Questions
1. Regarding the pathophysiology of myasthenia gravis, what is/are the possible mechanisms by which acetylcholine receptor antibodies interfere with neuromuscular transmission?
A. Binding to the acetylcholine receptor and blocking the binding of acetylcholine
B. Cross-linking acetylcholine receptors, thereby increasing their rate of internalization
C. Binding of complement resulting in destruction of the muscle end plate
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
2. All of the following statements are correct regarding the medial lemniscus EXCEPT:
A. Near the sensory decussation, its blood supply comes from the anterior spinal artery.
B. The medial lemniscus can be found in close proximity to the anterolateral tract in the medulla. Its somatotopy in the pons is such that leg fibers are lateral to arm fibers.
C. The fibers of the medial lemniscus arise from the cuneate and gracile nuclei.
D. Brainstem lesions involving medial lemniscus fibers usually include adjacent structures, resulting in motor and sensory losses.
E. None of the above statements are correct.
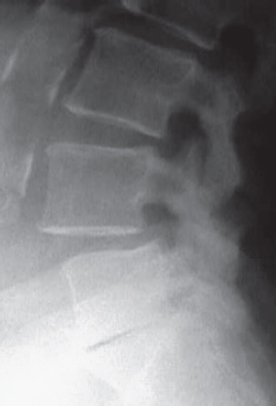
3. All the following findings are associated with the abnormality seen on the scan shown here EXCEPT:
A. Ankylosing spondylitis
B. Positive FABER test
C. Positive thigh thrust
D. Pain upon internal rotation of the hip
E. Positive thigh compression text
4. Which of the following lines at the craniocervical junction extends from the basion to the opisthion?
A. McRae’s line
B. McGregor’s line
C. Chamberlain’s line
D. Wackenheim’s line
E. Anterior marginal line
5. The somatotopic arrangement in the ventral horn is such that the
A. flexors are dorsal to extensors and limbs are medial to trunk.
B. extensors are dorsal to flexors and limbs are medial to trunk.
C. flexors are dorsal to extensors and limbs are lateral to trunk.
D. extensors are dorsal to flexors and limbs are lateral to trunk.
6. All of the following techniques may be used to aid in identifying the level of interest in a thoracic diskectomy procedure EXCEPT:
A. Intraoperative lateral fluoroscopy with counting levels starting from the sacrum and moving rostral with midline needle localizers
B. Intraoperative anteroposterior (AP) fluoroscopy with counting levels starting from the 12th rib and moving rostral with midline needle localizers
C. Intraoperative AP fluoroscopy with counting levels starting from the first rib and moving caudal with midline needle localizers
D. Neuronavigation with skin surface fiducial registration
E. Neuronavigation with spinal bony landmark registration within the proximity of the level of interest
7. The MRI scan shown here represents an opportunistic infection in a 25-year-old man with acute myelogenous leukemia. All the following statements are true EXCEPT:
