibitory pathway of the hippocampus. B. excitatory pathway of the hippocampus. C. inhibitory pathway of the hypothalamus. D. excitatory pathway of the hypothalamus. E. none of the above 80. Which triangle contains the foramen spinosum? A. Parkinson’s triangle B. Kawase’s triangle C. Glasscock’s triangle D. Inferior medial triangle E. Paramedial triangle 81. The most common type of headache is A. cluster. B. tension. C. migraine. D. postconcussive. E. due to temporal arteritis. 82. The trochlear nerve can be found in which cistern? A. cerebellomedullary B. interpeduncular C. ambient D. chiasmatic E. pontine 83. Which scalene muscle(s) insert on the first rib? A. anterior scalene B. anterior and medial C. medial and posterior D. anterior and posterior E. anterior, medial, and posterior 84. A lesion of the left geniculocalcarine tract and the corpus callosum is most likely to cause A. pure word blindness. B. pure word deafness. C. mutism. D. anomic aphasia. E. global aphasia. 85. All of the following are true regarding hemispherectomy EXCEPT: A. Improvement in IQ is often seen postoperatively. B. Behavior is improved after surgery. C. It is not necessary to preserve the septum pellucidum. D. Plugging the foramen of Monro with a piece of temporalis muscle is often performed. E. Patients are usually mute for about a week after surgery. 86. The principle behind multiple subpial transection for epilepsy is that A. horizontal fibers have a limited functional role. B. vertical fibers have a limited functional role. C. the pia has a limited functional role. D. all of the above E. none of the above 87. The presenting symptom of a hypothalamic hamartoma is most commonly A. headache. B. vomiting. C. visual field disturbance. D. sexual precocity. E. seizures. 88. All of the following are true of the tumor in this pathology slide EXCEPT: A. It is found in superficial brain regions. B. It shows intracellular accumulation of lipids. C. It corresponds to World Health Organization (WHO) grade II. D. It carries a dismal prognosis. E. It presents in patients with a long history of seizures. 89. Schaffer collaterals carry A. excitatory input from CA1. B. excitatory input from CA3. C. inhibitory input from CA1. D. inhibitory input from CA3. E. none of the above 90. The size of the medial group of lenticulostriate arteries from M1 is__________ related to the size of the ipsilateral recurrent artery of Heubner. A. directly B. inversely C. not at all D. exponentially E. logarithmically 91. Which amino acids are precursors for catecholamines? A. phenylalanine and tyrosine B. phenylalanine and tryptophan C. tyrosine and tryptophan D. arginine and tyrosine E. phenylalanine and arginine 92. All of the following structures are supplied by the anterior spinal artery EXCEPT: A. pyramids B. medial lemniscus C. fibers of cranial nerve XII D. gracile and cuneate nuclei E. anterior two thirds of the spinal cord 93. During a clinic appointment, patients are asked to sit with their arms dependent, hold their breath, and tilt their head back and turn it to the side. Meanwhile the doctor is checking for the presence or absence of a radial pulse. What is being described? A. Allen’s test B. Ayer’s test C. Adson’s test D. Addis test E. Dix-Hallpike maneuver 94. The corticobulbar tract is located in which area of the internal capsule? A. anterior limb B. posterior limb C. retrolenticular limb D. sublenticular limb E. genu 95. The medial forebrain bundle interconnects the following areas EXCEPT: A. septal nuclei B. raphe nuclei C. locus ceruleus D. medulla E. hypothalamus 96. Cerebellar tonsillar displacement is seen A. in Chiari I. B. in Chiari II. C. in Crouzon’s syndrome. D. all of the above E. none of the above 97. The most severe forms of hypothalamic cachexia are seen in lesions A. of the lateral hypothalamus. B. of the anterior hypothalamus. C. of the posterior hypothalamus. D. of the ventromedial hypothalamus. E. of the suprachiasmatic hypothalamus. 98. The region of the cortex most closely associated with the conscious perception of smell is A. the temporal. B. the cingulate. C. the prefrontal. D. the posterior parietal. E. the anterior parietal. 99. The most prominent inhibitor to apoptosis is A. Bax. B. Bcl-2. C. PAX. D. HSP-90. E. none of the above 100. Which of the following pathologic diagnosis is most likely associated with this hemorrhagic lesion? A. melanoma B. choriocarcinoma C. breast carcinoma D. renal cell carcinoma E. choroid plexus papilloma 101. The highest incidence of phenylketonuria (PKU) is in which country? A. Ireland B. Japan C. Australia D. Sweden E. Mexico 102. The straight sinus is formed from the union A. of the internal cerebral vein and basal vein. B. of the inferior sagittal sinus and vein of Galen. C. of the basal vein and great cerebral vein. D. of the inferior sagittal vein and basal vein. E. of the precentral cerebellar vein and internal cerebral vein. 103. A lesion of the vestibular labyrinth that causes images in the visual fields to move back and forth is best described A. as ocular flutter. B. as ocular dysmetria. C. as ocular bobbing. D. as oscillopsia. E. as opsoclonus. 104. Atropine mainly affects which type of synapses? A. parasympathetic preganglionic B. parasympathetic postganglionic C. sympathetic postganglionic D. all of the above E. none of the above 105. Wernicke’s encephalopathy is due to deficiency A. of vitamin B1. B. of vitamin B2. C. of vitamin B6. D. of vitamin B12. E. none of the above 106. The solitary pathways are concerned A. with taste. B. with thoracic viscera. C. with sudden changes in blood pressure. D. all of the above E. none of the above 107. The greatest difference between diffuse astrocytomas (WHO grade II) and anaplastic astrocytomas (WHO grade III) is A. the MIB-1 fraction. B. the presence of mitotic activity. C. the presence of necrosis. D. angiogenesis. E. the presence of gemistocytes. 108. The most common intraconal orbital mass is A. the neurilemmoma. B. the fibrous histiocytoma. C. the hemangiopericytoma. D. the cavernous hemangioma. E. none of the above 109. Which abnormality does the following EKG show? A. Hypokalemia B. Quinidine toxicity C. Hypothermia D. Myocardial infarction E. None of the above 110. The location of the apex in most arteriovenous malformations is A. cortical. B. insular. C. parietal. D. occipital. E. periventricular. 111. In catecholamine biosynthesis, the rate-limiting step during conditions of neuronal activation is A. dopamine β-hydroxylase. B. tyrosine hydroxylase. C. aromatic amino acid decarboxylase. D. monoamine oxidase. E. phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase. 112. The venous angle is seen angiographically by the junction of which two veins? A. septal and caudate B. septal and terminal C. terminal and caudate D. internal cerebral and terminal E. basal and internal cerebral 113. Ocular bobbing may be seen in which of the following? A. hydrocephalus B. pontine infarct C. hepatic encephalopathy D. trauma E. all of the above 114. The most likely diagnosis for the following lesion seen on CT is A. aneurysmal bone cyst. B. epidermoid granuloma. C. osteosarcoma. D. hemangioma. E. osteoid osteoma. 115. The striae medullares (rhombencephali) arise A. from the septal nuclei. B. from the habenular trigone. C. from the arcuate nuclei. D. from the amygdala. E. none of the above 116. The delivery of nutrients and removal of wastes from the vertebral disc is dependent A. on arterioles and venules. B. on capillaries penetrating the disc. C. on diffusion. D. all of the above E. none of the above 117. Which of the following statements is true of the olivocochlear bundle? A. It is part of the ascending auditory pathway to the dorsal cochlear nucleus. B. It can be seen readily in brainstem sections of the upper pons. C. It communicates directly with the medial lemniscus. D. Stimulation of it inhibits acoustic fiber responses to auditory stimuli. E. It arises from the inferior olivary nucleus and projects to the cochlea. 118. Which of the following orbital tumors is at highest risk of tumor seeding and recurrence during removal? A. cavernous hemangioma B. pleomorphic adenoma of the lacrimal gland C. neurilemmoma D. hemangiopericytoma E. fibrous histiocytoma 119. The pterygoid plates are composed of which bones? A. sphenoid and temporal B. sphenoid and vomer C. palatine and sphenoid D. palatine E. none of the above 120. Brodmann area 44 comprises A. Wernicke’s area. B. the visual cortex. C. Broca’s area D. the prefrontal area. E. the frontal eye field. 121. The genetic defect in a particular movement disorder called dopa-responsive dystonia is due to a mutation affecting A. dopa β-hydroxylase formation. B. the synthesis of a tyrosine hydroxylase cofactor. C. the norepinephrine transporter. D. vesicle formation in the catecholamine neuron. E. the breakdown of catecholamines. 122. Which of the following arteries supplies the deep cerebellar nuclei? A. posterior inferior cerebellar artery B. superior cerebellar artery C. thalamogeniculate branches D. posterior choroidal artery E. none of the above 123. In the comatose patient, extensor movements of the arms and weak flexor movements of the legs are most likely to occur with a lesion A. above the red nucleus. B. at the red nucleus. C. between the red nucleus and above the vestibular nuclei. D. at the vestibular nuclei. E. below the vestibular nuclei. 124. “Crocodile tears” or lacrimation from gustatory stimulation is classically described as the result of aberrant regeneration of fibers A. from cranial nerve III reaching the ciliary ganglion. B. from cranial nerve V reaching the ciliary ganglion. C. from cranial nerve VII reaching the ciliary ganglion. D. from cranial nerve III reaching the sphenopalatine ganglion. E. from cranial nerve VII reaching the sphenopalatine ganglion. 125. Syringomyelia affecting the lower cervical area may result in attenuation or abolition of which of the following somatosensory evoked potentials? A. N13 B. N20 C. P40 D. N22 E. None of the above 126. If an instrumentation system is too stiff, disuse osteoporosis can occur around the instrumentation. This statement is related A. to Sherrington’s law. B. to Flouren’s law. C. to Wolff’s law. D. to Delpech’s principle. E. to Jackson’s law. 127. In comparison to chordomas, chondrosarcomas A. arise more laterally. B. result in more neurologic deficits at presentation. C. are nearly always S-100 positive. D. display all of the above features. E. display none of the above features. 128. Which of the following conditions would benefit most from thalamotomy? A. medically refractory essential tremor B. rigidity associated with Parkinson’s disease C. intention tremor from cerebellar stroke D. bradykinesia associated with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) E. dyskinesia associated with striatonigral degeneration 129. Which of the following is the best measure of the “equator” of the spinal cord when performing a cordotomy for pain management? A. just ventral to the dentate ligament B. just dorsal to the dentate ligament C. at the attachment of the dentate ligament D. the midway point between the exit of the dorsal and ventral rootlets E. ~5 mm from the anterior spinal artery 130. When is the earliest time one would expect to observe after radiation therapy the following changes on a T2-weighted MRI taken in a patient who under-went a tumor resection? A. 1 month B. 3 months C. 14 months D. 48 months E. 72 months 131. Levels of L-dopa are virtually unmeasurable in the CNS under basal conditions A. because the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase is low. B. because L-dopa is localized in vesicles. C. because the activity of aromatic amino acid decarboxylase is high. D. because dopamine ?-hydroxylase is localized in the vesicles. E. because the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase is high. 132. The facial nucleus and the spinal trigeminal nucleus and tract are supplied by which artery? A. PICA B. AICA C. SCA D. Basilar E. Anterior choroidal 133. Which of the following statements regarding the length constant of a nerve fiber is true? A. The length constant is directly proportional to the membrane resistance. B. It is the distance along a fiber where a change in the membrane potential by a given current decays to half its original value. C. The length constant is directly proportional to the axial resistance. D. The length constant is greater in unmyelinated than myelinated fibers. E. none of the above 134. Dysfunction of which cell is the main problem in Raynaud’s phenomenon? A. red blood cell B. sympathetic neuron C. platelet D. mast cell E. fibroblast 135. Epidural hematomas in children are the result A. of an arterial injury. B. of bone oozing. C. of bleeding from the periosteal surface. D. all of the above E. none of the above 136. Spondylolysis most often occurs A. at L1. B. at L2. C. at L3. D. at L4. E. at L5. 137. The finding seen in the following photograph is caused by damage A. to a nerve arising from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. B. to a nerve arising from the roots of the brachial plexus. C. to the dorsal scapular nerve. D. to the thoracodorsal nerve. E. none of the above 138. The typical target in thalamotomy for reduction of tremor is A. Vim B. Vop C. Voa D. VC E. none of the above 139. Which of the following structures are derived from the telencephalon? A. caudate B. putamen C. amygdala D. all of the above E. none of the above 140. The precuneus (Brodmann areas 7 and 31) is located A. on the medial surface of the frontal lobe. B. in the secondary visual cortex. C. within the occipital lobe. D. on the medial surface of the parietal lobe. E. on the medial surface of the occipital lobe. 141. Which is FALSE regarding the catecholaminergic neuron? A. Dopamine β-hydroxylase (DBH) is a copper containing glycoprotein. B. Phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT) methylates norepinephrine (NE) to form epinephrine. C. Tyrosine hydroxylase is released from cells when its product, norepinephrine, is released. D. The final enzyme in the dopamine pathway is amino acid decarboxylase (AADC). E. The final enzyme in the NE pathway is DBH. 142. Neural crest derivatives include all of the following EXCEPT: A. Schwann cells B. bipolar cells C. leptomeninges D. chromaffin cells of the suprarenal medulla E. parafollicular cells 143. Which of the following is located in the bony modiolus of the cochlea? A. scala vestibuli B. cochlear duct C. organ of Corti D. spiral ganglion E. basilar membrane 144. Damage to this area leaves the patient transiently mute, with complete recovery in a few weeks. A. Broca’s area B. Wernicke’s area C. Arcuate fasciculus D. Uncinate fasciculus E. Supplementary motor area 145. The foramen spinosum is located A. in the sphenoid bone anterior to the greater and lesser superficial petrosal nerves. B. in the sphenoid bone between to the greater and lesser superficial petrosal nerves. C. in the temporal bone posterior to the greater and lesser superficial petrosal nerves. D. in the temporal bone between the greater and lesser superficial petrosal nerves. E. in none of the above locations 146. Spondyloptosis corresponds to Meyerding grade A. I. B. II. C. III. D. IV. E. V. 147. Golgi tendon organs are A. sensitive to stretch. B. in series with extrafusal fibers. C. encapsulated. D. all of the above E. none of the above 148. During a thalamotomy procedure, what are the indications that the electrode is in the correct location? A. Low-frequency (2 Hz) stimulation causes driving of the tremor. B. The patient reports contralateral paresthesias. C. High-frequency (50 Hz) stimulation results in tremor suppression. D. All of the above E. None of the above 149. Olfactory glomeruli are made up A. of granule and tufted cells. B. of granule and mitral cells. C. of tufted and mitral cells. D. of granule cells only. E. none of the above 150. The sylvian triangle is defined by points along which artery/arteries? A. MCA only B. MCA and ACA C. ACA, MCA, and PCA D. MCA and PCA E. ACA, MCA, and PCA 151. Select the FALSE statement regarding monoamine oxidase. A. MAOA has high affinity for norepinephrine and serotonin. B. MAOA is selectively inhibited by clorgyline. C. MAOB has high affinity for o-phenylethylamines. D. MAOA and MAOB are associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane. E. MAOB is selectively inhibited by deprenyl. 152. The superior part of the fourth ventricle is derived from which of the following vesicles? A. metencephalon B. myelencephalon C. mesencephalon D. prosencephalon E. none of the above 153. This structure is a projection of the spiral limbus that overlies the hair cells of the organ of Corti. A. tectorial membrane B. basilar membrane C. vestibular membrane D. Reissner’s membrane E. None of the above 154. Which fibers are associated with the gag reflex? A. spinal trigeminal nucleus projections to the nucleus ambiguus B. solitary projections to the nucleus ambiguus C. solitary projections to the salivatory nucleus D. salivatory nucleus projections to the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus E. none of the above A. Lumbar laminectomy of L4-S1 B. Lumbar hemilaminectomy at L4 on left side C. Pedicle screw fusion of L4-L5 D. Pedicle screw fusion of L3-S1 E. Pedicle screw fusion of L3-L4 156. Which of the following receptors is activated by baclofen and is insensitive to bicuculline? A. GABA-A B. GABA-B C. GABA-C D. All of the above E. None of the above 157. All of the following structures pass through the anulus of Zinn (tendinousring) EXCEPT: A. cranial nerve III, superior division B. nasociliary nerve C. cranial nerve IV D. cranial nerve III, inferior division E. cranial nerve VI A. Proteus B. Streptococcus C. Staphylococcus D. Pseudomonas 158. A 16-year-old boy who sustained a parietal skull fracture after a motorcycle accident 159. A 60-year-old woman with chronic ear infection 160. A 3-month-old baby with irritability and decreased oral intake 161. Tranylcypromine is A. an inhibitor of MAOA. B. an inhibitor of MAOB. C. an inhibitor of catechol methyltransferase (COMT). D. a reuptake inhibitor of serotonin. E. an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. 162. Which is the embryologic structure that becomes the ventral white commissure in the adult? A. basal plate B. floor plate C. alar plate D. sulcus limitans E. None of the above A. There is involvement of the upper eyelid. B. Radiotherapy is not effective. C. Hemiparesis is contralateral to the facial lesion. D. The triad classically consists of nevus flammeus, venous malformation, and glaucoma. E. Abnormalities of chromosome 9 are seen. 164. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is produced A. by the choroid plexus. B. by the ependymal surface. C. by the brain parenchyma. D. by bulk flow from the brain. E. all of the above 165. In patients with known systemic cancer, what percentage of single brain lesions are cerebral abscesses or primary brain tumors? A. less than 0.1% B. 1% C. 15% D. 30% E. 50% 166. Vigabatrin has anticonvulsant properties related to its interference A. of GABA breakdown. B. of GABA synthesis. C. of GABA reuptake. D. all of the above E. none of the above 167. The indusium griseum is a remnant A. of the habenula. B. of the hippocampus. C. of the hypothalamus. D. of the gyrus of Heschl. E. none of the above 168. A patient who had a thalamotomy for parkinsonian tremor earlier in the month has noticed weakness of the arm. The most likely explanation for this is that the lesion placed during the thalamotomy was too A. medial. B. lateral. C. anterior. D. posterior. E. mild. 169. Which immunosuppressive agent works at the level of the T cell by inhibiting expression of interleukin-2 (IL-2)? A. azathioprine B. cyclosporine C. methotrexate D. all of the above E. none of the above 170. Posterior thalamoperforating arteries are the perforators that arise from which artery? A. Pcom B. Pcom and P1 C. P1 and P2 D. P2 E. P1. 171. Which nucleus of the hypothalamus gives rise to dopamine innervation of the median eminence? A. supraoptic B. dorsomedial C. lateral D. arcuate E. ventromedial 172. The alar plate gives rise to all of the following EXCEPT: A. gracile and cuneate nuclei B. inferior olivary nuclei C. solitary nucleus D. spinal trigeminal nucleus E. nucleus ambiguus 173. Which of the following is FALSE regarding hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT)? A. It is related to abnormalities in the endoglin gene. B. Neurologic symptoms are common and may be related to associated pulmonary AVMs. C. Presentation may be with GI bleeding, hemoptysis, or epistaxis. D. It is autosomal recessive. E. Pulmonary and cerebral AVMs are associated with the 9q gene. 174. In preparation for placement of a ventriculostomy catheter, a resident measures a point 2.5 cm from the midline and 1 cm anterior to the coronal suture. The point that is being measured is A. Keen’s point. B. Kocher’s point. C. McEwen’s point. D. Barker’s point. E. the sylvian point. 175. A 60-year-old man with the following MRI finding is most likely to present with the following signs on examination: A. bilateral limb ataxia B. ipsilateral Horner’s syndrome C. contralateral abducens palsy D. ipsilateral tongue paralysis E. none of the above 176. All of the following epilepsy drugs have hepatic enzyme-inducing properties EXCEPT: A. carbamazepine B. phenytoin C. clonazepam D. primidone E. phenobarbitone 177. The interposed nuclei project A. to the contralateral red nucleus. B. to the ipsilateral red nucleus. C. to the contralateral thalamus. D. to the ipsilateral thalamus. E. none of the above 178. All of the following symptoms may improve after pallidotomy EXCEPT: A. drug-induced dyskinesias B. painful dystonias C. on/off fluctuations D. bradykinesia E. postural instability 179. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the femoral triangle? A. The femoral nerve lies outside the femoral sheath. B. The femoral nerve is lateral to the femoral artery. C. It is bounded superiorly by the inguinal ligament. D. It is covered superficially by the fascia lata. E. It is bounded laterally by the adductor longus. 180. The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) originates A. from the vertebral artery. B. from the distal one third of the vertebral artery. C. from the proximal two thirds of the basilar artery. D. from the posterior cerebral artery. E. from the distal two thirds of the basilar artery. 181. Which is FALSE regarding serotonin? A. It is metabolized to melatonin in the pineal gland. B. The majority of body stores of serotonin are found in the CNS. C. Two critical enzymes take part in its synthesis. D. Tryptophan is the precursor amino acid. E. It has an indole structure. 182. The basal plate gives rise to all of the following EXCEPT: A. oculomotor nucleus B. trochlear nucleus C. substantia nigra D. red nucleus E. superior colliculus 183. Livedo reticularis, subendothelial smooth muscle cell proliferation, and presentation with multiple ischemic strokes are features A. of Sneddon’s syndrome. B. of Seddon’s syndrome. C. of Scheie’s syndrome. D. of Schmidt’s syndrome. E. of Schanz’s syndrome. 184. During the abdominal portion of the operation for a ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt, if the surgeon is below the arcuate line, which structures would lie behind the rectus abdominus? A. external oblique aponeurosis B. internal oblique aponeurosis C. transversus abdominis aponeurosis D. transversalis fascia E. none of the above 185. Which of the following posterior fossa tumors has the tendency to arise from the floor of the fourth ventricle? A. medulloblastoma B. ependymoma C. astrocytoma D. hemangioblastoma E. none of the above 186. Which of the following is true of Lissauer’s tract? A. fibers are derived from the lateral division of the dorsal roots B. contains Aδ fibers C. contains C fibers D. all of the above E. none of the above 187. The limen insula can be found A. in the occipital lobe. B. at the junction of the insula and frontal lobe. C. within the third ventricle. D. in cross sections through the pons. E. in none of the above. A. to the thalamus. B. to the internal capsule. C. to the optic tract. D. to the amygdala. E. to the putamen. 189. Which of the following structures is NOT within the adductor canal? A. femoral artery B. femoral vein C. great saphenous vein D. nerve to vastus medialis E. saphenous nerve 190. An important landmark for identifying the junction of the tegmentum and the cerebral peduncle is A. the anterior pontomesencephalic vein. B. the lateral mesencephalic vein. C. the precentral cerebellar vein. D. the vein of Galen. E. the superior vermian vein. 191. This amino acid is not only a precursor to GABA but is also a neurotransmitter. A. glycine B. glutamate C. arginine D. tyrosine E. tryptophan For the actions and metabolisms in questions 192 to 195, choose the correct medications. A. hydralazine B. phentolamine C. nitroglycerine D. nitroprusside 192. Metabolized by the kidneys, equal effects on arterial and venous vasodilatation 193. Metabolized by the liver, more potent venous vasodilatation 194. Metabolized by the kidneys, more potent arterial vasodilatation 195. Metabolized by the liver, more potent arterial vasodilatation 196. Which of the following findings is LEAST likely to be associated with the following MRI scan? A. elevated serum angiotensin converting enzyme B. eosinophilic granuloma C. meningitis D. elevated adrenocorticotrophic hormone E. sarcoidosis 197. A central facial palsy would only involve A. the ipsilateral upper face. B. the ipsilateral lower face. C. the contralateral upper face. D. the contralateral lower face. E. none of the above 198. Palatal nystagmus is most likely due to a lesion A. of the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. B. of the corticospinal tract. C. of the cerebral peduncle. D. of the central tegmental tract. E. of the frontal eye field. 199. The single best predictor for patients with esthesioneuroblastoma is A. completeness of primary tumor excision. B. TP53 overexpression. C. the presence of Homer-Wright rosettes on pathology. D. neuron-specific enolase expression. E. the destruction of the cribriform plate. A. increased latency in wave 3. B. decreased latency in wave 4. C. decreased latency in wave 5. D. increased latency in wave 4. E. increased latency in wave 5. 201. The best characterized glutamate-containing neurons are found A. in the Purkinje cells of the cerebellum. B. in the pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex. C. in the pyramidal cells of the hippocampus. D. in the septal region. E. in the lateral entorhinal cortex. 202. All of the following statements are true of nuclear chain fibers EXCEPT: A. They receive group Ia primary afferent fibers. B. They receive group II secondary afferent fibers. C. They are associated with flower spray endings. D. They are associated with static gamma efferent fibers. E. They respond to muscle tension. 203. Patients who continue to display mental status changes after correction of diabetic ketoacidosis should be investigated A. for cysticercosis. B. for histoplasmosis. C. for lyme disease. D. for mucormycosis. E. for hydatid disease. 204. Which of the following is FALSE with regard to shunt nephritis? A. It is a well-described complication of VP shunts. B. It is due to deposition of immune complexes in the glomeruli of kidneys. C. The diagnosis is suspected with hematuria, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and decreased complement levels. D. Proper treatment entails removing the entire shunt. E. There is an elevated peripheral WBC count. 205. Regarding dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor (DNET), which of the following is FALSE? A. Male predominance has been noted. B. It is a surgically curable cause of partial seizures. C. There is an abundance of mitoses with no necrosis. D. It is a mixed glial and neuronal neoplasm. E. Shows on CT as a hypodense pseudocystic lesion. A. transsphenoidal resection B. bromocriptine C. angiography D. ophthalmologic evaluation E. transcranial resection 207. The saccule sends fibers to the______vestibular ganglion that project to the______vestibular nucleus. A. superior, superior B. superior, inferior C. inferior, superior D. inferior, inferior E. none of the above 208. Which of the following tracts traverse the restiform body? A. olivocerebellar B. reticulocerebellar C. dorsal spinocerebellar D. all of the above E. none of the above 209. A favorable prognosis in neuroblastomas is related A. to n-Myc amplification. B. to 1p deletion. C. to TrkA expression. D. to older age. E. none of the above A. at the mastoid tip. B. at the keyhole. C. at the asterion. D. at the bregma. E. at the lambda. 211. The definitive marker for cholinergic neurons is A. acetyl CoA. B. acetylcholinesterase. C. choline acetyltransferase. D. choline. E. sensitivity to hemicholinium-3. 212. Tanycytes are most likely to be found A. in the wall of the third ventricle. B. in a high-grade glioma. C. in a low-grade glioma. D. in the cauda equina. E. none of the above For the statements in questions 213 to 216, choose the appropriate structure on the diagram: 214. Innervates the sartorius muscle 215. Enables leg abduction 216. Meralgia paraesthetica 217. The vagus nerve leaves the medulla A. between the pyramid and the olive. B. between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle. C. from the same sulcus as CN XII. D. from the dorsomedial sulcus. E. from none of the above. 218. Bilateral damage to the medial basal occipitotemporal cortex results A. in astereognosis. B. in prosopagnosia. C. in alexia without agraphia. D. in auditory agnosia. E. in autotopagnosia. 219. Neuroblastomas may present A. with spinal cord compression. B. with Ondine’s curse. C. with opsoclonus syndrome. D. with diarrhea. E. all of the above 220. One of the most significant prognostic indicators for successful prolactinoma surgery is A. results of the Goldman perimetry field. B. being male. C. the preoperative prolactin level. D. age of the patient. E. being female. 221. Nitric oxide synthase is responsible A. for conversion of R-arginine into NO. B. for conversion of citrulline into NO. C. for production of NO and L-arginine. D. for production of NO and citrulline. E. none of the above 222. Which Rexed lamina is homologous to the spinal trigeminal tract? A. I B. II C. III and IV D. VII E. IX 223. The most common presentation of vein of Galen malformation in the neonate is A. an intracranial bruit with heart failure. B. subarachnoid hemorrhage. C. hydrocephalus. D. developmental delay. E. ocular symptoms. 224. Which of the following associations based on this MRI scan is FALSE? A. subarachnoid hemorrhage B. progressive ascending paraplegic syndrome C. the definitive therapy is microsurgical elimination D. tend to bleed in elderly patients E. it may represent a vascular anomaly 225. The arcuate eminence is the bony landmark of the A. superior petrosal sinus. B. superior semicircular canal. C. middle meningeal artery. D. vein of Labbe. E. none of the above 226. Which of the following is true of the medial posterior choroidal artery? A. It is a branch of the posterior cerebral artery. B. It supplies the choroid plexus of the third ventricle. C. It supplies the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles. D. all of the above E. none of the above 227. The calamus scriptorius can be found A. in the third ventricle. B. in the fourth ventricle. C. in the lateral ventricle. D. at the cauda equina. E. none of the above 228. Brain waves that are characteristic for deep sleep and have a frequency of 1 to per second are A. α waves. B. β waves. C. theta waves. D. delta waves. E. none of the above 229. Which cranial nerves innervate muscles that attach to the styloid process? A. VII, IX, X B. IX, X C. IX, X, XII D. VII, X E. VII, IX, XII 230. All of the following are true regarding hyperbaric oxygen therapy in postoperative neurosurgical infection, EXCEPT: A. It increases the oxygen tension in the infected tissues. B. It results in a direct bactericidal effect on anaerobic organisms. C. It results in improved phagocytosis of Staphylococcus. D. It should be used as an adjunct to surgery and antibiotics. E. It is a temporizing measure until definitive therapy can be instituted. 231. Allodynia is a condition A. where a painful response is produced by an innocuous mechanical stimulus. B. where a painful response is felt in an amputated limb. C. where a painful response is felt on the opposite side of the body. D. where there is sensitization of spinocerebellar neurons. E. all of the above 232. The nucleus dorsalis of Clarke corresponds to which Rexed lamina? A. I B. II C. III and IV D. VII E. IX 233. All of the following are true of encephaloceles EXCEPT: A. Occipital encephaloceles are the most common type. B. Frontoethmoidal (sincipital) are the most common type in Southeast Asia and among Australian aborigines. C. Parietal encephaloceles are associated with Chiari II malformation in up to one third of cases. D. Basal encephaloceles are associated with defects along the sphenoid bone. E. Children with basal encephaloceles have a low risk of developing meningitis. 234. On a horizontal section of the brain, the anterior limb of the internal capsule can be found A. between the thalamus and the globus pallidus. B. between the caudate and the corpus striatum. C. between the caudate and the thalamus. D. between the thalamus and putamen. E. none of the above For the structures in questions 235 to 238, choose their appropriate location on the following MRI: 235. Supplementary motor cortex 237. Premotor cortex 238. Heschl’s gyrus 239. Which of the following are true of the greater occipital nerve? A. It emerges inferior to the inferior obliquus capitis muscle. B. It is accompanied by the occipital artery. C. It is a sensory nerve. D. All of the above E. None of the above 240. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding arachidonic acid metabolism? A. Aspirin inhibits both cyclooxygenase (COX) isoforms. B. Arachidonic acid is a substrate for production of ceramide. C. Thromboxane synthesis inhibitors lead to depletion of arachidonic acid. D. Arachidonic acid is a substrate for COX I. E. Prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) is a product of the COX enzyme. 241. The basal ganglia output for eye movements is A. the subthalamic nucleus. B. the substantia nigra pars compacta. C. the substantia nigra pars reticulata. D. the globus pallidus interna. E. the globus pallidus externa. 242. Which area receives dorsal roots? A. dorsal lateral sulcus B. dorsal intermediate sulcus C. ventral lateral sulcus D. dorsal median sulcus E. ventral intermediate sulcus 243. Which statement is true in a 4-year-old with the following MRI findings? A. Biopsy is usually indicated to confirm the diagnosis. B. Hyperfractionated radiation therapy has not been shown to improve sur vival. C. Comprise 30% of pediatric CNS tumors. D. No proven chemotherapeutic regimen. E. Most lesions will regress spontaneously. For the medications in questions 244 to 247, choose their correct effects on the cardiovascular system: A. Increases refractory period, decreases contractility, increases preload (or left ventricular end diastolic pressure) B. Decreases refractory period, decreases contractility, decreases preload C. Decreases refractory period, decreases contractility, increases preload D. Decreases refractory period, increases contractility, increases preload 244. Procainamide 245. Propranolol 246. Phenytoin 247. Lidocaine 248. All of the following are true of Lhermitte-Duclos disease EXCEPT: A. It is also called dysplastic gangliocytoma of the cerebellum. B. There is demyelination of the granular cell layer of the cerebellum. C. There is thickening of one or more cerebellar folia. D. Calcification and hydrocephalus may occur in this disorder. E. A laminated pattern of folia on T2-weighted MRI is suggestive. 249. Which of the following is consistent with the diagnosis of typical trigeminal neuralgia? A. unilateral symptoms B. sensory deficit C. decreased corneal reflex D. all of the above E. none of the above 250. N-Butylcyanoacrylate is used A. for cranioplasty. B. for endovascular procedures. C. for topical wound dressings. D. for vasospasm in the ICU. E. none of the above 251. A 24-year-old man is brought into the emergency room after having a motor cycle accident. He has a scalp wound that is bleeding profusely. His eyes open only after his name is loudly called; however, he is confused when asked about the details of the accident. He obeys commands in all extremities. In this case, the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score is A. 15. B. 14. C. 13. D. 12. E. 11. 252. The ciliospinal center of Budge can be found at which spinal cord level? A. midcervical B. upper thoracic C. lower thoracic D. lumbar E. sacral 253. The serum level of phenytoin is increased by all of the following EXCEPT: A. cimetidine B. chloramphenicol C. valproic acid D. uremia E. aspirin A. pain and temperature of the body B. pain and temperature of the face C. Horner’s syndrome D. falling E. none of the above 255. Which of the following fractures is most commonly associated with anterior cord syndrome? A. clay shoveler’s fracture B. wedge fracture C. teardrop fracture D. Chance fracture E. transverse process fracture 256. What are the similarities between thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TTP) and idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)? A. decreased numbers of platelets B. immune-mediated C. treated with platelet replacement D. all of the above E. none of the above 257. All of the following structures are derived from ectoderm EXCEPT: A. pia B. dura C. arachnoid D. glia E. ependyma 258. The most common primary tumor of the septum pellucidum is A. meningioma. B. oligodendroglioma. C. astrocytoma. D. ependymoma. E. none of the above 259. The most common conflicting vessel in trigeminal neuralgia is A. the AICA. B. the PICA. C. the SCA. D. the satellite veins. E. none of the above 260. The ELANA technique may be helpful A. in vertebrobasilar ischemia. B. in controlling ICP. C. in vasospasm. D. in tumor biology. E. in spinal fusion. 