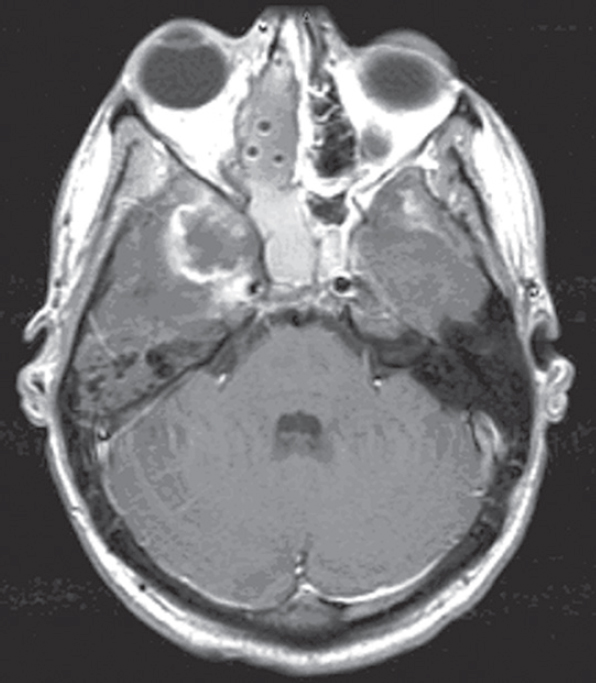
A. Pathology reveals pleomorphic short and wide septate hyphae.
B. It can be treated with Cancidas, voriconazole, and AmBisome.
C. It causes hemorrhagic necrosis and ischemic strokes.
D. The organism originates in the soil.
E. It may be seen with an immunocompromised patient.
8. Somatic motor efferents to the urethral sphincter are located in
A. intermediolateral cell columns of the sacral cord.
B. Onuf’s nucleus.
C. Barrington’s nucleus.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
9. Cerebral ischemia begins when cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) falls below
A. 100 mm Hg.
B. 75 mm Hg.
C. 50 mm Hg.
D. 23 mm Hg.
E. 8 mm Hg.
10. Regarding the anatomy near the cavernous sinus, the borders of the clinoidal triangle are cranial nerves
A. I and II.
B. II and III.
C. III and IV.
D. IV and V.
E. None of the above
11. Which of the following is FALSE regarding myasthenia gravis?
A. The first presentation is usually weakness of the extraocular muscles.
B. Weakness fluctuates and fatigues over the course of the day.
C. Speech may be hypernasal or hoarse in some patients.
D. It may present with a head drop.
E. Dysphagia is worst at breakfast and improves during the course of the day.
12. All of the following are true of polymyositis EXCEPT:
A. It involves a symmetric weakness of proximal limb and trunk muscles.
B. Its onset is insidious.
C. Ocular muscles are usually spared.
D. Muscles are not tender to palpation.
E. Skin changes typically occur before muscle abnormalities.
13. Protein 14-3-3 is elevated in the CSF in which of the following conditions?
A. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
B. Demyelinating disease
C. Head trauma
D. Meningoencephalitis
14. Which of the following statements is most accurate regarding the nerve supplying the teres minor muscle?
A. It has a contribution from the lateral cord.
B. It is an extension of the posterior cord.
C. Ventral rami C8 and T1 are major contributors to this nerve.
D. It is derived from the same cord as the musculocutaneous nerve.
E. None of the above
15. The pterion is formed by the junction of the all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Frontal bone
B. Sphenoid bone
C. Zygomatic bone
D. Temporal bone
E. Parietal bone
16. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the sonic hedgehog (SHH) gene?
A. SHH has been found to have the critical roles in development of the limb and midline structures in the brain and spinal cord.
B. Mutations in the human SHH gene, cause holoprosencephaly type 3 as a result of the loss of the ventral midline.
C. The SHH transcription pathway has been linked to the formation of embryonic cerebellar tumors such as medulloblastoma.
D. SHH has been shown to act as an axonal guidance cue: SHH attracts retinal ganglion cell axons at high concentrations and repels them at lower concentrations.
E. SHH plays a critical role in the induction of the floor plate and diverse ventral cell types within the neural tube.
17. Regarding infection in a trauma patient with the X-ray shown here, the most common pathogen is
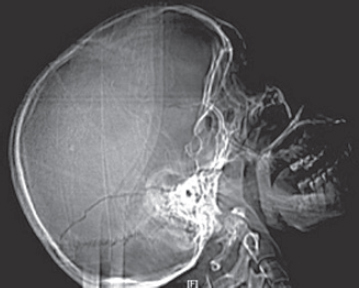
A. Staphylococcus aureus.
B. Pseudomonas.
C. Proteus.
D. Streptococcus pneumoniae.
18. Which of the following is incorrect regarding the zona incerta?
A. It is a zone of gray matter between the thalamic and lenticular fasciculi.
B. It is composed of cells that are continuous laterally with the thalamic reticular nucleus.
C. Unlike the thalamic reticular nucleus, the neurons of this zone do not display immunoreactivity for the calcium binding protein calbindin D-28k.
D. It receives corticofugal fibers from the precentral cortex.
E. All of the above statements are correct.
19. All the following are potential contraindications for vagal nerve stimulation placement EXCEPT:
A. Upper cranial nerve deficits
B. Presence of a single vagus nerve only
C. Cardiac arrhythmias
D. Lung disease
E. Ulcers
20. The anterior loop of the internal carotid artery lies in the floor of this triangle.
A. Lateral triangle
B. Anterior lateral triangle
C. Parkinson’s triangle
D. Anterior medial triangle
E. None of the above
21. Jitter is best described as
A. synchronous muscle fiber activation between fibers of different motor units.
B. a difference in timing of muscle fiber activation between two fibers in a single motor unit.
C. a difference in timing of muscle fiber activation between two fibers of different motor units.
D. the complete failure of neuromuscular transmission at one muscle fiber in a pair.
E. None of the above
22. Ataxia may be seen in all of the following syndromes EXCEPT:
A. Claude’s syndrome
B. Benedikt’s syndrome
C. Nothnagel’s syndrome
D. Basilar artery syndrome
23. Which of the following is the least common complication of vagal nerve stimulation placement in the pediatric population?