261. This cervical spine MRI demonstrates A. metastatic disease. B. a jumped facet. C. a burst fracture. D. a teardrop fracture. E. an epidural abscess. 262. A 64-year-old woman presents to a clinic with a left thalamic arteriovenous malformation (AVM). The lesion appears to be ~5 cm in its greatest dimension. The AVM drains exclusively to the deep venous system via several stenotic veins. How would one best grade this AVM? A. Spetzler-Martin grade 3 B. Spetzler-Martin grade 3A C. Spetzler-Martin grade 4 D. Spetzler-Martin grade 4A E. Spetzler-Martin grade 5 263. Which type of breathing pattern is associated with a dorsomedial lesion in the medulla? A. apneustic B. Biot C. central neurogenic hyperventilation D. Kussmaul E. Cheyne-Stokes 264. Which of the following structures is supplied mainly by the anterior choroidal artery? A. globus pallidus externa, posterior limb of the internal capsule B. globus pallidus interna, posterior limb of the internal capsule C. globus pallidus externa, anterior limb of the internal capsule D. globus pallidus interna, anterior limb of the internal capsule E. none of the above 265. A feature that distinguishes pronator teres syndrome from carpal tunnel syndrome is that the former A. is due to repetitive usage. B. causes aching and fatiguing of the muscles involved. C. causes nocturnal exacerbations. D. exhibits numbness in the palm area. E. is a better candidate for surgery. 266. Bleeding time is increased by all of the following EXCEPT: A. thrombocytopenia B. uremia C. factor XIII deficiency D. vWF deficiency E. NSAIDs 267. Which of the following is a paired structure? A. subforniceal organ B. subcommissural organ C. area postrema D. all of the above E. none of the above 268. Which of the following taste sensations is coupled to G-proteins when activated? A. sweet and sour B. sweet and bitter C. bitter and salty D. sour only E. salty only A. V1 only B. V2 only C. V3 only D. V2 and V3 E. V1, V2, and V3 270. Gerstmann’s syndrome classically includes all the following EXCEPT: A. dysgraphia B. left-right confusion C. finger agnosia D. dyscalculia E. astereognosis 271. A 50-year-old man is seen in a clinic 6 months after being involved in a motor vehicle accident. He has noticed a palpable lump growing on the left side of his head (see x-ray). On examination, the lesion is painless when palpated. Which of the following lesions is most likely? A. fibrous dysplasia B. osteoma C. eosinophilic granuloma D. giant cell tumor E. epidermoid 272. Which of the following cranial nerves exit the brainstem between the pyramid and the olive? A. cochlear B. glossopharyngeal C. vagus D. accessory E. hypoglossal 273. All of the following regarding stage 4 sleep are true EXCEPT: A. Dreaming occurs. B. Nightmares occur. C. It is of decreased duration with hypothyroidism. D. Somnambulism occurs. E. It is of increased duration after sleep deprivation. 274. Increased risk of hemorrhage from warfarin is seen A. with phenobarbital. B. with carbamazepine. C. with cephalosporins. D. with penicillin. E. with all of the above 275. Which of the following muscles are typically involved in anterior interosseous syndrome? A. flexor digitorum profundus B. flexor pollicis longus C. pronator quadratus D. all of the above E. none of the above A. inferior petrosal sinus B. jugular bulb C. sigmoid sinus D. transverse sinus E. PICA 277. Which of the following has an intact blood–brain barrier (BBB)? A. subforniceal organ B. subcommissural organ C. area postrema D. all of the above E. none of the above 278. Dysgeusia is often associated with the use of A. penicillin. B. captopril. C. steroids. D. all of the above E. none of the above A. observation B. surgical excision C. gamma knife D. partial surgical treatment E. embolization 280. Which of the following is NOT associated with chronic alcoholism? A. cerebral atrophy B. Wernicke encephalopathy C. central pontine myelinolysis D. Foster-Kennedy syndrome E. Marchiafava-Bignami disease A. early Alzheimer’s disease B. Pick’s disease C. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease D. Huntington’s disease E. diffuse Lewy body dementia 282. All of the following statements about fibrillation potentials are true EXCEPT: A. They are a triphasic potential. B. They typically last 5 to 15 milliseconds. C. They are caused by denervation. D. They are seen with poliomyelitis, ALS, and peripheral nerve injury. E. They may be associated with positive sharp waves. 283. Bursts of 13 Hz lasting from half a second to 2 seconds are characteristic A. of stage 1 sleep. B. of stage 2 sleep. C. of stage 3 sleep. D. of stage 4 sleep. E. of REM sleep. A. petrous bone B. hyperostosis C. anterior clinoid process D. posterior clinoid process E. petrous bone 285. The transverse scapular ligament may be the cause of an entrapment syndrome that results in shoulder pain and muscle atrophy. The nerve that is trapped is A. a direct branch of the C5 root. B. a branch from the middle trunk. C. a branch from the posterior cord. D. a branch from the superior trunk. E. none of the above 286. Which of the following cranial nerves travel through medial lemniscal fibers on exiting the brainstem? A. III B. IV C. VI D. VII E. XII 287. Normal cerebral blood flow is A. 50 mL/100 mg/min. B. 50 mL/100 g/min. C. 50 mL/mg/min. D. 50 mL/g/min. E. 50 mL/kg/min. 288. Which of the following disorders is/are associated with gustatory dysfunction? A. Bell’s palsy B. familial dysautonomia C. Raeder’s paratrigeminal syndrome D. all of the above E. none of the above 289. Total excision of the lesion shown in the imaging is most likely to improve A. attention. B. memory. C. visuoconstructive ability. D. executive function. E. cognitive function. 290. Which of the following is caused by the JC virus? A. central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) B. progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) C. bovine spongiform encephalitis (BSE) D. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) E. none of the above 291. During saccadic movement of the eyes A. there is increased activity of STN (subthalamic) neurons. B. there is increased activity of SNpr (pars reticulata) neurons. C. there is decreased activity of SNpr neurons. D. there is increased activity of GPe (globus pallidus pars externa) neurons. E. none of the above 292. All the following are true statements regarding fasciculation potentials EXCEPT: A. They have three to five phases. B. They last from 5 to 15 milliseconds. C. They are associated with nerve fiber irritability. D. They are not visible through the skin. E. They may be associated with hypocalcemia, hypothermia, and nerve entrapments. 293. Calexcitin is a signaling molecule that amplifies calcium elevation in response to learning-associated synaptic transmitters in a model system of learning and memory (marine snail Hermissenda). Which of the following is FALSE regarding calexcitin? A. Neural mechanisms regarding associative learning rarely are conserved between different species. B. Calexcitin binds guanosine triphosphate (GTP), which is important in cell signaling. C. At the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, it has been shown to bind to the ryanodine receptor with high affinity. D. Calexcitin directly inactives voltage-dependent potassium currents. E. It is a high-affinity substrate for the α-isozyme of protein kinase C (PKC). 294. Which of the following has been described with oat cell carcinoma of the lung? A. anti-Hu antibodies B. Eaton-Lambert syndrome and limbic encephalitis C. ectopic ACTH secretion D. syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) E. all of the above 295. On an EKG, a J-point elevation is characteristic of A. hypocalcemia. B. hypokalemia. C. hypothermia. D. hypothyroidism. E. subendocardial ischemia. 296. Which of the following encephaloceles have the greatest chance of normal intellectual development and are least likely to develop hydrocephalus? A. anterior encephaloceles B. parietal encephaloceles C. basal encephaloceles D. occipital encephaloceles E. encephaloceles of the clivus 297. The brain tumor shown in this pathology slide expresses a high frequency of this mutation. A. TP53 B. PTEN C. EGFR D. all of the above E. none of the above 298. Which of the following may be features of anaplastic oligodendroglioma? A. microvascular proliferation B. necrosis C. pseudopalisading D. all of the above E. none of the above 299. Which structure straddles the posterior reach of the sylvian fissure? A. angular gyrus B. supramarginal gyrus C. middle temporal gyrus D. superior parietal lobule E. none of the above 300. Avellis’ syndrome is most likely caused by a lesion in which area? A. medulla B. pons C. hypothalamus D. thalamus E. midbrain 301. Bicuculline is A. a glutamate agonist. B. a glutamate antagonist. C. a dopamine agonist. D. a GABA agonist. E. a GABA antagonist. 302. All of the following statements regarding Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease are true EXCEPT: A. It may be associated with a footdrop. B. It is a condition of disordered myelination from decreased production of PMP22 (peripheral myelin protein). C. It is the most common inherited peripheral neuropathy. D. It is associated with a mutation on chromosome 17. E. It is characterized by peroneal muscle atrophy. 303. Neurons that give rise to the ventral trigeminothalamic tract arise A. from the trigeminal motor nucleus and the spinal trigeminal tract. B. from the dorsal aspect of the principle sensory nucleus and the spinal trigeminal tract. C. from the ventral aspect of the principle sensory nucleus and the spinal trigeminal tract. D. from the ventral aspect of the principle sensory nucleus and the mesencephalic tract. E. from the dorsal aspect of the principle sensory nucleus and the mesencephalic tract. 304. All of the following regarding motion perception is true EXCEPT: A. Motion is perceived by an object’s change of position on the retina. B. The sensation of movement is known as the phi phenomenon. C. Images that change positions more than 15 times per second are indistinguishable from continuous motion. D. The motion system is disabled at rates above 50 Hz. E. There is no physical process occurring on the retina that corresponds to the perceived sensation of motion. 305. Which tract decussates in the dorsal tegmental decussation? A. rubrospinal tract B. medial vestibulospinal tract C. tectospinal tract D. all of the above E. none of the above 306. In paranasal sinus cancers, sphenoid sinus involvement is noteworthy since it A. is the major predictor of later tumor recurrence. B. demands use of special instruments. C. will more likely result in anosmia postoperatively. D. all of the above E. none of the above 307. Which of the following is a distinct interneuron between receptor and ganglion cell? A. rods B. cones C. horizontal cells D. amacrine cells E. bipolar cells 308. Ependymoma is immunoreactive A. for GFAP. B. for S-100. C. for vimentin. D. for all of the above E. for none of the above 309. The caudal remnant of the median prosencephalic vein unites with the developing internal cerebral veins to form A. the straight sinus. B. the vein of Galen. C. the confluence of sinuses. D. the inferior sagittal sinus. E. none of the above 310. Which of the following statements is NOT true of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease (PMD)? A. It has been linked to severe deficiency of myelin specific lipids. B. It is X-linked recessive in the classical form. C. The connatal form (type II) is milder than the classical form. D. It manifests as a “tigroid” pattern of perivascular myelin preservation on MRI. E. Rare female cases have been described. 311. Which afferent cerebellar tract does NOT pass through the inferior cerebellar peduncle? A. reticulocerebellar B. vestibulocerebellar C. trigeminocerebellar D. pontocerebellar tract E. olivocerebellar tract 312. All of the following statements regarding the cerebellum are true EXCEPT: A. The floccular-nodular lobe receives input from the vestibular nuclei. B. The anterior lobe receives input from the spinocerebellar tracts. C. The vermis sends fibers to the VL thalamus and motor cortex. D. The intermediate zone functions with posture, tone, and ipsilateral limb movements. E. A lesion of the interposed nuclei causes intention tremor. 313. Which of the following inhibitory synaptic connections is found exclusively in the olfactory bulb? A. dendrodendritic B. axodendritic C. axoaxonic D. axosomatic E. dendroaxonic 314. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the parvocellular sys tem of the lateral geniculate nucleus? A. It is a small cell with a compact dendritic tree. B. It represents a minority of the total ganglion cell number. C. It projects to layer 4Cβ in the striate cortex. D. It is involved with color processing. E. It has low contrast sensitivity and high acuity. 315. All the following are true regarding venous air embolism EXCEPT: A. It manifests as a decrease in end tidal CO2. B. Air should be aspirated from the right atrium if it occurs. C. The patient should be placed in the left lateral decubitus position. D. The head should be lowered if possible. E. End tidal CO2 changes cannot precede precordial Doppler changes. 316. The stria terminalis is a fiber tract that parallels A. the caudate vein. B. the septal vein. C. the basal vein of Rosenthal. D. the internal cerebral vein. E. the thalamostriate vein. 317. What are the major contents of the proximal portion of the cubital fossa, in order from medial to lateral? A. median nerve, brachial artery, biceps brachii tendon, radial nerve B. median nerve, biceps brachii tendon, radial nerve, brachial artery C. biceps brachii tendon, median nerve, radial nerve, brachial artery D. brachial artery, biceps brachii tendon, radial nerve, median nerve E. none of the above 318. All of the following are medial rotators of the arm EXCEPT: A. the pectoralis major B. the subscapularis C. the teres major D. the teres minor E. the latissimus dorsi 319. The medial posterior choroidal artery when viewed on an angiogram occupies the same location as this structure seen on the venous phase of the angiogram. A. vein of Galen B. basal vein of Rosenthal C. internal cerebral vein D. thalamostriate vein E. caudate vein 320. Occlusion of which of the following arteries is most likely to result in ipsilateral hypoglossal palsy? A. basilar B. anterior spinal C. vertebral D. PICA E. AICA 321. The Botzinger complex is a cluster of cells that is involved in A. excitatory control of cardiac function. B. inhibitory control of cardiac function. C. excitatory control of respiratory function. D. inhibitory control of respiratory function. E. none of the above 322. The upper subscapular nerve arises from which segment of the brachial plexus? A. superior trunk B. medial trunk C. lateral cord D. posterior cord E. medial cord 323. All of the following are true of Moyamoya syndrome EXCEPT: A. The majority of adults with this disease present with ischemia. B. The age of onset of symptoms displays a bimodal distribution. C. It is of unknown etiology. D. Involves progressive stenosis of the supraclinoid carotid arteries with the concomitant formation of rich collaterals at the skull base. E. It is associated with Down syndrome and neurofibromatosis. 324. All of the following are true of valproic acid EXCEPT: A. It is effective in generalized tonic clonic seizures. B. It is ~90% protein bound. C. It has a long half-life. D. It may be associated with platelet dysfunction. E. It may result in liver dysfunction. 325. Which of the following anesthetics allows patients to emerge faster from anesthesia and has the least effect on metabolism of antiepileptic drugs? A. enflurane B. isoflurane C. nitrous oxide D. halothane E. ketamine 326. The glomus is a prominent tuft of choroid plexus found A. in the frontal horn. B. in the temporal horn. C. in the atrium. D. in the occipital horn. E. in none of the above 327. Which of the following groups of nerves is most likely to be affected by fractures of the humerus? A. axillary, musculocutaneous B. median, musculocutaneous C. axillary, radial, ulnar D. median, radial, ulnar E. median, radial 328. Apraxia usually results from a lesion A. of the precentral gyrus. B. of the postcentral gyrus. C. of the premotor cortex. D. of the prefrontal cortex. E. of the cingulate gyrus. 329. On an angiogram, the colliculocentral point is halfway between the tuberculum sellae and the sinus confluence. This point is closest to which structure? A. vein of Galen B. basal vein of Rosenthal C. internal cerebral vein D. straight sinus E. precentral cerebellar vein 330. Theta activity can be described for which of the following frequencies? A. 5 Hz B. 10 Hz C. 15 Hz D. 20 Hz E. 25 Hz 331. Cells of which area have true unipolar neurons? A. motor nucleus of V (trigeminal) B. mesencephalic nucleus of V C. sensory nucleus of V D. red nucleus E. locus ceruleus 332. The spinal border cells found in the ventral horns at L1-S2 give rise A. to first-order neurons of the ventral spinocerebellar tract. B. to second-order neurons of the ventral spinocerebellar tract. C. to first-order neurons of the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. D. to second-order neurons of the dorsal spinocerebellar tract. E. none of the above 333. Narcolepsy is associated with A. HLA-B27. B. HLA-A24. C. HLA-B40. D. HLA-B54. E. HLA-DR2. 334. Both retrospective and prospective studies of anterior temporal lobectomy have shown that seizure control in medial temporal lobe epilepsy is related to the extent of A. anterior resection. B. posterior resection. C. lateral resection. D. medial resection. E. none of the above 335. Overall, the most common cause of chorea is A. Huntington’s chorea. B. chorea gravidarum. C. senile chorea. D. Hysterical chorea. E. Sydenham’s chorea. 