A. Hoarseness
B. Coughing
C. Shortness of breath
D. Nausea
E. Increased drooling
24. A lesion of which of the following structures would most significantly impair memory?
A. Amygdala
B. Fornix
C. Dorsomedial nucleus of the thalamus
D. Mammillary body
E. Area 44
25. Which of the following is NOT associated with the findings on this X-ray?
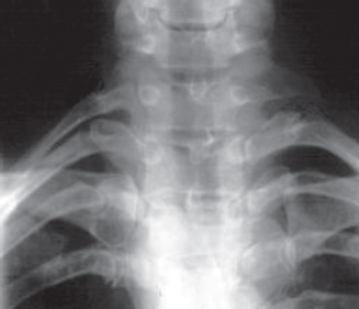
A. Weakness of hand intrinsic flexors
B. Horner’s syndrome
C. Raynaud’s syndrome
D. Traction meningocele
E. Ulnar paresthesias
26. Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome is associated with all the following EXCEPT:
A. Multiple subcutaneous lipomas
B. Macrocephaly
C. Hemangiomas
D. Intracranial arteriovenous malformations
E. Capillary malformation or “port-wine stain”
27. Where is the extreme capsule located?
A. Between the claustrum and the putamen
B. Between the claustrum and the insular cortex
C. Between the putamen and the globus pallidus externus
D. Between the globus pallidus externus and the globus pallidus internus
E. Above the caudate nucleus
28. Which of the following neurotransmitters promotes penile erection?
A. Serotonin
B. Dopamine
C. Noradrenaline
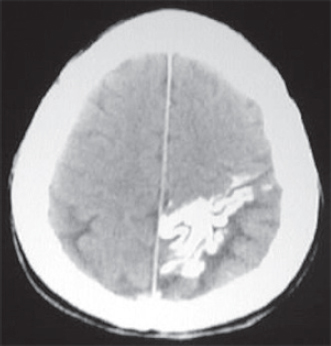
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
29. The peak reduction in intracranial pressure (ICP) after administration of mannitol occurs in about
A. 4 hours.
B. 2 hours.
C. 1 hour.
D. 30 minutes.
E. 15 minutes.
30. The borders of the paramedial triangle are cranial nerves
A. I and II.
B. II and III.
C. III and IV.
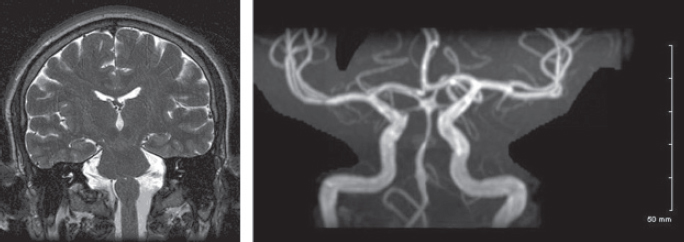
D. IV and V.
E. None of the above
31. The Tensilon test
A. is not sensitive but very specific for myasthenia gravis (MG).
B. is not particularly useful in ocular MG.
C. when negative, rules out the diagnosis of MG.
D. shows no correlation with subsequent response to pyridostigmine.
E. is not affected by the quantity of acetylcholine receptors.
32. In posterior interosseous syndrome, there is a fingerdrop but no wristdrop because of sparing of the
A. extensor carpi radialis longus.
B. extensor carpi radialis brevis.
C. extensor digitorum.
D. extensor carpi ulnaris.
33. What is the Spetzler–Martin grade of this arteriovenous malformation (AVM) found in a 30-year-old asymptomatic healthy patient?
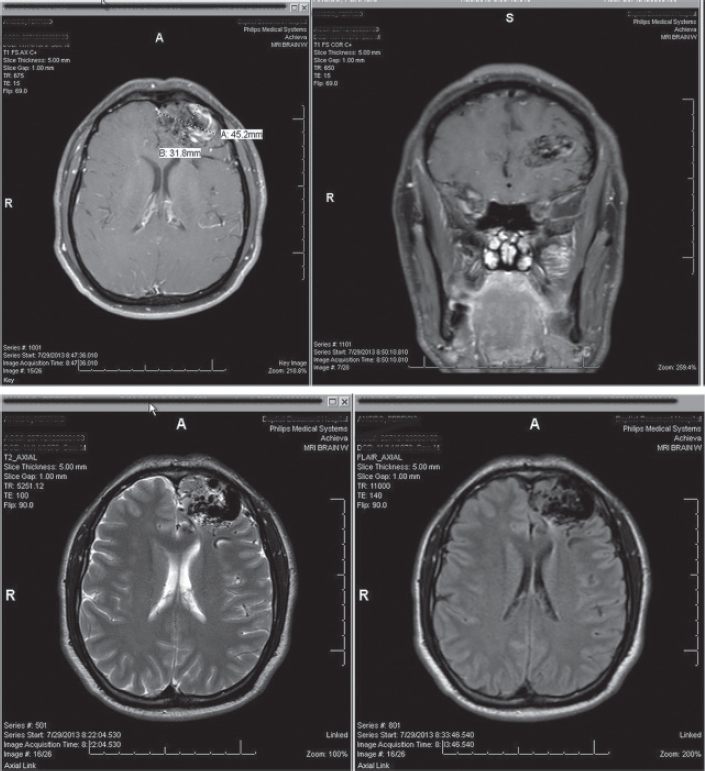
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
34. Interruption of the inferior geniculocalcarine fibers results in which of the following?
A. Ipsilateral superior quadrantanopia
B. Contralateral superior quadrantanopia
C. Ipsilateral inferior quadrantanopia
D. Contralateral inferior quadrantanopia
35. Which of the following may be seen with ocular myoclonus?
A. Vertical oscillation of the eyes occurring with movements of the palate
B. Hypertrophy of the inferior olivary nucleus
C. Prior lesions of the central tegmental tract
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
36. All of the following characterize Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) EXCEPT:
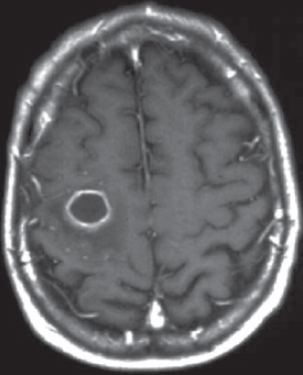
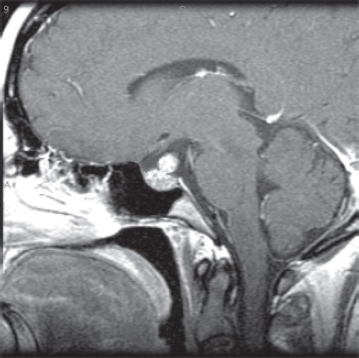
A. Late hypoxemia
B. Diffuse infiltrate
C. Leaky capillaries
D. Association with sepsis and trauma
E. Protein content of fluid greater than with pulmonary edema
37. In a healing wound, maximum collagen deposition occurs at
A. 2 weeks.
B. 4 weeks.
C. 6 weeks.
D. 8 weeks.
E. 10 weeks.
38. All of the following are true regarding the condition depicted by this histopathology EXCEPT:
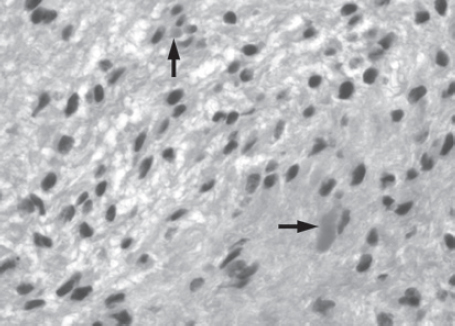
A. It is histologically characterized by a biphasic pattern.
B. Rosenthal fibers are a prerequisite for this diagnosis.
C. It may mimic oligodendroglioma.
D. It is a CNS neoplasm seen with neurofibromatosis type 1.
E. Recurrence is usually a reformation of the cyst rather than the solid tumor.
39. Barbiturates presumably act by which of the following mechanisms?
A. Inverse steal phenomenon
B. Decrease CMR
C. Decrease oxygen consumption
D. Scavenge free radicals
E. All of the above
40. Parkinson’s (infratrochlear) triangle is defined by cranial nerves
A. II and III.
B. III and IV.
C. IV and V1.
D. V1 and V2.
E. V2 and V3.
41. Which of the following is true of myasthenia gravis?
A. The majority of acetylcholine receptor antibodies are of the M subtype.
B. Cyclosporine is used as a first-line treatment.
C. Corticosteroids may reduce the risk of secondary generalization in the ocular form.
D. Pathological abnormalities of the thymus are found in less than 5% of patients.
E. Weakness confined to the ocular muscles beyond 3 years is associated with poor prognosis.
42. The border of the foramen lacerum is formed by the
A. sphenoid bone.
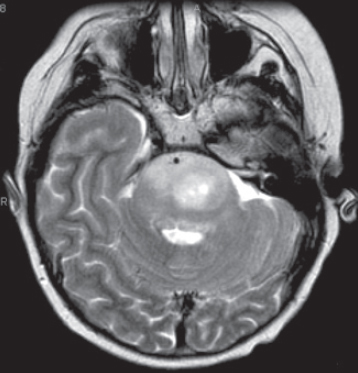
B. temporal bone.
C. sphenoid and temporal bones.
D. sphenoid, temporal, and occipital bones.
E. occipital bone.
43. Absence of inflammation is typical of the following diseases EXCEPT:
A. Neuropathy from diphtheria
B. Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease
C. Paraneoplastic necrotizing myelopathy
D. Central pontine myelinolysis
E. Tolosa–Hunt syndrome