336. Side effects of this medication include A. myopathy. B. susceptibility to infection. C. posterior subcapsular cataracts. D. all of the above E. none of the above 337. Which of the following is true concerning relationships to the flexor retinaculum? A. The ulnar artery is superficial to it. B. The median nerve is deep to it. C. The ulnar nerve is superficial to it. D. all of the above E. none of the above 338. If a patient has already had a thalamotomy for tremor and now seeks treatment for tremor of the other hand, which deep brain stimulation (DBS) procedure should be done? A. thalamotomy B. Vim stimulation C. GPi stimulation D. any of the above is a reasonable choice E. none of the above 339. Temozolomide is a novel chemotherapeutic agent approved for use in treating A. meningioma. B. glioblastoma multiforme. C. anaplastic astrocytoma. D. ependymomas. E. choroid plexus carcinoma 340. The H-reflex is most useful to assess A. polyneuropathy. B. cervical radiculopathy. C. myopathy. D. S1 radiculopathy. E. median nerve compression. 341. Which of the following is NOT a normal phenomenon in the aging neuron? A. lipofuscin accumulation B. Lewy bodies C. Marinesco bodies D. Alzheimer changes E. colloid inclusions 342. A patient is asked to close his or her eyes during the neurologic exam and the doctor places a key in the patient’s hand. The ability of the patient to tell what the object is depends on the integrity of which pathway? A. dorsal column B. spinospinal C. ventral spinocerebellar D. dorsal spinocerebellar E. spinothalamic 343. All of the following are true regarding intracranial pressure monitoring EXCEPT: A. Pressure gradients between left and right sides of the brain and supra- and infratentorial compartments may be present. B. The incidence of hemorrhage after insertion is about 1%. C. Irrigating the tubing decreases the contamination rate of ventricular catheters. D. Decreased intracranial compliance is suggested when the “b wavelet” is greater than the “a wavelet.” E. There is no clear consensus as to whether to use prophylactic antibiotics. 344. Which of the following is a FALSE statement regarding the corticospinal tract? A. In the pyramidal decussation, arm areas of cortex cross rostral to those that arise from leg areas. B. It receives contributions from somatomotor cortex, prefrontal regions, and parietal areas. C. Glutamate is present in cortical efferent fibers that project to the spinal cord. D. Leg fibers are lateral to arm fibers at most levels of this particular tract. E. Area 4 and postcentral gyrus fibers terminate in the same spinal cord lamina. 345. The middle cerebral artery supplies all of the following structures EXCEPT: A. inferior parietal lobule B. Broca’s area C. Wernicke’s area D. primary auditory cortex E. paracentral lobule 346. During a transcallosal approach to a tumor, the risk of left hemialexia is minimized by preserving A. the genu of the corpus callosum. B. the cingulate gyrus. C. the pericallosal artery. D. the splenium of the corpus callosum. E. none of the above 347. The clivoaxial angle is normally about A. 13 degrees. B. 30 degrees. C. 100 degrees. D. 130 degrees. E. 180 degrees. 348. The sensorimotor region is located in which part of the GPi? A. anteromedial B. anterolateral C. posteromedial D. posterolateral E. none of the above 349. The following lesion is resected from the lumbar spine. Which of the following statements is FALSE? A. The majority of these lesions arise from a ventral nerve root. B. Ten to 15% extend through the dural root sleeve. C. The fourth through sixth decades represent the peak incidence of occur rence. D. These masses are typically described as smooth, globoid, and do not pro duce enlargement of the nerve. E. They are suspended eccentrically from the nerve root with a discrete attachment. 350. Which of the following is particular to type I muscle fibers? A. anaerobic B. fast C. stain dark with ATPase at pH 9.4 D. found in red muscle E. have few mitochondria 351. Which of the following pathologic inclusions is intranuclear? A. Pick bodies B. Lewy bodies C. Cowdry type B bodies D. Bunina bodies E. Lafora bodies 352. All of the following tracts decussate EXCEPT: A. lateral spinothalamic B. ventral spinocerebellar C. ventral corticospinal D. dorsal spinocerebellar E. ventral spinothalamic 353. Which of the following is most accurate about Meniere’s disease? A. Nystagmus is horizontal and ipsilateral to the affected side. B. Nystagmus is vertical. C. Falling and past-pointing are contralateral. D. Nystagmus is contralateral to the affected side. E. none of the above 354. Which of the following thalamic nuclei has reciprocal connections with the inferior parietal lobule? A. pulvinar B. anterior nucleus C. centromedian nucleus D. VA nucleus E. VL nucleus 355. Visual-verbal disconnection syndrome is most likely to be seen with sectioning A. of the anterior commissure. B. of the hippocampal commissure. C. of the body of the corpus callosum. D. of the genu of the corpus callosum. E. of the splenium of the corpus callosum. 356. Pineal tumors usually displace the precentral cerebellar vein A. anterosuperiorly. B. posterosuperiorly. C. anteroinferiorly. D. posteroinferiorly. E. none of the above 357. Which of the following structures can be found two thirds of the way from the vomer to the foramen magnum? A. occipital condyle B. inion C. pharyngeal tubercle D. pituitary gland E. sphenoid sinus 358. Which of the following arteries supply choroid plexus? A. posterior inferior cerebellar artery B. posterior cerebral artery C. anterior choroidal artery D. all of the above E. none of the above 359. Platelet activation results in an increased affinity of the glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor for binding A. of fibrinogen. B. of thrombin. C. of factor V. D. of factor VIII. E. of factor X. 360. Which statement regarding hepatolenticular degeneration disease is FALSE? A. Serum ceruloplasmin is low. B. Urinary copper is increased. C. The gene locus is on chromosome 13. D. Inheritance is autosomal dominant. E. Early in the course of the disease, liver biopsy shows a high copper content. 361. Which of the following is FALSE regarding Bergmann glia? A. They serve as guides for migrating granular cell neurons during development. B. They have cell bodies located in the molecular layer of the cerebellar cortex. C. They undergo reactive gliosis adjacent to infarcts. D. They extend long cytoplasmic processes through the molecular layer to the subpial surface. E. They are inconspicuous until stimulated by local damage. 362. A 62-year-old male presents with cauda equina syndrome from a herniated disc. All of the following statements are true EXCEPT: A. signs are frequently unilateral B. classically involves spinal roots inferior to L3 C. may result in profound motor defects D. may result in urinary or fecal incontinence E. usually results in a Babinski sign 363. The vestibule contains A. the kinetic labyrinth. B. the ampullae. C. the static labyrinth. D. the cochlear duct. E. none of the above 364. The ipsilateral central tegmental tract gives projections to which nucleus of the thalamus? A. VA B. VL C. VPL D. VPM E. none of the above 365. A meningioma located at the lateral tentorial notch with major extension infratentorially would be best managed A. with a lateral suboccipital retrosigmoid approach. B. with a combined subtemporal presigmoid approach. C. with a infratentorial supracerebellar approach. D. with a suboccipital transtentorial approach. E. with none of the above approaches 366. Pineal calcifications are considered abnormal if encountered in patients younger than A. 6 years. B. 12 years. C. 18 years. D. 26 years. E. 30 years. 367. Which of the following ligaments is found between the anterior tubercle of the atlas and the dens? A. anterior longitudinal ligament B. posterior longitudinal ligament C. alar ligament D. transverse ligament E. none of the above 368. The most frequent site for a subependymoma is A. the third ventricle. B. the fourth ventricle. C. the left lateral ventricle. D. the right lateral ventricle. E. the septum pellucidum. 369. The lamina terminalis is continuous A. with the anterior commissure. B. with the fornix. C. with the splenium of the corpus callosum. D. with the mammillary body. E. with the pineal gland 370. Damage to Brodmann area 8 on the right results A. in both eyes being deviated to the right at rest. B. in both eyes being deviated to the left at rest. C. in the right eye being “down-and-out.” D. in the patient being unable to look upward. E. in both eyes being deviated upward. 371. Immunoreactivity to transthyretin and S-100 would most likely be seen A. in oligodendroglioma. B. in low-grade astrocytoma. C. in pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma. D. in choroid plexus papilloma. E. in schwannoma. 372. EEG activity becomes isoelectric at a cerebral blood flow A. of 7 mL/100 g/min. B. of 16 mL/100 g/min. C. of 30 mL/100 g/min. D. of 35 mL/100 g/min. E. of 45 mL/100 g/min. 373. All of the following are true regarding the lateral vestibulospinal tract EXCEPT: A. It arises from the ipsilateral Deiter’s nucleus. B. It is located in the lateral pontine tegmentum. C. It crosses the midline with medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) fibers. D. It facilitates extensor muscle tone in the antigravity muscles. E. It is found at all spinal cord levels. 374. Lesions of this thalamic nucleus are found in patients with Korsakoff’s amnestic state. A. anterior nucleus B. centromedian nucleus C. pulvinar D. VA E. mediodorsal nucleus 375. Before one transects the tentorium, which cranial nerve must be identified? A. III B. IV C. V D. VI E. VII 376. All the following statements regarding germ cell tumors are true EXCEPT: A. They are the most common pineal region neoplasm. B. They occur predominantly in males. C. They commonly occur at around age 40 and above. D. They are 5 to 10 times more likely in Japan. E. They are infiltrated by T-cell lymphocytes. 377. All of the following regarding CNS sarcoid are true EXCEPT: A. It is sensitive to steroids. B. It may mimic multiple sclerosis. C. It can involve cranial nerves. D. It is characterized pathologically by caseating granulomas. E. Leptomeningeal involvement is common. 378. Which of the following is the most frequent brain tumor in the first year of life? A. choroid plexus tumor B. gliosarcoma C. cystic astrocytoma D. oligodendroglioma E. glioblastoma multiforme 379. A “square” anterior cerebral artery (ACA) shift on a cerebral angiogram suggests that there may most likely be a mass in which area? A. frontal lobe B. temporal lobe C. parietal lobe D. occipital lobe E. basal ganglia 380. The motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve is located A. in the upper midbrain. B. in the lower midbrain. C. in the upper pons. D. in the middle pons. E. in the lower pons. 381. Circumventricular organs include all of the following EXCEPT: A. obex B. subcommissural organ C. median eminence D. organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis E. area postrema A. pericallosal B. anterior communicating C. posterior communicating D. middle cerebral E. superior hypophyseal 383. All of the following are true statements of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) EXCEPT: A. It is a branch of the vertebral artery. B. It supplies the vestibular nuclei in the medulla. C. It supplies the medial lemniscus in the medulla. D. It supplies the inferior cerebellar peduncle. E. It supplies the lateral spinothalamic tract. 384. The optic disk A. is located lateral to the fovea. B. contains myelinated axons from the retinal ganglion cell layer of the retina. C. contains only cones. D. all of the above E. none of the above 385. Which muscle is the border of the superior and inferior suboccipital triangles? A. rectus capitis posterior major B. superior obliquus capitis C. inferior obliquus capitis D. longissimus capitis E. none of the above 386. The key to translabyrinthine dissection is anatomic identification A. of the trigeminal nerve. B. of the abducens nerve. C. of the facial nerve. D. all of the above E. none of the above 387. All of the following are true of thoracic spine meningiomas EXCEPT: A. The great majority of spinal meningiomas occur in females. B. The most common presenting symptom is pain. C. Plain film calcification is often seen. D. Inversion recovery sequences and use of gadolinium increase detection sensitivity. E. Calcospheres may be seen. A. teres minor B. teres major C. latissimus dorsi D. subscapularis E. infraspinatus 389. Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE regarding radiation injury after stereotactic radiosurgery? A. Time of development is directly related to the rate of turnover of the cells. B. Cell loss after radiation occurs in connection with the cell division. C. Time of development is directly dependent on the radiation dose. D. Slowly proliferating tissue like CNS may take years to show the effects. E. It can be minimized with careful dose planning. 390. Inherited mitochondrial disorders include all of the following EXCEPT: A. Leigh’s disease B. MERFF C. MELAS D. Kearns-Sayre syndrome E. Kawasaki disease 391. Chromosomal alterations that are known to occur in tumors include all of the following EXCEPT: A. Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at 1p and 19q in oligodendrogliomas B. LOH at 22 in ependymomas C. LOH at 17 in astrocytomas D. Monosomy of 22 in ATRT E. Amplification of N-myc in glioblastoma 392. During routine preoperative screening for meningioma excision, the single greatest contraindication to surgery would be A. myocardial infarction within the last 6 months. B. age greater than 75. C. greater than five ventricular ectopic beats per minute. D. smoking more than one pack of cigarettes a day. E. being hepatitis C positive. 393. All of the following tracts pass through the inferior cerebellar peduncle EXCEPT: A. dorsal spinocerebellar B. cuneocerebellar C. fastigiovestibular D. olivocerebellar E. vestibulocerebellar 394. A lower altitudinal hemianopia is the result A. of unilateral destruction of the cuneus. B. of bilateral destruction of both cunei. C. of unilateral destruction of the lingual gyrus. D. of bilateral destruction of both lingual gyri. E. none of the above 395. During clipping of the following unruptured aneurysm, what is the best maneuver to minimize rupture? A. temporary clipping of the carotid in the neck B. lumbar drainage C. preoperative use of steroids D. keeping the patient intubated until surgery E. minimal retraction 396. The reasons for monitoring wave 5 during acoustic neuroma surgery include: A. It is an indication of the activity peripheral to the tumor. B. It is easier to detect than the other waves. C. Wave 5 is an accurate predictor of hearing postoperatively regardless of N1. D. all of the above E. none of the above 397. All of the following are true of multiple sclerosis EXCEPT: A. Axons are intact. B. Unidentified bright objects (UBOs) may be seen on MRI. C. Active lesions show contrast enhancement. D. Initial symptoms are referable to motor function. E. About 10% have a positive family history. 398. All of the following are structures of the circuit of Papez EXCEPT: A. anterior thalamus B. cingulated gyrus C. fornix D. hippocampus E. dorsomedial thalamus 399. The neurosurgeon accredited with developing modern-day stereotactic radiosurgery is A. M. Gazi Yasargil. B. Harvey Cushing. C. Lars Leksell. D. Walter Dandy. E. Wilder Penfield. 400. A nonfluent, expressive aphasia can result from damage to A. Brodmann area 40. B. Brodmann area 41. C. Brodmann area 42. D. Brodmann area 43. E. Brodmann area 44. 401. Elevated levels of N-acetyl aspartic acid in the urine and CSF is seen A. in adrenoleukodystrophy. B. in Canavan’s disease. C. in Alexander’s disease. D. in Krabbe’s disease. E. in metachromatic leukodystrophy. 402. The most commonly observed platelet dysfunction encountered in surgical patients A. is due to hemophilia A. B. is due to factor V deficiency. C. is due to aspirin. D. is due to heparin. E. is due to vitamin K deficiency. 403. All of the following are RNA viruses EXCEPT: A. poxvirus B. picornavirus C. paramyxovirus D. reovirus E. rhabdovirus 404. Hematoporphyrin derivative (HPD) is used A. in radiotherapy. B. in chemotherapy. C. in gene therapy. D. in photochemotherapy. E. none of the above 405. The most sensitive cranial nerve to radiation is A. I B. II C. III D. IV E. V 406. The mastoid emissary vein is a useful guide to approximate the location A. of the junction of the transverse and sigmoid sinuses. B. of the jugular bulb. C. of the AICA. D. all of the above E. none of the above 407. In the spinal cord, lamina 3 and 4 are also known as A. the substantia gelatinosa. B. the nucleus proprius. C. the zona intermedia. D. all of the above E. none of the above 408. The cerebellar glomerulus includes all of the following EXCEPT: A. mossy fiber terminal B. Golgi cell dendrite C. granule cell dendrite D. Purkinje cell E. Golgi cell axon terminal 409. The most common histologic feature detected as a late sign of radiation injury is A. cellular apoptosis. B. endothelial cell proliferation. C. demyelination of the nerve fibers. D. diffuse vasculitis. E. focal white matter necrosis. 410. Which spinal cord level has the most gray matter and the least white matter? A. cervical B. thoracic C. lumbar D. sacral E. none of the above 411. This disorder, resulting from a mutation of a signaling molecule (Notch3 on chromosome 19), leads to subcortical white matter ischemic damage. A. MERRF B. CADASIL C. MPS IV D. HHT E. VHL 412. The most common side effect of high-dose dexamethasone is A. hyperglycemia. B. psychosis. C. exacerbation of peptic ulcer. D. aseptic necrosis. E. skin rash. 413. All of the following regarding cryptococcal meningitis is true EXCEPT: A. Patients rarely complain of headache. B. Nausea, vomiting, mental status changes, and cranial nerve palsies are features. C. It is caused by an encapsulated budding yeast. D. In some communities, it is more common than toxoplasmosis as a cause of presenting neurologic illness associated with HIV infection. E. Infection occurs by the inhalation of organisms resulting in a primary pulmonary focus of infection. 414. What percentage of cerebrospinal fluid leaks from basilar skull fractures will resolve spontaneously? A. 5% B. 25% C. 45% D. 65% E. 85% A. PRL. B. ACTH. C. TSH. D. all of the above E. none of the above 416. During the caloric test, the superior vestibular nerve constitutes the main afferent A. from the superior semicircular canal. B. from the lateral semicircular canal. C. from the posterior semicircular canal. D. all of the above E. none of the above 417. The inferior orbital fissure is mainly formed A. by the sphenoid bone only. B. by the sphenoid and ethmoid bones. C. by the zygomatic and palatine bones. D. by the sphenoid and maxilla. E. none of the above 418. Many spinocerebellar fibers are distributed A. to the medial vermal region of the anterior lobe. B. to the lateral region of anterior lobe. C. to the medial vermal region of posterior lobe. D. to the lateral region of posterior lobe. E. none of the above 419. Which of the following is NOT an indication for stereotactic radiosurgery? A. cerebral arteriovenous malformation B. metastatic tumor from non–small-cell lung carcinoma C. 1.0 cm acoustic schwannoma limited to the IAC D. 1.5 cm petrous apex meningioma not distorting the brainstem E. 1.0 cm aneurysm at the top of basilar artery A. Initial symptoms present between the ages of 20 and 40 years. B. It may cause longstanding ventriculitis. C. It is associated with midline fusion defect. D. It demonstrates linear growth. E. The surgeon must avoid spillage of tumor contents in the subarachnoid space. 421. All of the following disorders are autosomal recessive EXCEPT: A. maple syrup urine disease B. adrenoleukodystrophy C. Wilson’s disease D. Refsum’s disease E. homocystinuria 422. In cerebral salt wasting syndrome, patients are usually A. hypervolemic and hypernatremic. B. hypervolemic and hyponatremic. C. hypovolemic and hypernatremic. D. hypovolemic and hyponatremic. E. none of the above 423. All of the following are true of toxoplasmosis EXCEPT: A. It is the most common cause of intracerebral mass associated with HIV infection when CD4 counts fall below 100/mm3. B. Chorea in a patient with AIDS may be pathognomonic of toxoplasmosis. C. Radiographic images show an asymmetric target sign. D. The presenting neurologic symptom is nonfocal and superimposed on a global encephalopathy. E. Therapy includes pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine. 424. The fracture that initiates a leptomeningeal cyst most commonly involves A. the frontal bone. B. the sphenoid bone. C. the temporal bone. D. the parietal bone. E. the occipital bone. 425. Which of the following medical therapies for pituitary tumors is known for its side effect of gallstone formation? A. bromocriptine B. GnRH agonists C. octreotide D. all of the above E. none of the above 426. Which of the following are reasonable criteria for recommending patients for stereotactic surgery for acoustic neuroma? A. The patient is elderly with a medium-sized tumor. B. The patient has recently been hospitalized and is on two heart medications and a water pill. C. The tumor is on the side of the patient’s only hearing ear. D. all of the above E. none of the above 427. Bill’s bar is a bony protuberance that separates A. the facial and superior vestibular nerves. B. the facial and inferior vestibular nerves. C. the acoustic and superior vestibular nerves. D. the acoustic and inferior vestibular nerves. E. none of the above 428. Which of the following persistent circulations is the most common? A. trigeminal artery B. otic artery C. hypoglossal artery D. proatlantal intersegmental artery E. fetal posterior communicating artery A. audiogram with pure tones and speech reception B. counseling regarding the options of surgery or radiosurgery. C. workup for a planned craniotomy D. consent for angiography and possible embolization E. observation 430. An upper homonymous quadrantanopsia is most likely to arise from a lesion A. to the ipsilateral parietal lobe. B. to the contralateral parietal lobe. C. to the ipsilateral temporal lobe. D. to the contralateral temporal lobe. E. to the occipital cortex. 431. The following neurogenetic diseases display trinucleotide repeat EXCEPT: A. fragile X syndrome B. myotonic dystrophy C. olivopontocerebellar atrophy D. Huntington’s disease E. Machado-Joseph disease 432. A patient approaching local anesthetic overdose will typically complain A. of chest tightening. B. of lightheadedness. C. of tingling around the mouth. D. of shortness of breath. E. of nothing. A. There is progressive attenuation of the cerebellar and premotor areas, but no change of activity in the primary motor cortex. B. There is progressive attenuation of the cerebellar, but no change in the premotor and primary motor cortices. C. There is no change in the cerebellar, but progressive attenuation of the premotor and primary motor cortices. D. There is no change in the cerebellar and premotor cortices, but progressive attenuation of the primary motor cortex. E. There is no change in activity of the cerebellar, premotor, or primary motor cortex. 434. All of the following are true of extradural hematomas EXCEPT: A. They can appear crescentic. B. The lucid interval is seen in ~80% of patients. C. A dry eye postoperatively is from traction injury of a nerve. D. Outcome correlates well with the clinical state prior to surgery. E. Poor outcome is correlated with delay in surgery. 435. Major indications for craniotomy for pituitary tumors is/are A. tumor extension into the middle fossae. B. a dumbbell-shaped tumor with constriction in the middle. C. a tumor claimed to be fibrous on previous transphenoidal resection. D. all of the above E. none of the above 436. An Auditory Brainstem Implant (ABI) is most useful during tumor removal when placed A. in the third ventricle. B. in the jugular vein. C. in the lateral recess of the fourth ventricle. D. in the lumbar cistern. E. none of the above 437. The nerve that innervates the rhomboids and levator scapula arises from which segment of the brachial plexus? A. root B. trunk C. division D. cord E. branch 438. Which of the following conditions is associated with neurofibrillary tangles? A. Alzheimer’s disease B. Down syndrome C. progressive supranuclear palsy D. SSPE E. all of the above 439. A patient has a subarachnoid hemorrhage from the aneurysm shown here. During surgery via right craniotomy, what part of normal brain may be removed to gain better visualization of the aneurysm? A. temporal tip B. the area lateral to cranial nerve I C. right-sided inferior frontal gyrus D. all of the above E. none of the above 440. The ophthalmic artery pierces the dura to enter the orbit near A. the anterior clinoid process. B. the oculomotor nerve. C. the optic strut. D. the trochlear nerve. E. the vomer. 441. The cuneus lies between which sulci? A. sulcus cinguli and parieto-occipital sulcus B. calcarine and cingulate C. sylvian and calcarine D. parieto-occipital and calcarine E. none of the above 442. Regarding cerebral aneurysms, which of the following statements is FALSE? A. Oxyhemoglobin and bilirubin are the agents likely producing the meningeal response. B. The size of an intracerebral hematoma is directly related to the chance of the patient developing vasospasm. C. Only ~1% of cerebral aneurysms results in subdural bleeding. D. It has a single layer of endothelium. E. The most important factor in assessing bleeding risk is the temporal relationship to the previous bleed. 443. Volatile anesthetics A. reduce cerebral metabolic rate (CMR) and increase cerebral blood flow (CBF). B. reduce CMR and CBF. C. increase CMR and CBF. D. increase CMR and reduce CBF. E. have no effect on CMR and increase CBF. 444. Prolonged ulnar and median F response latencies could represent a conduction block A. in the upper trunk. B. in the upper and middle trunk. C. in the middle trunk. D. in the middle and lower trunk. E. in the lower trunk. 445. An abnormal skin histamine response is a characteristic feature A. of Horner’s syndrome. B. of Frey’s syndrome. C. of Chagas’ disease. D. of Familial dysautonomia. E. none of the above 446. Which foramen of the cranial base is situated at the junction of the occipital and temporal bone? A. foramen ovale B. foramen magnum C. jugular foramen D. all of the above E. none of the above 447. Which tract is a projection from the habenula? A. diagonal band of Broca B. fasciculus retroflexus C. ansa lenticularis D. lenticular fasciculus E. none of the above 448. Which of the following is/are true of microaneurysms? A. They form as part of normal aging but are not affected by hypertension. B. They form as part of normal aging and are accentuated by hypertension. C. They are not part of the normal aging process and are not affected by hypertension. D. They are not part of normal aging and are accentuated by hypertension. E. none of the above 449. A contrast enhanced, axial, T1-weighted MRI scan of a 56-year-old male is shown here. The most likely symptoms he might have are A. dizziness, ataxia, balance problems. B. expressive aphasia with positive Romberg’s sign. C. tinnitus and reduced hearing in right ear with frequent falling. D. ptosis of the right eye with weakness of external ocular muscles. E. weakness in the right side of body especially in the upper limbs. 450. Which artery is most closely associated with cranial nerves VII and VIII? A. superior cerebellar artery B. basilar artery C. AICA D. PICA E. vertebral artery 451. The medulla includes all of the following structures EXCEPT: A. olive B. tuberculum cinereum C. vagal trigone D. facial colliculus E. origin of the glossopharyngeal nerve 452. Regarding vascular malformations, which of the following statements is FALSE? A. Arteriovenous malformations can contain neural parenchyma. B. Calcification is common in cavernous malformations. C. Hemosiderin-laden macrophages are common in venous malformations. D. Capillary malformations do not show progressive growth. E. Early angiographic filling is seen with AVMs. 453. In a patient with subarachnoid hemorrhage, calcium channel blocking agents can be expected to have a A. beneficial effect, improve angiographic vasospasm, and increase CBF. B. beneficial effect, improve angiographic vasospasm. C. beneficial effect. D. detrimental effect. E. detrimental effect and decrease CBF. 454. The anatomy of PICA is such that important branches to the deep cerebellar nuclei leave the vessel at the top of the cranial loop. The name of this point and the segment of PICA it arises from are A. the plexal point, tonsillomedullary segment. B. the choroidal point, tonsillomedullary segment. C. the plexal point, telovelotonsillar segment. D. the choroidal point, telovelotonsillar segment. E. none of the above 455. The principal neuroanatomical substrate of perceptual organization is A. the anterior right hemisphere. B. the posterior right hemisphere. C. the anterior left hemisphere. D. the posterior left hemisphere. E. none of the above 456. The sigmoid sinus and the superior petrosal sinuses are boundaries A. of Trautmann’s triangle. B. of Parkinson’s triangle. C. of Wernicke’s triangle. D. of Labbé’s triangle. E. of Calot’s triangle. 457. The lateral lemnisci are connected A. by the trapezoid body. B. by the commissure of Probst. C. by the juxtarestiform body. D. all of the above E. none of the above 458. A solid, contrast-enhancing mass of the third ventricle that stains intensely for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is most likely a A. choroid plexus tumor. B. colloid cyst. C. central neurocytoma. D. choroid glioma. E. glioblastoma multiforme. 459. One of the contradictions of stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of metastatic tumors is A. three tumors, each measuring 1 to 1.5 cm within the right hemisphere. B. solitary left parietal tumor measuring 2 cm ˇ 2 cm ˇ 1.8 cm. C. a 2.5-cm left mesial temporal tumor with clinical signs of impending herniation. D. tumors both in the supratentorial and infratentorial compartments. E. None of the above are contraindications. 460. The sphenoparietal sinus can be found A. at the outer aspect of the lesser wing of the sphenoid. B. at the inner aspect of the lesser wing of the sphenoid. C. at the outer aspect of the greater wing of the sphenoid. D. at the inner aspect of the greater wing of the sphenoid. E. at the cavernous sinus. 461. The precuneus (area 7) can be found A. on the lateral aspect of the frontal lobe. B. on the medial aspect of the frontal lobe. C. on the lateral aspect of the occipital lobe. D. on the medial aspect of the occipital lobe. E. on the medial aspect of the parietal lobe. 462. The most common vascular malformation is A. capillary telangiectasia. B. venous malformation. C. arteriovenous malformation. D. cavernous malformation. E. dural arteriovenous fistula. 463. The anterior meningeal artery typically arises A. from the ophthalmic artery. B. from the maxillary artery. C. from the middle meningeal artery. D. from the occipital artery. E. from the facial artery. 464. The caudal anterior limb of the internal capsule is supplied A. by the middle cerebral artery. B. by the internal cerebral artery. C. by the recurrent artery of Heubner. D. by the posterior communicating artery. E. none of the above 465. The external urethral sphincter is composed mainly of _______ fibers arranged in a _______ fashion. A. type I, longitudinal B. type II, longitudinal C. type I, circular D. type II, circular E. none of the above 466. Regarding atlanto-occipital dislocation all of the following are true EXCEPT: A. It should be suspected in a multitrauma victim with mandibular fractures and submental lacerations. B. Prevertebral soft tissue swelling may be the only clue to its diagnosis. C. The gap between the occipital condyles and condylar surface of the atlas is greater than 5 mm. D. The distance between the tip of the dens and basion is less than 12 mm. E. The clivus line is not tangential to the odontoid. 467. The action potential in the neuron is initiated A. at the dendrite. B. at the soma. C. at the hillock. D. at the node of Ranvier. E. at the axon terminal. 468. Which of the following conditions is most often associated with chronic temporal lobe epilepsy? A. pilocytic astrocytoma B. ganglioglioma C. DNET D. astrocytoma E. pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma 469. Which of the following is NOT a functional indication for stereotactic radiosurgery? A. trigeminal neuralgia refractory to medication B. glossopharyngeal neuralgia in a patient with carbamazepine hypersensitivity. C. unilateral essential tremors refractory to medication D. Parkinson’s tremor in the left upper extremity with levodopa-induced dyskinesias E. Huntington’s chorea 470. Regarding the venous drainage of the insula, which of the following statements is true? A. The entire insula drains to the deep venous system. B. The entire insula drains to the superficial venous system. C. The anterior portion of the insula drains to the deep system. D. The posterior portion of the insula drains to the superficial system. E. none of the above 471. Which of the following separates the anterior cerebellar lobe from the posterior cerebellar lobe? A. posterolateral fissure B. horizontal fissure C. dorsolateral fissure D. primary fissure E. postlunate fissure 472. Regarding spinal vascular malformations, which of the following is FALSE? A. Dural arteriovenous fistulas are believed to be acquired. B. Normal neural parenchyma is seen within juvenile AVMs. C. Glomus AVMs may have associated aneurysms. D. Acute progression is most likely due to venous congestion. E. Dural AV fistulas have a female predilection. 473. The ischemic penumbra has a cerebral blood flow A. of 1 to 8 mL/100 g/min. B. of 8 to 23 mL/100 g/min. C. of 23 to 30 mL/100 g/min. D. of 30 to 40 mL/100 g/min. E. of 40 to 50 mL/100 g/min. 474. What is the area interposed between the lenticular fasciculus and the thalamic fasciculus? A. substantia nigra B. pedunculopontine nucleus C. zona incerta D. subthalamic nucleus E. none of the above 475. Which of the following areas modulate control of micturition? A. medial parts of the frontal lobes B. preoptic region of the hypothalamus C. basal ganglia D. all of the above E. none of the above 476. The juxtarestiform body is ______ to the ______ cerebellar peduncle. A. lateral, inferior B. lateral, superior C. medial, inferior D. medial, superior E. none of the above 477. The flower spray ending is associated with which nerve type? A. IA B. IB C. II D. III E. IV 478. When performing a caudalis rhizotomy, which tract is penetrated to access the target? A. ventral spinocerebellar tract B. dorsal spinocerebellar tract C. gracile fasciculus D. cuneate fasciculus E. none of the above 479. The arterial dicrotic notch A. has no corresponding area in the intracranial pressure (ICP) waveform. B. corresponds to the area between P1 and P2 of the ICP waveform. C. corresponds to the area between P2 and P3 of the ICP waveform. D. corresponds to the area after P3 of the ICP waveform. E. none of the above 480. The basal vein of Rosenthal begins at this area on the base of the brain. A. anterior perforated substance B. posterior perforated substance C. tuber cinereum D. medial geniculate body E. lateral geniculate body 481. The calcified glomus of the choroid plexus seen on CT is most often found A. in the frontal horn. B. in the third ventricle. C. in the trigone. D. in the occipital horn. E. in the foramen of Monro. 482. Decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles occurs in which area of the brain? A. cerebellum B. rostral midbrain C. rostral pons D. caudal midbrain E. caudal pons 483. Cranial nerves IX, X, and XI are supplied A. by the superior thyroid artery. B. by the ascending pharyngeal artery. C. by the lingual artery. D. by the facial artery. E. by the occipital artery. 484. Attempted lateral gaze where there is destruction of the abducens nucleus results A. in ipsilateral lateral and medial rectus palsies. B. in ipsilateral lateral and contralateral medial rectus palsies. C. in contralateral lateral and ipsilateral medial rectus palsies. D. in contralateral lateral and medial rectus palsies. E. none of the above 485. Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) is most useful to monitor the function A. of the medial lemniscus. B. of the lateral lemniscus. C. of the corticospinal tracts. D. all of the above E. none of the above 486. The lateral subnucleus of cranial nerve III innervates A. the inferior rectus. B. the inferior oblique. C. the medial rectus. D. all of the above E. none of the above 487. Deep pressure and joint position is localized to Brodmann’s area A. 3a. B. 3b. C. 2. D. 1. E. none of the above 488. Which of the following is the least consistent feature of conus syndrome? A. symmetric involvement B. pain C. saddle anesthesia D. bladder and bowel symptoms E. sudden onset 489. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors most commonly affect cranial nerve A. III. B. IV. C. V. D. VI. E. VII. 490. The superior ophthalmic vein courses most closely with which cranial nerves? A. IV (trochlear) and V (trigeminal) B. III (oculomotor) and IV C. III and II (optic) D. V and VI (abducens) E. II and IV 491. The caudate nucleus forms A. the medial wall of the frontal horn. B. the floor of the temporal horn. C. the lateral wall of the occipital horn. D. the roof of the lateral ventricle. E. none of the above 492. Which of the following is true regarding the dorsal trigeminothalamic tract? A. It arises from the principal sensory nucleus of V. B. It terminates on the VPM thalamus. C. It conveys touch and pressure information from the face. D. It is an uncrossed tract. E. All of the above 493. Valveless emissary veins are found in which layer of the scalp? A. skin B. subcutaneous tissue C. galea D. loose areolar tissue E. periosteum 494. Apocrine sweat glands in the axilla are innervated by what type of fibers? A. adrenergic fibers B. cholinergic fibers C. nitric oxide D. VIP E. none of the above 495. The greatest decline in water content of the nucleus pulposus occurs A. just after birth. B. in childhood. C. in adolescence. D. in young adulthood. E. in late adulthood. 