44. Wernicke’s area is BEST described as including
A. area 39.
B. supramarginal, area 40, and posterior one-third of the superior temporal gyri.
C. angular and posterior one-third of the superior temporal gyri.
D. areas 39 and 40.
E. supramarginal and posterior one-third of the superior temporal gyri.
45. Anti-pause cell antibody may be seen with childhood infections or paraneoplastic syndrome in adults. Immune-mediated defects in pause cell function most likely result in
A. opsoclonus.
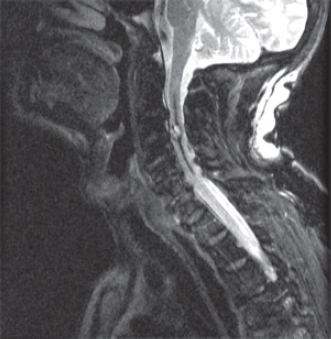
B. square wave jerks.
C. downbeat nystagmus.
D. upbeat nystagmus.
E. None of the above
46. The origin of axons that mediate the swallowing reflex is the
A. solitary nucleus.
B. dorsal motor nucleus of X.
C. nucleus ambiguus.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
Match these MRI scan findings with the following comments:
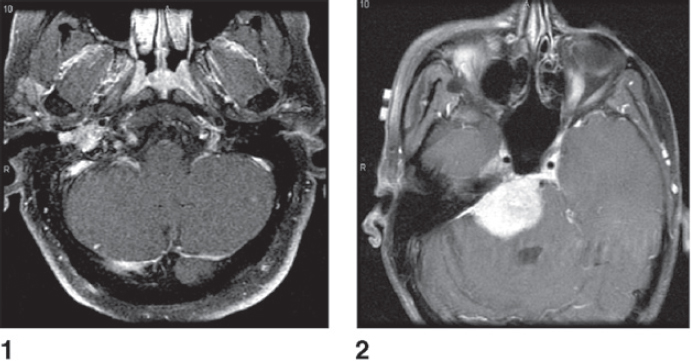
A. Scan 1
B. Scan 2
C. Both scans 1 and 2
D. Neither scan 1 nor scan 2
47. Hypertension
48. Early facial nerve involvement
49. Hypotension and bronchoconstriction during resection
50. Explosive diarrhea
51. Early hearing loss and tinnitus
52. Laboratory manifestations of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) include all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Increased fibrinogen level
B. Prolonged PT
C. Prolonged PTT
D. Thrombocytopenia
E. Fragmented RBCs
53. The mastoid air cells are innervated by
A. V1.
B. V2.
C. V3.
D. IX.
E. X.
54. Which of the following statements is most accurate regarding the band of Gennari?
A. It divides the third layer of the cortex of areas 17 and 18.
B. It divides the third layer of the cortex of area 17.
C. It divides the fourth layer of the cortex of areas 17 and 18.
D. It divides the fourth layer of the cortex of area 17.
E. It divides the fourth layer of the cortex of areas 17, 18, and 19.
55. The following are prenuclear structures for vertical gaze EXCEPT:
A. Nucleus of Darkshevich
B. Posterior commissure
C. Interstitial nucleus of Cajal
D. Rostral interstitial nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF)
E. Nucleus prepositus hypoglossi
56. Which of the following neurons or nerve cell processes is/are particularly involved with new, novel movements?
A. Mossy fibers
B. Betz cell
C. Climbing fibers
D. All of the above
57. Which of the following disease states is characterized by high trophic hormone and low target hormone?
A. Cushing’s disease
B. Graves’s disease
C. Adrenal tumors
D. Addison’s disease
E. None of the above
58. Which of the following intrinsic muscles of the thumb does NOT insert on the proximal phalanx?
A. Adductor pollicis
B. Abductor pollicis brevis
C. Flexor pollicis brevis
D. Opponens pollicis
E. Extensor pollicis brevis
59. Which of the following statements is FALSE with regard to the scan shown here?