496. The tapeta are fibers A. from the claustrum. B. from the globus pallidus. C. from the corpus callosum. D. from the thalamus. E. none of the above 497. Dressing apraxia is most often described with lesions A. of the dominant frontal lobe. B. of the nondominant frontal lobe. C. of the dominant parietal lobe. D. of the nondominant parietal lobe. E. none of the above 498. Cerebrospinal fluid is reabsorbed into the bloodstream A. through the valveless arachnoid villi. B. through the pressure insensitive valves of the arachnoid villi. C. through the pressure sensitive one-way valves of the arachnoid villi. D. through the pressure insensitive valveless arachnoid villi. E. none of the above A. CLIP. B. Beta-lipotropin. C. Alpha-MSH. D. POMC. E. none of the above 500. Regarding myasthenia gravis (MG), which of the following statements is FALSE? A. It involves autoantibodies directed against acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. B. The prevalence is between 1 in 10,000 and in 15,000. C. Juvenile MG is more common in Asians. D. There is an increased incidence of an underlying thymoma in late-onset MG. E. Late-onset MG is more common in females. 501. The internal carotid artery (ICA) enters the cranium via a canal formed A. by the sphenoid bone. B. by the occipital bone. C. by the sphenoid and temporal bones. D. by the temporal bone. E. by the temporal and occipital bones. 502. All of the following are true of the trochlear nerve EXCEPT: A. It has a nucleus located in the midbrain tegmentum at the level of the inferior colliculus. B. It decussates in the superior medullary velum. C. It exits the brainstem from the dorsal surface. D. It courses lateral to the frenulum of the superior medullary velum. E. Damage to the nucleus results in dysfunction of the superior oblique muscle on that side. 503. The asterion is located at the intersection A. of the lambdoid, occipitomastoid, and parietomastoid sutures. B. of the lamboid, sagittal, and occipitomastoid sutures. C. of the lambdoid, sagittal and parietomastoid sutures. D. of the sagittal and occipitomastoid sutures. E. none of the above 504. Which nucleus of the hypothalamus is involved with the dissipation of heat? A. posterior nucleus B. ventromedial nucleus C. lateral nucleus D. anterior nucleus E. none of the above 505. Which of the following joints lack an intervertebral disc? A. occipitoatlantal joint B. atlantoaxial joint C. sacrum D. all of the above E. none of the above 506. The diagnosis of syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) is made by the following observations EXCEPT: A. serum sodium <135 mEq/L B. serum osmolarity <280 mOsm/L C. hypervolemia D. urine sodium >20 mmol/24 h E. urine osmolarity > serum osmolarity 507. Which of the following congenital conditions results in a deficit in abduction of the eye resulting from failure of development of motoneurons in the sixth nerve nucleus? A. Marcus Gunn syndrome B. Joubert’s syndrome C. De Morsier’s syndrome D. Duane’s syndrome E. none of the above 508. Dilantin levels are increased by all of the following EXCEPT: A. cimetidine B. coumadin C. carbamazepine D. isoniazid E. sulfa drugs 509. Which of the following fiber tracts end as climbing fibers? A. olivocerebellar B. reticulocerebellar C. pontocerebellar D. all of the above E. none of the above 510. The most relevant factor in assessing prognosis of paraganglioma patients is A. tumor location. B. tumor size. C. time to surgery. D. response to chemotherapy and radiation. E. none of the above 511. The anteromedial middle fossa triangle is defined by cranial nerves A. IV and V1. B. V1 and V2. C. V2 and V3. D. V3 and VI. E. none of the above 512. Hyperperfusion encephalopathy most commonly involves which part of the brain? A. subcortical white matter of the occipital lobes bilaterally with little to no edema B. subcortical white matter of the occipital lobes bilaterally with edema C. the cortical ribbon of the parietal lobes bilaterally D. the cortical ribbon and subcortical white matter bilaterally E. the cortical ribbon with sparing of the subcortical U-fibers 513. Glasscock’s triangle is defined by the posterior border of V3 and which foramina? A. foramen ovale and spinosum B. foramen ovale and rotundum C. foramen rotundum and spinosum D. foramen spinosum and lacerum E. foramen lacerum and ovale 514. Which of the following is FALSE regarding hyperperfusion encephalopathy? A. The vast majority of patients recover completely. B. The edema tends to resorb completely. C. The vertebrobasilar system is vulnerable due to extensive sympathetic innervation. D. A similar condition may occur after a carotid endarterectomy. E. Patients with hyperperfusion encephalopathies often have labile blood pressures. 515. All of the following are correct statements about the central sulcus EXCEPT: A. It separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe. B. It separates the motor cortex from the sensory cortex. C. It extends into the paracentral lobule. D. It is usually continuous with the lateral sulcus. E. It is located on the lateral convex surface of the hemisphere. 516. Which of the following is NOT a feature of migraine headaches? A. normal intraocular pressure B. ipsilateral flushing C. decreased local skin temperature D. female predominance E. no aura is seen with common migraines. A. Anton’s syndrome. B. Adie’s syndrome. C. Cogan’s syndrome. D. Vernet’s syndrome. E. Balint’s syndrome. 518. During a selective amygdalohippocampectomy for intractable seizures, the surgeon must be aware that the most medial part of the amygdala is in close proximity A. to the basal ganglia. B. to the anterior commissure. C. to the caudate nucleus. D. all of the above E. none of the above 519. The anterior choroidal artery usually runs _____ to the posterior communicating artery, and _____ to the optic tract. A. lateral, parallel B. medial, parallel C. lateral, perpendicular D. medial, perpendicular E. none of the above 520. Which of the following muscles is a medial rotator of the thigh? A. piriformis B. obturator internus C. quadratus femoris D. gluteus minimus E. gluteus maximus 521. Lewy bodies may be seen in all the following EXCEPT: A. Parkinson’s disease B. Shy-Drager syndrome C. multiple system atrophy (MSA) D. diffuse Lewy body dementia E. paralysis agitans 522. The largest contributor to the internal cerebral vein is A. the septal vein. B. the thalamostriate vein. C. the caudate vein. D. the basal vein of Rosenthal. E. the vein of Galen. A. anterior to the target. B. posterior to the target. C. medial to the target. D. lateral to the target. E. close to the target. 524. Deficiencies of complement components C5 and C6-C9 predispose A. to Streptococcus pneumoniae. B. to Haemophilus influenzae. C. to Neisseria meningitidis. D. to Proteus. E. none of the above 525. Meningiomas of the ventricular system are most frequently located A. at the body. B. at the trigone. C. at the temporal horn. D. at the occipital horn. E. at the frontal horn. 526. In patients with multiple cerebral metastases, the most important determinant of survival is A. the size of the largest metastasis. B. the extent of systemic disease. C. the number of visible metastases on MRI. D. the neurologic condition preoperatively. E. the proximity to eloquent cortex. 527. Sensory axons that transmit information from the Golgi tendon organs are A. Ia (A-α). B. Ib (A-α). C. II (A-β). D. III (A-δ). E. IV (C). 528. The vast majority of spinal epidural abscesses can be best described as A. caused by staphylococci, and occur in the cervical cord. B. caused by streptococci, and occur in the cervical cord. C. caused by staphylococci, and occur in the thoracic cord. D. caused by streptococci, and occur in the thoracic cord. E. caused by staphylococci, and occur in the lumbar cord. 529. With regard to shunt infections, which of the following is FALSE? A. Staphylococcus is the organism implicated in a majority of cases. B. Symptoms include shunt failure, headache, nausea, and vomiting. C. Elevated temperature is a more reliable sign of infection in VA as opposed to VP shunts. D. There is a greater risk of shunt infection with distal revision than proximal revision. E. Staphylococcus infections may cause obstruction without fever. 530. Which of the following is the most common type of tumor arising in the sella following irradiation for pituitary adenoma? A. liposarcoma B. fibrosarcoma C. angiosarcoma D. chondrosarcoma E. osteosarcoma 531. Dopamine loss in Parkinson’s disease is believed to lead A. to disinhibition of the subthalamic nucleus. B. to high activity of Gpi/SNr. C. to inhibition of the motor thalamus. D. all of the above E. none of the above 532. Which of the following is true regarding the etiology of postoperative diabetes insipidus? A. It is due to disruption of the pituitary stalk. B. There is degeneration of distal axons in the region of dissection. C. Stored ADH is depleted. D. All of the above E. None of the above 533. Which of the following parasites present with cord compression in infected patients? A. strongyloides B. schistosomiasis C. paragonimiasis D. neurocysticercosis E. echinococcus 534. The mediodorsal nucleus of the thalamus is reciprocally connected A. to the cingulated gyrus. B. to the prefrontal cortex. C. to the substantia nigra. D. to the lateral lemniscus. E. to the inferior parietal lobule. 535. Lymphoma metastatic to the brain tends to localize A. to the subependymal. B. to the gray-white junction. C. to the meninges. D. to the frontal lobe. E. to the corpus callosum. 536. In developing an interforniceal plane for resection of an anterior third ventricular tumor, the surgeon must be most cognizant of what structure in the posterior component of the forniceal structure? A. anterior commissure B. posterior commissure C. hippocampal commissure D. all of the above E. none of the above 537. All the following are true of the centromedian nucleus of the thalamus EXCEPT: A. It is the largest of the intralaminar nuclei. B. It receives input from the globus pallidus. C. It projects to the striatum. D. It projects diffusely to the entire neocortex. E. It is reciprocally connected to areas 41 and 42. 538. The stylomastoid foramen is located _____ to the insertion of the _______ belly of the digastric muscle. A. medial, anterior B. medial, posterior C. lateral, anterior D. lateral, posterior E. none of the above 539. Mutism following transcallosal surgery may be the result A. of division of the anterior corpus callosum. B. of retraction on the fornix. C. of circulatory disturbance in the SMA. D. all of the above E. none of the above 540. Which of the following are sources of input to the red nucleus? A. dentate nucleus B. globose nucleus C. emboliform nucleus D. all of the above E. none of the above 541. Which of the following is a noncompetitive alpha-blocker? A. phentolamine B. atropine C. phenylephrine D. amphetamine E. phenoxybenzamine 542. All of the following are true statements regarding the cerebral metabolic rate (CMRO2) EXCEPT: A. Forty percent of the energy consumed is for maintenance of ionic gradients. B. Once EEG silence is induced, barbiturates will not produce further reductions in (CMRO2). C. Once EEG silence is induced, temperature reduction does produce further reductions in (CMRO2). D. Normal rate is ~5.5 mL/100 g/min. E. Ketamine anesthesia decreases CMRO2. 543. The globus pallidus projects to which thalamic nuclei? A. centromedian B. ventral anterior C. ventral lateral D. all of the above E. none of the above 544. The major blood supply to the tumor shown here is A. from the posterior cerebral artery. B. from the posterior choroidal artery. C. from the middle cerebral artery. D. from the anterior choroidal artery. E. none of the above 545. Preoperative testing for the tumor shown here should include which of the following? A. α-fetoprotein B. β-HCG C. CBC, PT, PTT D. all of the above E. none of the above 546. The most medial fibers in the crus cerebri are A. frontopontine. B. corticobulbar. C. corticospinal. D. parietopontine. E. none of the above 547. A 45-year-old woman is brought into the urgent care center after being involved in a motor vehicle accident while driving home with her husband. Her husband was ejected from the car from the force of the impact and did not survive. On initial exam her eyes open to pain, and she mumbles only sounds. She localizes on the right arm, withdraws on the left side and the right leg is not examined due to the possibility of a fracture. The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of this case is A. 11. B. 10. C. 9. D. 8. E. 7. For the MRI scans in questions 548 to 550, choose the most likely diagnosis: A. Meningioma B. Hemangiopericytoma C. Ewing’s sarcoma D. Sinonasal carcinoma metastases E. Breast carcinoma metastases 548. 549. 551. Relative contraindications for surgery for spinal metastasis include all of the following EXCEPT: A. multiple myeloma B. recurrence after maximal radiation C. multiple lesions at multiple levels D. total paralysis for greater than 24 hours E. expected survival less than 4 months 552. The usual radiation dose for spinal epidural metastasis is: A. 20 Gy in 2-Gy fractions over 10 days. B. 30 Gy in 3-Gy fractions over 10 days. C. 60 Gy in 6-Gy fractions over 10 days. D. 100 Gy in 10-Gy fractions over 10 days. E. 200 Gy in 50-Gy fractions over 30 days. For the findings in questions 553 to 556, choose the correct toxins: A. Tetanus B. Botulism C. Diphtheria D. Reye’s syndrome 553. Predilection to sensory and motor nerves of the limbs and ciliary muscle/nerve 554. Risus sardonicus 555. Initial symptom is usually difficulty in convergence of the eyes. 556. Encephalopathy typically develops 4 to 7 days after the onset of the illness. 557. Which statement is true about the presentation of multiple myeloma in the spine? A. Hypocalcemia occurs in 25% of patients. B. Bone pain is characteristic at rest and with movement. C. Occurrence of amyloidosis. D. Invasion of the spinal canal occurs in over 50% of patients. E. Definitive diagnosis can be made by plain x-ray. 558. Criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma include all of the following EXCEPT: A. biopsy-proven plasmacytoma. B. myeloma cells in a single peripheral blood smear. C. plasma cells greater than 10 of 1000 cells on marrow morphology. D. radiographic survey demonstrating lytic lesions. E. monoclonal immunoglobulins in the urine or blood. 559. The Batson’s plexus route of spinal metastases represents which type of spread? A. perinervous B. arterial C. venous D. direct extension E. none of the above For the diseases in questions 560 to 564, choose the correct chromosomal abnormality: A. 5q B. 5p C. 4 D. 9 E. none of the above 560. Landouzy-Dejerine 561. Werdnig-Hoffman 562. Myotonic muscular dystrophy 563. Cri-du-chat 564. Friedreich’s ataxia For the statements in questions 565 to 569, choose the answer option that is correct. A. verapamil B. diltiazem C. digoxin D. procainamide E. esmolol 565. Preferred agent for patients with systolic heart failure 566. Side effects of hypotension and negative inotropic effect 567. Indicated for chronic rate control of atrial fibrillation 568. Contraindicated in patients with prolonged Q-T interval 569. Indicated for rate control of atrial fibrillation in the setting of a hyperadrenergic state 570. A 56-year-old woman just had a large frontal tumor resected. The tumor was positive for reticulin on immunostaining. The tumor histology contained mitotic figures as well as necrosis and pseudopalisading. The most likely diagnosis is A. ganglioglioma. B. gliosarcoma. C. glioblastoma multiforme. D. gliomatosis cerebri. E. germinoma. 571. Which of the following is true regarding management of the injury shown here? A. Those with mild neurologic deficits and accessible lesions are better managed by repair than ligation. B. Proximal occlusion may be accomplished by an anterior approach with mobilization of the sternocleidomastoid. C. Endovascular embolization with detachable balloons may be used for management. D. All of the above are true. E. None of the above is true. For the syndromes in questions 572 to 577, choose the corresponding metal. A. Mercury B. Manganese C. Arsenic D. Aluminum E. Lead 572. Peripheral neuropathy, malaise, nausea, and vomiting 573. Encephalitis in children 574. Rigidity, bradykinesia 575. Irritability, seizures, ataxia, coma 576. Peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, renal tubular necrosis 577. Mimics the deficit of cortical cholinergic neurotransmission seen in Alzheimer’s 578. Out of the following choices, which represents the most common source of arterial embolus? A. left atrium B. left ventricle C. pulmonary veins D. aorta E. ventricular aneurysms 579. Potassium depletion would MOST likely result from which of the following diseases? A. diabetic ketoacidosis B. Cushing’s syndrome C. high intestinal obstruction D. diarrhea E. uremia 580. Which of the following is the first sign of hypomagnesemia? A. seizures B. tetany C. hypotension D. loss of deep tendon reflexes E. stupor 581. All the following are appropriate concentrations of ions in Ringer’s lactate solution EXCEPT: A. Na+ 130 mEq/L B. Cl· 109 mEq/L C. Lactate 28 mEq/L D. Ca2+ 16 mEq/L E. K+ 4 mEq/L 582. All of the following statements are associated with the type of tumor exemplified by this MRI scan EXCEPT: A. The male-to-female ratio is 1.5:1. B. The thoracic location is most common. C. It is usually low grade. D. It is the most common intramedullary tumor in children. E. Examination may reveal a combination of upper and lower motor neuron signs. For the disorders in questions 583 to 585, choose the disease option that is correct: A. amyotrophic lateral sclerosis B. systemic lupus erythematosus C. metachromatic leukodystrophy D. Lesch-Nyhan disease E. Niemann-Pick disease 583. Arylsulfatase A deficiency 584. Superoxide dismutase mutation 585. HGPRT deficiency For the diseases in questions 586 to 590, choose the serum level option that is correct. A. increased calcium, normal phosphate, and increased alkaline phosphatase B. decreased calcium, increased phosphate, and normal alkaline phosphatase C. decreased calcium, decreased phosphate, and increased alkaline phosphatase D. normal calcium, normal phosphate, and increased alkaline phosphatase 586. Rickets 587. Paget’s disease 588. Hyperparathyroidism 589. Primary osteoporosis 590. Hypoparathyroidism For the gas and electrolyte data in questions 591 to 595, choose the acid-base disorder option that is correct. A. chronic respiratory acidosis B. nonanion gap metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis C. metabolic alkalosis & respiratory acidosis D. wide anion gap metabolic acidosis E. chronic respiratory alkalosis 591. pH 7.44, pCO2 32 mm Hg, pO2 90 mm Hg; serum sodium 140 mEq/L; potassium 4.2 mEq/L; chloride 109 mEq/L; bicarbonate 21 mEq/L 593. pH 7.40, pCO2 51 mm Hg, pO2 87 mm Hg; serum sodium 140 mEq/L; potassium 4.5 mEq/L; chloride 97 mEq/L; bicarbonate 31 mEq/L 594. pH 7.32, pCO2 50 mm Hg, pO2 63 mm Hg; serum sodium 140 mEq/L; potassium 4.0 mEq/L; chloride 100 mEq/L; bicarbonate 28 mEq/L 595. pH 7.29, pCO2 20 mm Hg, pO2 87 mm Hg; serum sodium 137 mEq/L; potassium 4.5 mEq/L; chloride 100 mEq/L; bicarbonate 9 mEq/L For the syndromes in questions 596 to 598, choose the answer option that is correct. A. scan 1 B. scan 2 C. scans 1 and 2 D. none of the above 596. Valve prosthesis 597. Man-in-a-barrel syndrome 598. Perforating branch occlusion A. the tuberoinfundibular nucleus. B. the preoptic nucleus. C. the paraventricular nucleus. D. the mamillary bodies. E. none of the above 600. Efferent pupillary defects are seen in the following disorders EXCEPT: A. Adie’s pupil B. posterior communicating artery aneurysm C. Foster Kennedy syndrome D. Horner’s syndrome E. third nerve lesion 601. Relative afferent pupillary defects are seen in the following disorders EXCEPT: A. macular degeneration B. optic neuritis C. papilledema D. metabolic optic neuropathy E. retinal lesion 602. Hypoxemia due to a 50% shunt is most likely to be improved by which of the following measures? A. decreasing the positive end expiratory pressure to 0 cm H2O B. hyperventilation C. improving mixed venous oxygen content D. oxygen supplementation E. none of the above 603. The half-life of platelets used for transfusion is A. 96 hours. B. 72 hours. C. 48 hours. D. 24 hours. E. 12 hours. 604. Which phase of blood coagulation is the most time consuming? A. conversion of prothrombin to thrombin B. activation of contact factors C. generation of thromboplastin D. release of phospholipids from platelets E. conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin For the statements in questions 605 to 607, choose the answer option that is correct. A. image 1 B. image 2 C. images 1 and 2 D. none of the above 605. Caused by arrested development 606. Acquired after dural thrombosis 607. Associated with blue rubber nevus syndrome For the pathological states in questions 608 to 612, choose the associated ocular finding option that is correct. A. ocular bobbing B. jerk nystagmus C. seesaw nystagmus D. downbeat nystagmus E. none of the above 608. Foramen magnum compression 609. Craniopharyngioma 610. Germinoma 611. Pentobarbital infusion 612. Pontine glioma A. granule cell B. Golgi cell C. Purkinje cell D. basket cell E. stellate cell 613. Forms the glomerulus together with the granule cell 614. Uses excitatory neurotransmitter 615. End in a rete of terminals around the cell bodies of the Purkinje cell 616. Synapse with the interposed nuclei 617. Which of the following is an early sign of cyanide poisoning? A. blurred vision B. diaphoresis C. apnea D. hallucinations E. all of the above 618. Which of the following minerals is important in wound healing? A. manganese B. zinc C. iron D. copper E. all of the above 619. The mechanism of action of aminoglycosides is best described by A. inhibition of DNA synthesis. B. cell membrane destruction. C. cell wall damage. D. inhibition of protein synthesis. E. none of the above 620. Antimicrobial agents causing neuromuscular blockade include all the following EXCEPT: A. streptomycin B. kanamycin C. neomycin D. polymyxin E. gentamicin A. The Allcock test is useful. B. External ventricular drainage following subarachnoid hemorrhage from this type of aneurysm is an accepted temporizing treatment. C. Proximal ligation is the preferred treatment. D. Vasospasm in this area is unlikely to cause respiratory compromise. E. A lumbar drain is contraindicated in this case. 622. In the following tumor resection case, which of these statements is FALSE? A. The dura needs to be opened at either end well past the lesion. B. Dilated veins are more likely to be encountered at the rostral end of the mass. C. Myelotomy is to be done as close to the midline as possible. D. Intracapsular decompression of the tumor is necessary to avoid any traction. E. C-arm guidance for localization may be helpful. 623. Accumulations seen in metachromatic leukodystrophy are A. sulfatides. B. galactocerebroside. C. ganglioside. D. long chain fatty acids. E. none of the above 624. The T-reflex represents A. flexor response as seen in decerebrate rigidity. B. crossed extensor reflex. C. monosynaptic stretch reflex. D. supramaximal stimulation of a mixed motor-sensory nerve. E. all of the above 625. The trochlear nerve arises from the brainstem at the level A. of the lower pons. B. of the upper pons. C. of the lower midbrain. D. of the upper midbrain. E. none of the above 626. A 57-year-old man with a known history of lung cancer presents with generalized muscle weakness. The most likely associated finding is A. opsoclonus. B. increased glutamic acid decarboxylase. C. anti–Purkinje cell antibodies. D. presynaptic acetylcholine receptor disorder. E. multiple sclerosis. 627. To produce a 1 mEq/L rise in serum potassium, the total body potassium stores need to increase by which quantity? A. 50 mEq B. 150 mEq C. 350 mEq D. 500 mEq E. 1000 mEq 628. If the C6 nerve root is severed, all the following may be affected EXCEPT: A. lateral cord B. ulnar nerve C. musculocutaneous nerve D. median nerve E. lower subscapular nerve For the innervation specified in questions 629 to 634, choose the plexus option that is correct. A. brachial plexus B. cervical plexus C. lumbar plexus D. cervical and brachial plexuses E. none of the above 629. Inferior belly of the omohyoid 630. C5 nerve root 631. Obturator nerve 632. Levator scapulae 633. External urethral sphincter 634. Sternocleidomastoid 635. Which of the following is a characteristic of narcolepsy? A. hallucinations while sleeping B. convulsions while sleeping C. daytime hyperalertness D. NREM onset of sleep E. gelastic seizures For the clinical disorders in questions 636 to 639, choose the vitamin excess or deficiency option that is correct. A. thiamine B. B6 C. cobalamine D. niacin E. vitamin A 636. Pseudotumor 637. Wet Beriberi 638. Increased serum homocysteine 639. Lower extremity paraesthesias For the pharmacologic agents in questions 640 to 643, choose the option that is correct. A. type A GABA agonist B. type B GABA agonist C. GABA antagonist D. no effect on GABA receptors 640. Barbiturates 641. Picrotoxin 642. Baclofen 643. Bicuculine 644. The two aneurysms seen in this intraoperative picture are A. anterior communicating and superior hypophyseal. B. basilar and anterior communicating. C. PICA and superior hypophyseal. D. PICA and basilar. E. basilar and posterior communicating. A. A common presenting sign is papilledema. B. It arises from the diencephalic recess of the postvelar arch. C. Risk of sudden death is attributable to CSF dynamics or disturbances in hypothalamic-related cardiovascular control. D. Lumbar puncture is part of the initial workup. E. The patient may require a shunt postoperatively. 646. All the following are associated with torsade de pointes EXCEPT: A. phasic changes of amplitude and polarity of ventricular complexes B. hypokalemia C. hypomagnesemia D. narrowed QT intervals E. may be predisposed by erythromycin 647. Which of the following enables one to distinguish early adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) from early cardiogenic pulmonary edema? A. In ARDS, the hypoxemia is more pronounced and the chest x-ray abnormalities are more evident. B. In ARDS, the hypoxemia is less pronounced and the chest x-ray abnormalities are more evident. C. In ARDS, the hypoxemia is more pronounced and the chest x-ray abnormalities are less evident. D. In ARDS, the hypoxemia is less pronounced and the chest x-ray abnormalities are less evident. E. None of the above 648. All of the following are recommended therapeutic measures for diabetic ketoacidosis EXCEPT: A. insulin B. alkali therapy C. potassium D. crystalloids E. phosphate 649. A 54-year-old male who is a heavy smoker presents with balance problems; below are his MRI scan and pathology slide from surgery. The most likely diagnosis is A. metastasis B. hemangioblastoma C. glioma D. CNS lymphoma E. pilocytic astrocytoma A. glioblastoma multiforme resection. B. radiation therapy. C. trauma. D. encephalitis. E. aneurysm 651. After a motorcycle accident, a patient is able to dorsiflex and invert his foot but is unable to evert his foot. The most likely nerve lesioned is A. the deep peroneal nerve. B. the superficial peroneal nerve. C. the common peroneal nerve. D. the sciatic nerve. E. the tibial nerve. 652. The brachial plexus structure just distal to the division is A. the trunk. B. the branch. C. the cord. D. the root. E. none of the above A. definitive clipping, temporary clipping, fissure splitting, dissection of M2 branch from dome B. dissection of M2 branch from dome, fissure splitting, temporary clipping, definitive clipping C. fissure splitting, temporary clipping, dissection of M2 branch from dome, definitive clipping D. temporary clipping, fissure splitting, dissection of M2 branch from dome, definitive clipping E. fissure splitting, dissection of M2 branch from dome, temporary clipping, definitive clipping 654. Molecular genetic alterations in glioma, not part of a specific syndrome, include all the following EXCEPT: A. overexpression of CDK4 B. deletion of p53 C. mutation of retinoblastoma D. amplification of K-ras E. overexpression of CDK6 655. Oligodendrogliomas exhibit loss of chromosomal regions on all the following EXCEPT: A. 1p B. 7q C. 9p D. 19q E. 22 656. All the following statements are true about the sympathetic nervous system EXCEPT: A. Stellate ganglionectomy is used in the treatment of long QT syndrome. B. Anhydrosis occurs with ganglionectomy. C. Each intercostal nerve is connected to the sympathetic trunk by at least one white ramus and two gray rami. D. The inferior hypogastric plexus lies in front of the promontory of the sacrum between the two common iliac arteries and is sometimes called the presacral nerve. E. Sympathetically conveyed stimulus to the sweat glands is transmitted by acetylcholine. For the statements in questions 657 to 659, choose the limbic structure option that is correct. A. cingulate gyrus B. hippocampus C. amygdala D. mammillary bodies E. anterior nucleus of the thalamus 657. Not part of the Papez circuit 658. Receives inputs from the nucleus of the solitary tract 659. Receives inputs from the medial septal nucleus 660. Which of the following has the highest incidence of associated platelet disorders? A. ALS B. Huntington’s disease C. acute respiratory distress syndrome D. AIDS E. multiple sclerosis 661. Which of the following is NOT associated with the finding on the scan? A. congestive heart failure B. pulmonary hypertension C. renal failure D. microcephaly E. subarachnoid hemorrhage 662. All the following are associated with this MRI finding EXCEPT: A. most common location is cervicothoracic. B. presence of a malignancy is a predisposing condition. C. increased incidence with epidural anesthesia D. incidence is 1:10,000 in the U.S. E. increased incidence with drug abuse 663. The leading cause of magnesium deficiency is A. antibiotic therapy. B. diuretics. C. secretory diarrhea. D. diabetes mellitus. E. Dilantin therapy. For the nerves in questions 664 to 667, choose the ganglion option that is correct. A. jugular B. nodose C. pterygopalatine D. ciliary E. superior cervical 664. Facial nerve 665. Oculomotor nerve 666. Arnold’s nerve 667. Deep petrosal nerve 668. All of the following may be used to differentiate between a lesion of the glossopharyngeal nerve and a lesion of the facial nerve EXCEPT: A. loss of sensation to the outer ear B. loss of taste on the tongue surface C. loss of salivatory secretion from a gland D. weakness of the pharynx E. strength of facial muscles 669. The inotropic drug of choice for acute management of systolic heart failure is A. Dopamine B. Dobutamine C. Neosynephrine D. Epinephrine E. Isoproterenol 670. The toxicity of nitroprusside in the setting of decreased renal blood flow is mediated A. by cyanide. B. by thiocyanate. C. by nitric oxide. D. by thiosulfate. E. by vitamin B12. For the diseases in questions 671 to 675, choose the answer option that is correct. A. 1 B. 2 C. 1 and 2 D. none of the above 671. Eosinophilic granuloma 672. Langerhans cell histiocytosis 673. Paget’s disease 674. Albright’s syndrome 675. Epidermoid 676. The most common cause of admission of HIV-infected patients to the ICU is A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. B. cytomegalovirus infections. C. toxoplasmosis. D. AIDS encephalitis. E. hydrocephalus. A. of 9%. B. of 0.9%. C. of 0.09%. D. of 0.009%. E. of 0.0009%. 678. Differential diagnosis of the following lesion includes the listed choices EXCEPT: A. chordoma B. epidermoid C. basilar tip aneurysm D. arachnoid cyst E. low-grade glioma For the functions in questions 679 to 683, choose the organelle option that is correct. A. Golgi organelle B. endoplasmic reticulum C. Both A and B D. none of the above 679. Functional ribosomes occur on the outside of its membrane but not on the inside. 680. Phosphorylation of oligosaccharides 681. Important in drug detoxification 682. Glycogen formation and breakdown 683. Lamellar or tube-like membranous system 684. Neuromelanin has the following characteristics EXCEPT: A. accumulates in neurons of the substantia nigra B. found in the locus ceruleus C. made by tyrosinase D. is a catecholamine waste product E. chelates metal ions such as aluminum and iron 685. Amygdala afferents include all the following EXCEPT: A. nucleus accumbens B. pyriform cortex C. solitary tract nucleus D. locus ceruleus E. prefrontal cortex 686. All the following are complications of total parenteral nutrition EXCEPT: A. hypercapnia B. acalculous cholecystitis C. impaired oxygenation D. calculous cholecystitis E. increased incidence of infection 687. Which of the following findings is most closely associated with the lesion on this scan? A. may have elevated carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) levels B. associated with Schiller-Duval bodies C. derived from extraembryonic tissue D. ingestion of food with fecal contamination E. none of the above 688. Which of the following is this scan of a seizure patient associated with? A. anti-Yo antibodies B. anti-Hu antibodies C. anti-Ri antibodies D. antibodies to presynaptic voltage gated receptors E. none of the above 689. Match the finding on this myelin stained section with the most likely associated presentation: A. a 40-year-old man with chronic encephalitis and Argyll-Robertson pupils B. a 15-year-old hyperglycemic patient with severe lower extremity weakness C. a 55-year-old man with spastic gait, weakness, and fasciculation in all extremities D. a 4-year-old boy with bilateral symmetric proximal limb weakness E. none of the above For the disorders in questions 690 to 693, choose the answer option that is correct. A. respiratory acidosis B. respiratory alkalosis C. both D. neither 690. Pulmonary embolism 691. Meningitis 692. Liver cirrhosis 693. Aminoglycosides 694. All the following statements are correct regarding this diffusion tractography scan EXCEPT: A. Water diffusion is hindered anteriorly by the presence of a large tumor. B. Connections between frontal and occipital lobe are impaired bilaterally. C. There are intersecting white matter tracts between the splenium and the fronto-occipital tracts. D. Tractography gives information about direction of flow. E. Bundles of axons provide a barrier to perpendicular diffusion and a path for parallel diffusion along the orientation of the fibers. 695. Which of the following is true regarding the finding on this MRI scan? A. associated with dermal sinus tract B. secretes histamine C. on histopathology, may see densely packed elongated spindle cells in interlocking fascicles with a tendency toward pallisading D. all of the above are true E. none of the above are true 696. All of the following findings may be associated with this MRI scan EXCEPT: A. abnormality in protein merlin B. posterior capsular lens opacities C. intertriginous freckling D. pigmented area of skin with excess hair E. may be associated with an autosomal disorder located on chromosome 22 697. Etiologies of distal renal tubular acidosis include all of the following EXCEPT: A. amphotericin B B. lithium C. toluene D. carbonic anhydrase inhibitors E. cyclamate 698. Which of the following is NOT a valid therapeutic measure in patients with addisonian crisis? A. hydrocortisone sodium succinate (Solu-Cortef) for glucocorticoid emergencies B. fludrocortisone (Florinef) for mineralocorticoid emergencies C. methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol) for glucocorticoid emergencies D. cortisone acetate for glucocorticoid emergencies E. intravenous fluids 699. Therapeutic measures for syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) include A. furosemide. B. phenytoin. C. lithium. D. all of the above E. none of the above 700. Which compatible plasma types can be given to a patient with blood type B? A. B and O plasma types B. B and AB plasma types C. B plasma type only D. all of the above E. none of the above 701. Neurogenic shock is characterized by which of the following? A. increased arteriolar tone B. increased in peripheral vascular resistance C. cool molten skin D. hypertension E. bradycardia 702. Gram negative septicemia in hospitalized patients is MOST likely to originate from A. urinary tract infection. B. pneumonia. C. wound infection. D. gastrointestinal infection. E. pressure ulcers. A. latex agglutination test B. tissue culture assay for cytotoxin C. stool culture D. stool microscopy E. polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis For the properties in questions 704 to 707, choose the anesthetic option that is correct. A. isoflurane B. enflurane C. thiopental D. halothane 704. Increases cerebral blood flow the most 705. Decreases intracranial pressure 706. Transient tachycardia in children 707. Increases systemic vascular resistance For the syndromes in questions 708 to 711, choose the option that is correct. A. neurofibromatosis type 1 B. neurofibromatosis type 2 C. both A and B D. none of the above 708. Autosomal-dominant inheritance 709. Retinal hemangioma 710. Iris hamartoma 711. Segmental and confined to one part of the body A. The neck of the aneurysm is unobstructed. B. The neck of the aneurysm is obstructed by the dome. C. The neck of the aneurysm is obstructed by the optic nerve. D. The neck of the aneurysm is obstructed by the carotid artery. E. The neck of the aneurysm is obstructed by the anterior clinoid process. 713. During microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia, the following intraoperative picture is taken and the offending artery is seen. What is the artery and what structure does it come close to more proximally in this picture? A. superior cerebellar artery, abducens nerve B. anterior inferior cerebellar artery, trochlear nerve C. superior cerebellar artery, trochlear nerve D. anterior inferior cerebellar artery, abducens nerve E. superior cerebellar artery, oculomotor nerve A. supracerebellar infratentorial approach for cyst resection B. midline frontal approach for cyst resection C. third ventriculostomy D. midline frontal approach for cyst decompression E. endoscopic cyst resection For the effects in questions 715 to 719, choose the correct medication option. A. meperidine B. thyroid hormones C. fluconazole D. papaverine 715. Inhibits antiparkinsonism effect of levodopa 716. Increases serum phenytoin levels 717. Enhances clotting factor catabolism 718. Decreases warfarin metabolism 719. May cause hypertension, rigidity, and excitation when used with monoamine oxidase inhibitors A. epinephrine B. isoflurane C. halothane D. thiopental E. all of the above 721. Which of the following neoplasms is LEAST likely to metastasize to the spine? A. lung carcinoma B. breast carcinoma C. colon carcinoma D. renal cell carcinoma E. prostate carcinoma 722. In relation to what vessel are the cords of the brachial plexus named? A. brachiocephalic artery B. axillary artery C. subclavian artery D. brachial artery E. internal carotid artery 723. Which type of spondylolisthesis is most common in gymnasts and football players? A. traumatic B. degenerative C. isthmic D. pathologic E. dysplastic For questions 724 to 729, choose the visual disturbance option that is correct. A. homonymous hemianopia B. upper homonymous quadrantanopia C. bilateral central scotomas D. monocular loss of vision with contralateral upper outer quadrantanopia E. lower homonymous quadrantanopia 724. Lesion of the optic nerve just distal to the chiasm 725. Occipital lobe infarction 726. PICA interruption 727. Methyl alcohol 729. Parietal lobe lesion For questions 730 to 732, choose the anatomic structure that is correct. A. Struthers’ ligament B. arcade of Struthers C. arcade of Frohse D. Guyon’s canal 730. Ulnar nerve entrapment 731. Extensor carpi ulnaris palsy 732. Brachial artery passes under this structure 733. Which of the following is the LEAST likely presenting sign in a patient with rhinorrhea and the following metrizamide CT scan finding? A. reservoir sign B. early morning headache C. meningitis D. visual deficits E. sinus congestion A. radicular pain B. scoliosis C. weakness D. atrophy E. none of the above 735. Of the following signs and symptoms, which is the most common in the presentation of an osteoblastoma? A. radicular pain B. scoliosis C. weakness D. atrophy E. none of the above 736. What mechanisms lead to neurologic deficits in patients with vertebral hemangiomas? 1. Epidural growth of the tumor 2. Expansion of bone with widening of the pedicle and lamina 3. Compression fracture of the involved vertebrae 4. Spinal cord ischemia due to steal phenomenon A. 1, 2, and 3 B. 1 and 3 C. 2 and 4 D. 1, 2, 3, and 4 737. DeQuervain’s syndrome is characterized by all the following EXCEPT: A. caused by frequent repetitive motion at the wrist B. pain and tenderness occurs in the wrist, near the thumb C. Finkelstein test is positive D. nerve conduction velocities are decreased E. difficulty gripping For the locations in questions 738 to 741, choose the answer option that is correct. A. fourth ventricle roof B. fourth ventricle floor C. both of the above D. neither of the above 739. Facial colliculus 740. Hypoglossal trigone 741. Rhomboid fossa 742. What is the best therapeutic option in a 1-year-old with the following lesion on MRI? A. surgical evacuation B. systemic antibiotics C. head wrapping D. radiation therapy E. VP shunt 743. The dorsal horn of the spinal cord is derived from A. the basal plate. B. the notochord. C. the neural crest cells. D. the somites. E. the endoderm. For the lesion locations in questions 744 to 747, choose the breathing pattern option that is correct. A. Cheyne-Stokes respiration B. apneustic respiration C. ataxic respiration D. central neurogenic hyperventilation 744. Medulla 745. Midbrain 746. Pons 747. Diencephalon For the descriptions in questions 748 and 749, choose the cerebellar element option that is correct. A. middle cerebellar peduncle B. inferior cerebellar peduncle C. nodulus D. flocculus E. none of the above 748. Devoid of pontine inputs 749. Contains only afferent fibers 750. All the following are associated with this angiogram finding EXCEPT: A. connects the basilar artery between the superior cerebellar and the anterior inferior cerebellar arteries by passing through the petrous bone B. connects the basilar artery by passing through the internal auditory meatus C. present in 0.1% of the population D. increased frequency of arteriovenous malformations E. second most common persistent fetal circulation For the needlestick injury infections in questions 751 to 753, choose the risk rates’ option that is correct. A. 75% B. 50% C. 25% D. 2% E. 0.3% 751. The risk of acquiring HIV from a hollow needle stick injury from an affected individual 752. The risk of acquiring hepatitis C from a hollow needle stick injury from an affected individual 753. The risk of acquiring hepatitis B from a hollow needle stick injury from an affected individual with an extremely low viral load A. tentorial subdural hemorrhage. B. subarachnoid hemorrhage. C. normal CT scan. D. dural sinus thrombosis. E. arteriovenous fistula. 755. All the following are features of malignant hyperthermia (MH) EXCEPT: A. autosomal-recessive inheritance pattern B. in 20% of cases there is no hyperthermia accompanying the muscle rigidity C. may be associated with autonomic instability D. may be caused by muscle relaxants E. a mutation in the ryanodine receptor is related to MH 756. Which of the following is the lesion on this MRI scan associated with? A. cerebral aneurysm B. arteriovenous malformation C. endocrinopathy D. venous angioma E. progressive supranuclear palsy 757. Which of the following changes are represented at the end plates of L4-L5 levels on this T2-weighted MRI? A. type 1 modic changes B. type 2 modic changes C. yellow marrow replacement D. hypovascularization of the end plates E. all of the above A. ataxia B. ipsilateral hearing deficits C. contralateral temperature sensation loss D. lateral rectus palsy E. balance problems 759. Which anesthetic agent is LEAST likely to cause further decrease in blood pressure in the face of hypovolemic shock? A. ketamine B. thiopental C. halothane D. enflurane E. isoflurane 760. Which of the following statements is NOT associated with the following images? A. Froin’s syndrome B. positive Queckenstedt’s test C. male predominance with peak age in mid-40s D. cellular type E. neoplastic disease A. syringobulbia B. elevated serum angiotensin-converting enzyme C. aqueductal stenosis D. Hallervorden-Spatz disease E. subdural hematoma For the functions in questions 762 to 765, choose the answer option that is correct. A. proximal renal tubular function B. distal renal tubular function C. kidney glomerular function D. none of the above 762. Secretion of H+ and reabsorption of Cl 763. Secretion of organic acids and reabsorption of amino acids 764. Secretion of K+ and reabsorption of Na+ 765. Function is maximal in young adulthood and decreases thereafter 766. Which of the following prognostic factors is true in the case of a 16-year-old boy with failure to thrive and the following findings on MRI? A. The most significant factor associated with recurrence is extent of resection. B. The most significant factor associated with recurrence is histology. C. MIB-1 LI >7% is associated with low likelihood of recurrence. D. Malignant transformation to carcinoma frequently occurs. E. Recurrence is dependent on the presence of intracytoplasmic inclusions. A. central neurocytoma B. oligodendroglioma C. ependymoma D. endodermal sinus tumor E. yolk sac tumor 768. The inferior frontal gyrus is bordered by which structure caudally? A. operculum B. sylvian fissure C. precentral sulcus D. rolandic fissure E. none of the above 769. The actions of nitroglycerine are mediated by the following mechanisms EXCEPT: A. Nitroglycerine binds the surface of endothelial cells. B. Nitroglycerine undergoes two chemical reductions to form nitric oxide. C. Nitric oxide promotes the formation of cyclic guanosine triphosphate. D. Nitric oxide moves out of the endothelial cell into adjacent smooth muscle cells. E. Nitric oxide has also been referred to as endothelium-derived relaxing factor. A. 1% per year B. 2% per year C. 4% per year D. 13% per year E. 26% per year 770. Symptomatic 70 to 90% stenosis of the carotid on angiogram 771. Asymptomatic 70 to 90% stenosis of the carotid on angiogram 772. Post–carotid endarterectomy in a preoperative symptomatic 70 to 90% stenosis of the carotid on angiogram 773. Which of the following causes hypokalemia? A. amphotericin B. angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors C. aspirin D. cyclosporine E. heparin 774. What is the most likely age of the following hemorrhage? A. 2 hours B. 2 days C. 12 days D. 22 days E. 32 days For the characteristics in questions 775 and 776, choose the substance option that is correct. A. ethanol B. acetone C. methanol D. ethylene glycol (antifreeze) 775. Lowest molecular weight 776. Most lethal 777. A patient with von Willebrand’s disease sustained a motorcycle crash and is losing blood from an open fracture. The blood product best suited for management is A. whole blood. B. fibrinogen. C. platelets. D. packed red blood cells. E. cryoprecipitate. 778. Which of the following is least likely to be associated with the finding on this MRI scan? A. ipsilateral Horner’s B. downbeat nystagmus C. loss of abdominal cutaneous reflex D. neurogenic bladder E. extremity weakness A. Bilateral sensory deficit B. Symmetric motor loss C. Loss of ankle jerk but preserved knee jerk D. Autonomic symptoms occur late E. Urinary retention and atonic anal sphincter cause overflow urinary incontinence and fecal incontinence. 780. Typical presentation of patients with cauda equina lesions include all the following EXCEPT: A. Sensory dissociation B. Asymmetric motor loss C. Late autonomic symptoms D. Absence of ankle jerk and knee jerk E. Numbness tends to be more localized to saddle area. 781. Which of the following structures is the second branch of the proximal aorta as it exits the left ventricle? A. brachiocephalic artery B. right subclavian artery C. left subclavian artery D. right carotid artery E. left carotid artery 782. Bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia results in which abnormality on physical exam? A. convergence deficit B. adduction deficit C. downward gaze palsy D. vertical gaze palsy E. Parinaud’s syndrome A. acetylcholine B. noradrenaline C. dopamine D. GABA E. glutamate 783. Inferior cervical ganglion 784. Locus ceruleus 785. Periaqueductal gray 786. In which disorder of speech is both repetition and comprehension affected? 1. transcortical sensory aphasia 2. Wernicke’s aphasia 3. conductive aphasia 4. global aphasia A. 1, 2, and 3 B. 1 and 3 C. 2 and 4 D. 4 E. 1, 2, 3, and 4 787. Watershed infarcts are seen in all the following EXCEPT: A. regional hypotension B. CBF below critical level C. atrial fibrillation D. cardiac arrest E. anaphylaxis 788. Which of the following arteries arises directly from the intracavernous carotid? A. artery of Bernasconi-Cassinari B. persistent stapedial artery C. Heubner’s artery D. McConnell’s capsula arteries E. vidian artery 789. All the following statements are true regarding the findings of the following scan EXCEPT: A. Fom 30 to 50% of patients are febrile. B. Spontaneous fusion of vertebral bodies may occur. C. H. influenzae may be a causative organism in juvenile cases. D. Radionuclide scans have a relatively low sensitivity. E. Increased incidence with intravenous drug abuse. 790. What is the significance of an elevated N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak on an MR spectroscopy scan? A. increased neuronal density B. increased metabolism C. increased excitatory neurotransmission D. necrosis E. none of the above Questions 791 and 792 are based on this radiograph. 791. Choose the correct answer based on the MRI finding in a 20-year-old woman with Hodgkin’s lymphoma and an opportunistic infection. The most likely organism is A. mucor. B. Aspergillus. C. coccidioidomycosis. D. amebiasis. E. viral. 792. Characteristic features of this organism include all the following EXCEPT: A. perivascular invasion B. hemorrhagic infarcts C. may cause paranasal sinus mycetoma D. Caseating granulomas are common. E. increased prevalence with the use of chemotherapy and corticosteroids A. intravenous antibiotics B. surgical resection C. systemic chemotherapy and whole brain radiation D. Ommaya reservoir placement and intrathecal chemotherapy E. ventriculoperitoneal shunt 794. Which of the following muscles is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve? A. stapedius B. tensor veli palatini C. stylopharyngeus D. posterior belly of digastric E. none of the above 795. Equals 2.4 L at rest and 2.4 L during exercise 796. Represents vital capacity minus expiratory reserve volume 797. Measured at about 4.4 to 5 L in healthy adults 798. Calculated after having patient inspire a mixture containing 10% helium from a spirometer at 21°C Questions 799 and 800 are based on the following MR spectroscopy study: 799. Point 1 being closest to normal and point 3 showing the most abnormality, which of the following statements with regard to spectroscopy is correct regarding point 3? A. elevated N-acetylaspartate (NAA) peak and normal Choline (Chol) and Creatine (Cr) peaks B. elevated Cr peak and decreased Chol and NAA peaks C. increased Chol/Cr ratio and decreased NAA peak D. increased Cr/Chol ratio and decreased NAA peak E. all of the above 800. What do these MR spectroscopy findings most likely represent? A. increased astrocytic density at point 3 as compared with point 1 B. presence of tumor cells at point 3 C. presence of necrosis at point 3 D. increased metabolism at point 3 E. all of the above A. oxygen delivery B. oxygen uptake C. oxygen extraction ratio D. oxygen content E. none of the above 802. Which of the following formulas describes shunt fraction? Pulmonary capillary O2 content = Cc O2 Venous O2 content = Cv O2 Arterial O2 content = Ca O2 A. Cc O2 – Ca O2 / Cv O2 – Ca O2 B. (Cc O2 – Cv O2)/ (Cc O2 – Ca O2) C. Cc O2 – Ca O2 / Cc O2 – Cv O2 D. (Cc O2 – Ca O2)/ (Cc O2 – Cv O2) E. (Cc O2 – Ca O2)/ (Cv O2 – Ca O2) 803. Which of the following is the formula for flow (Q) of nonpulsatile fluids? P = pressure r = radius L = length V = viscosity A. Q = Pπr4/8 VL B. Q = 8 PL/Vπr4 C. Q = Vπr4/8 PL D. Q = 8 Vπr4/PL E. None of the above A. immediately in the ER. B. before getting a CT scan. C. in the operating room. D. before antibiotics are given. E. after the patient has been stabilized in the field A. single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion (ACDF) B. two-level ACDF C. posterior decompression D. cervical corpectomy and fusion E. three-level ACDF
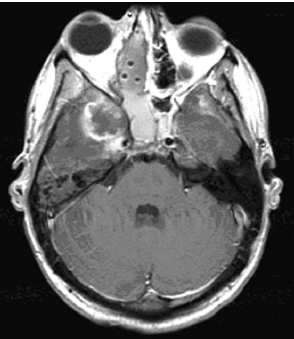
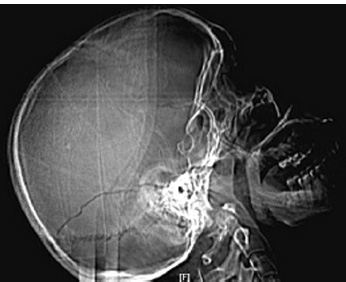
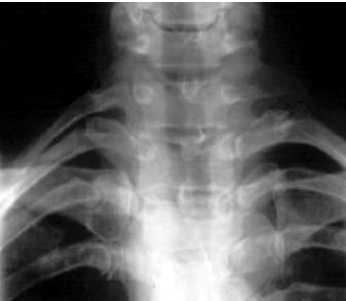
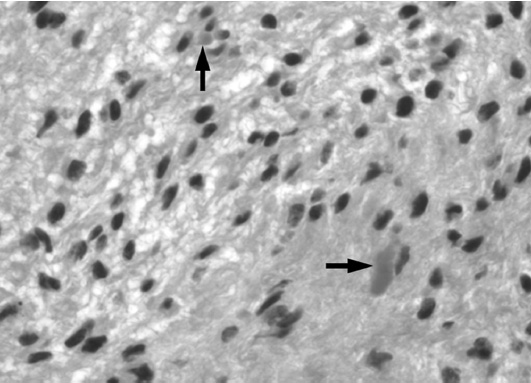
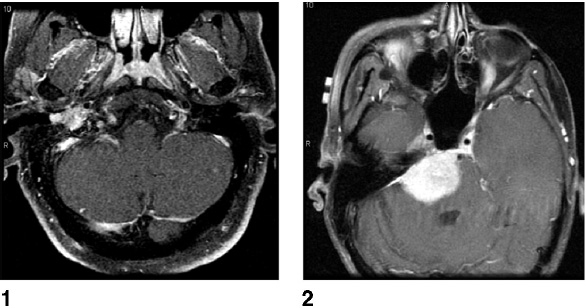
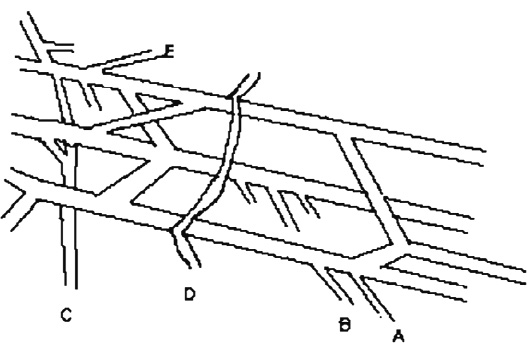
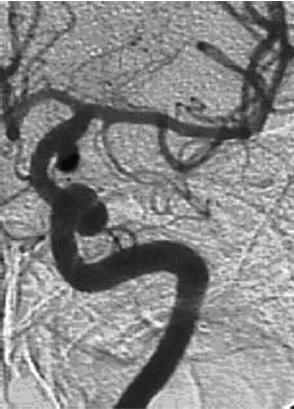
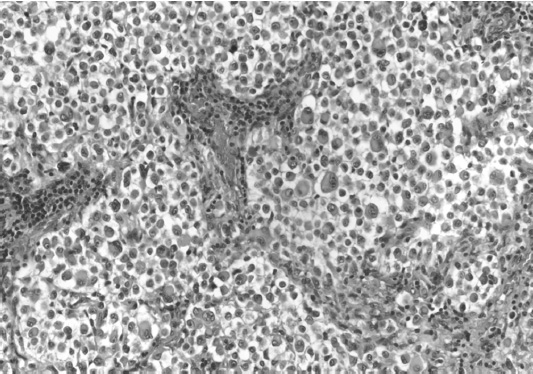
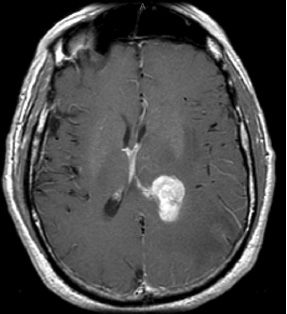
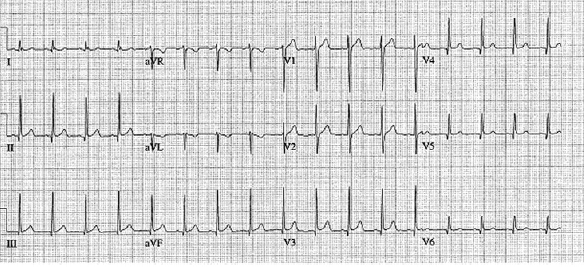
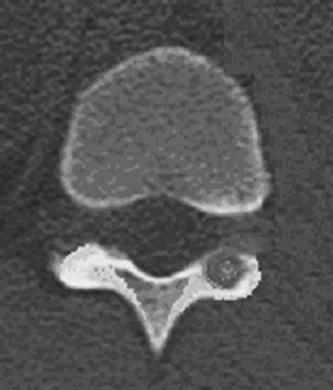
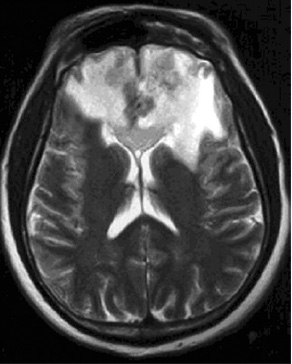
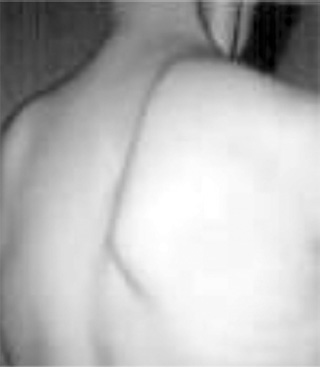
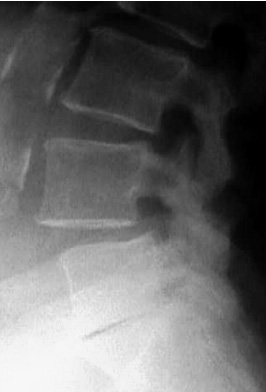
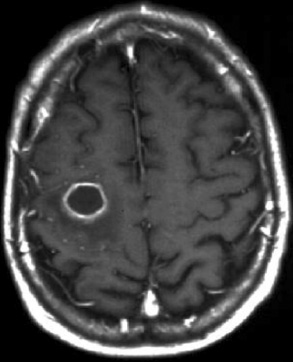
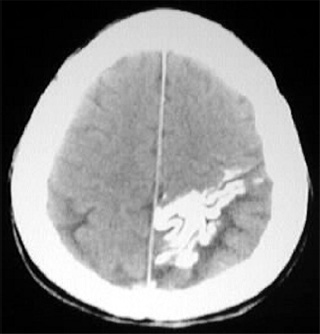
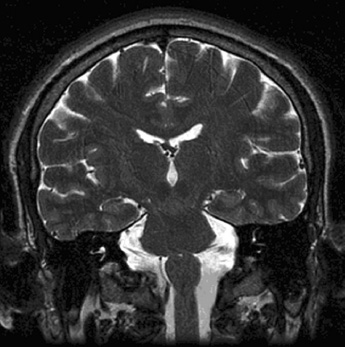
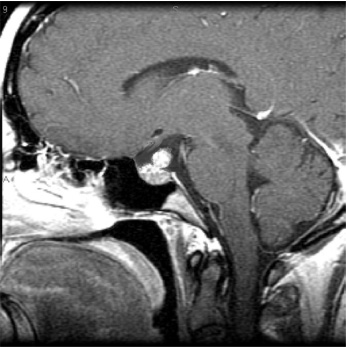
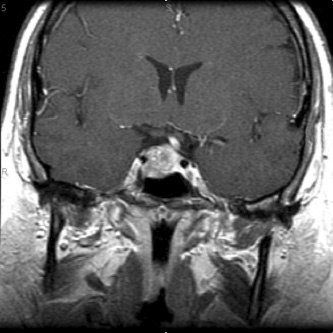
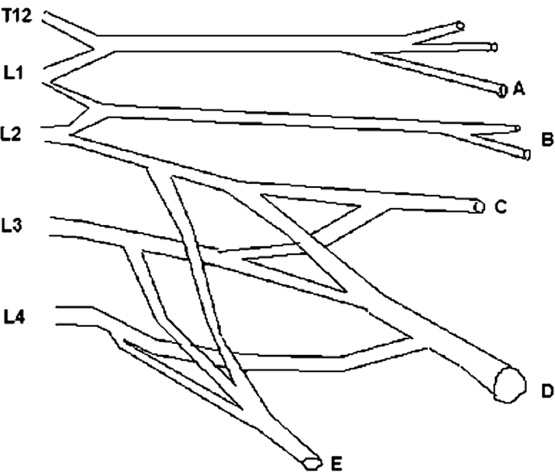
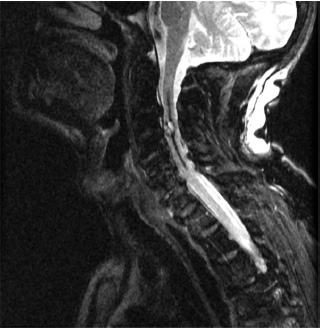
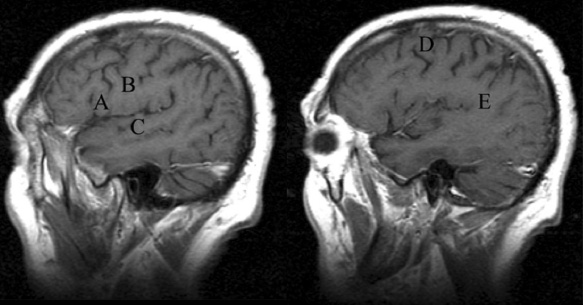
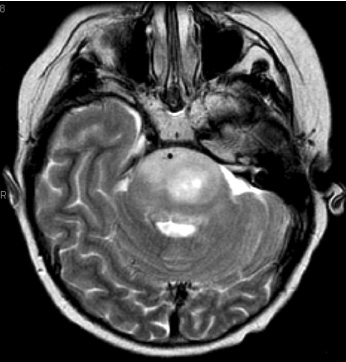
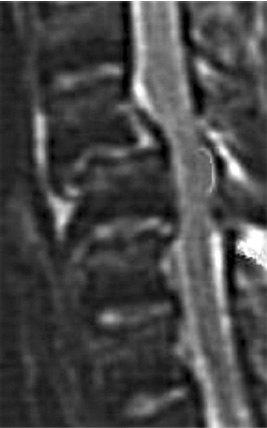
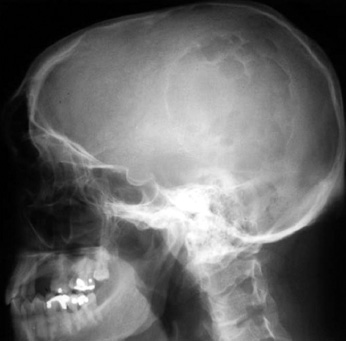

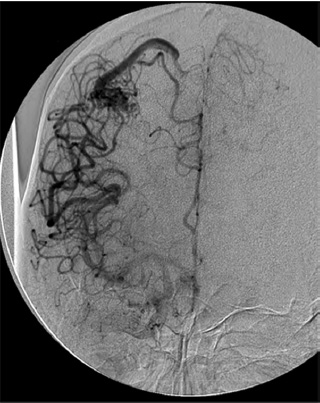
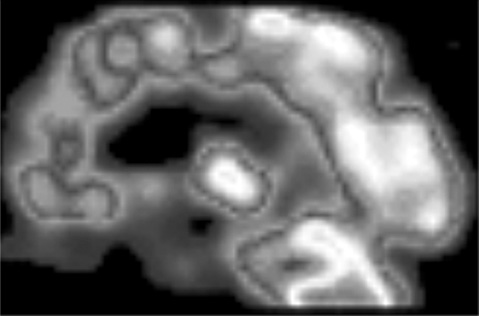
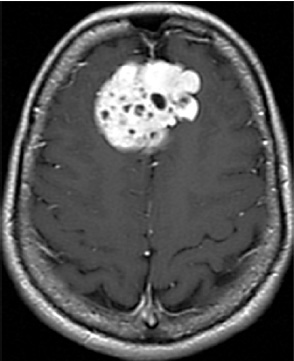
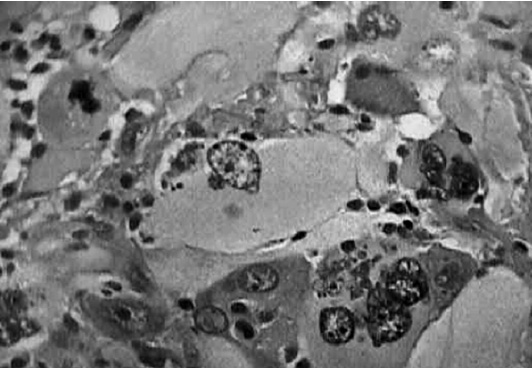
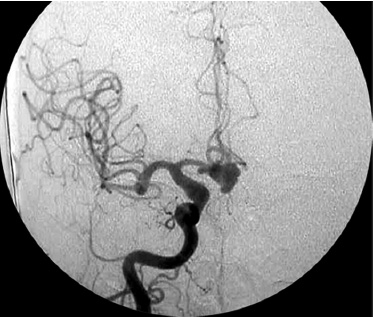
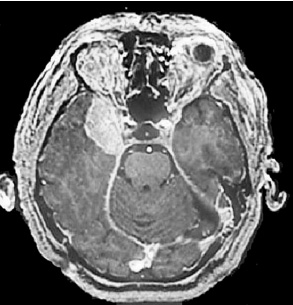
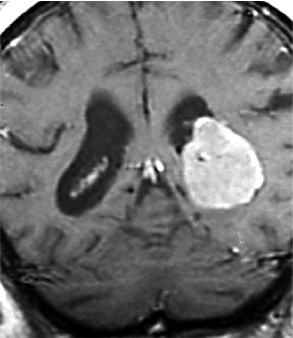
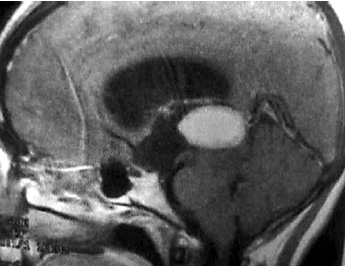
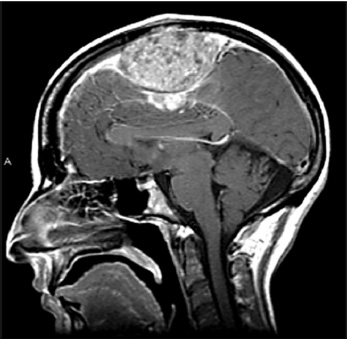
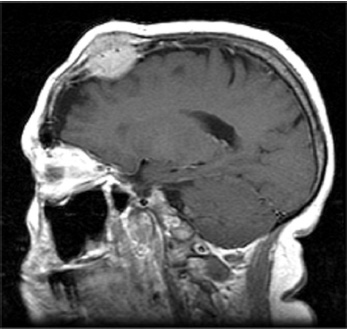
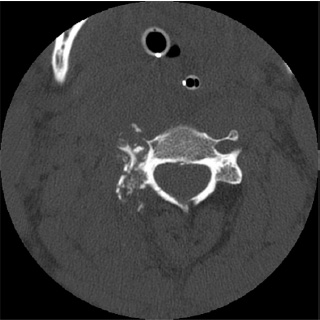
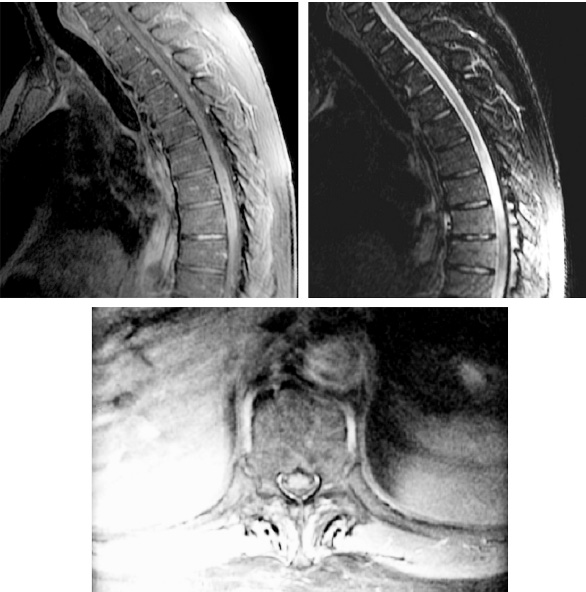
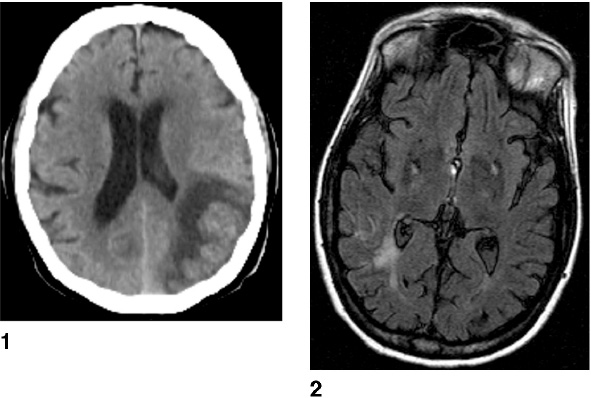
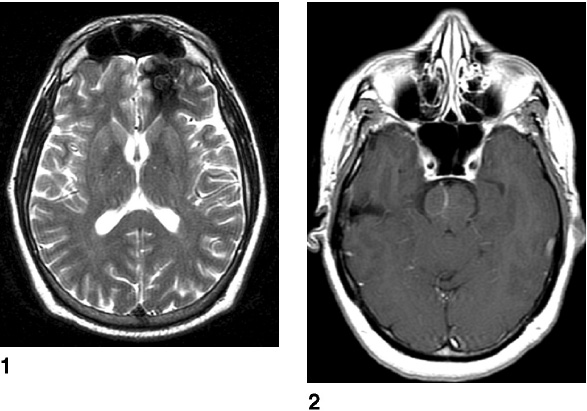
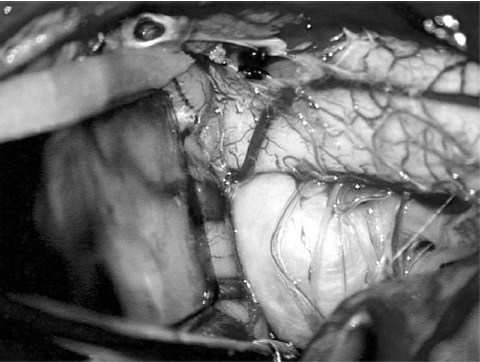
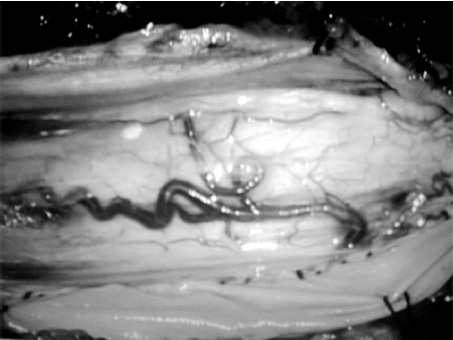
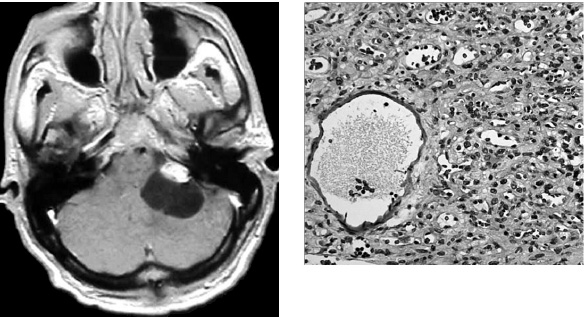
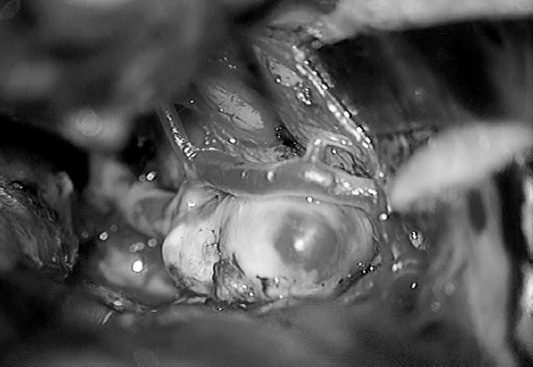
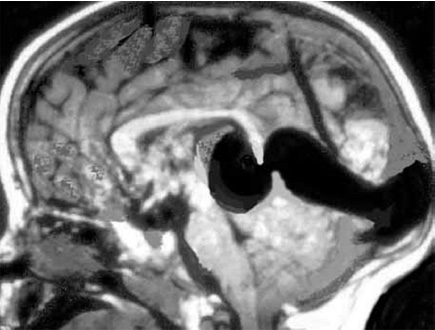
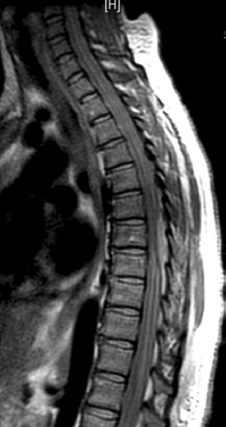
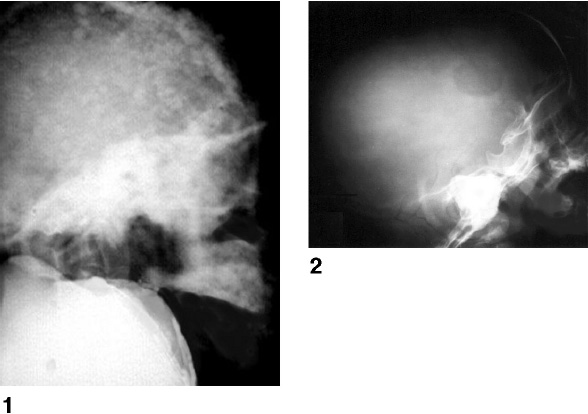
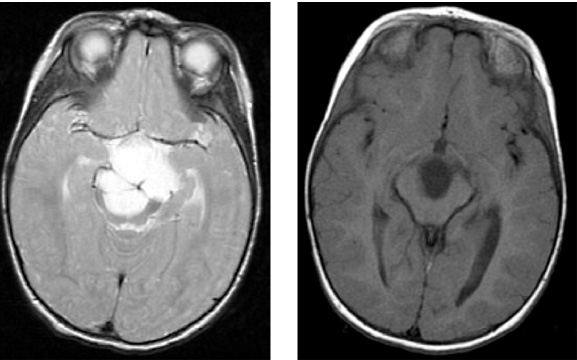
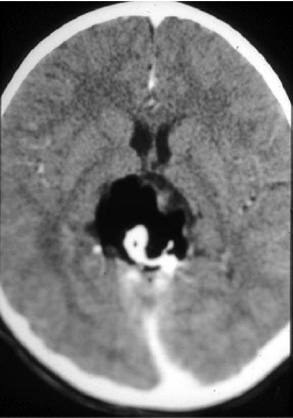
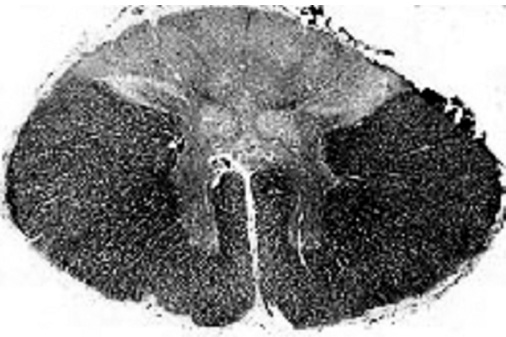
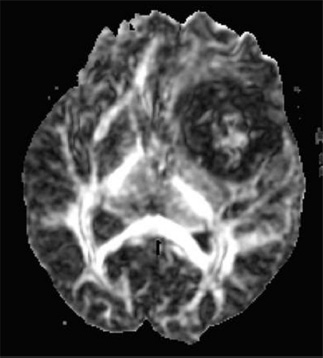
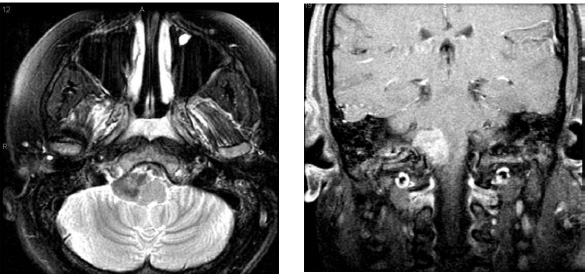
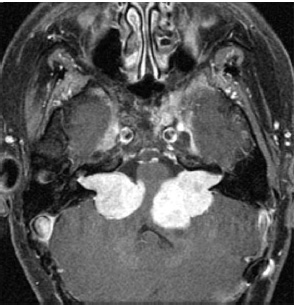
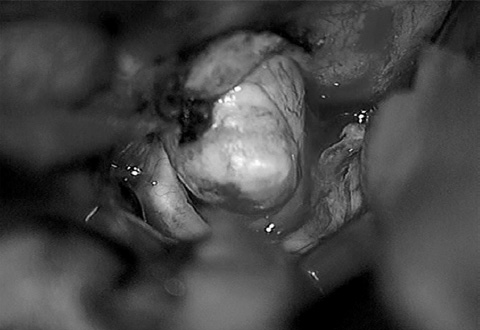
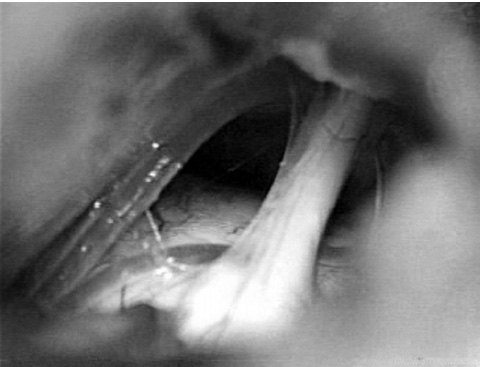
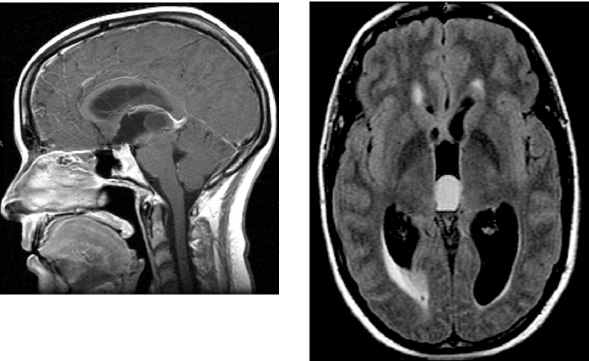
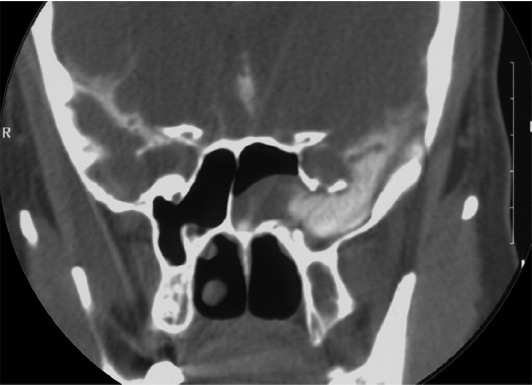
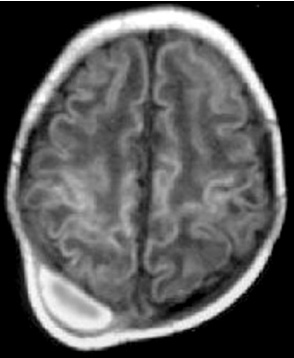
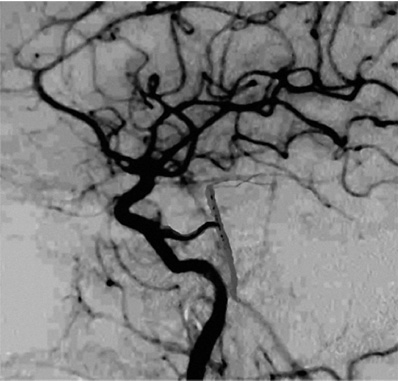
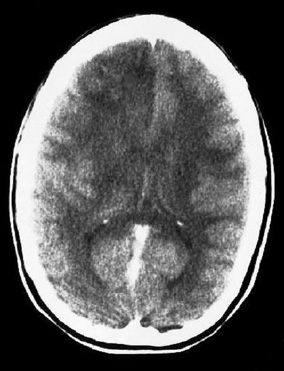
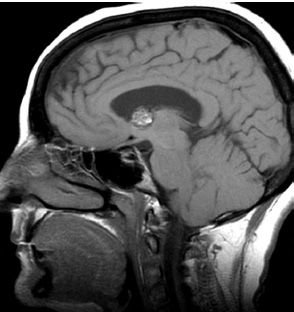
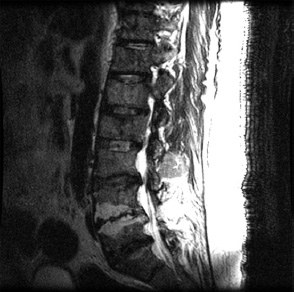
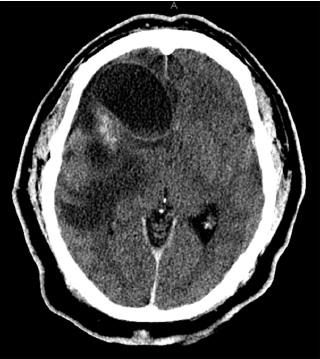
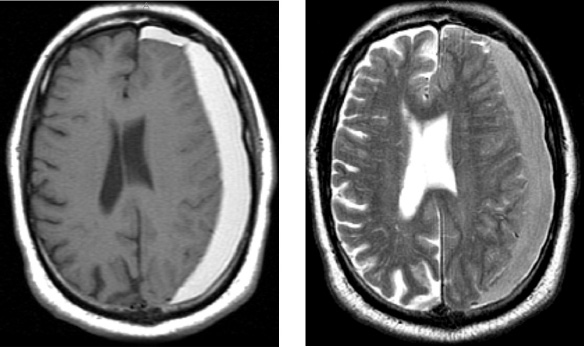
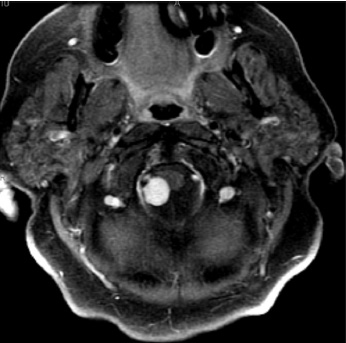
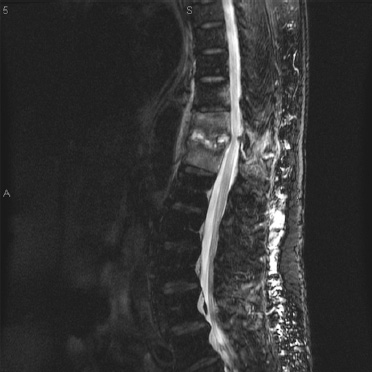
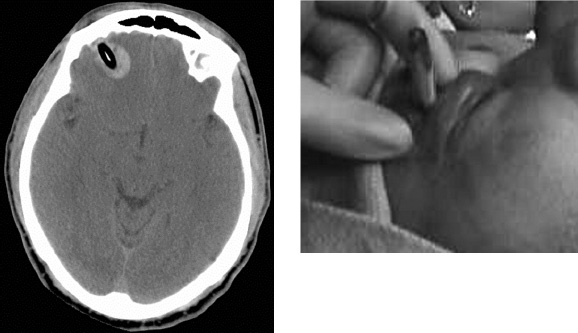
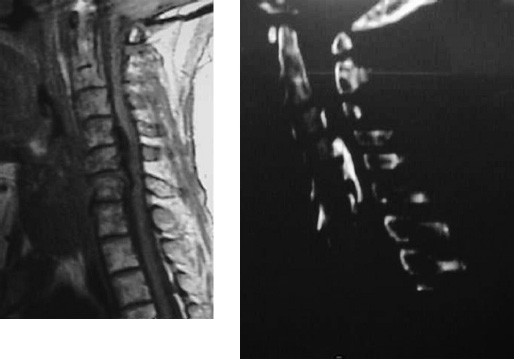
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Questions
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree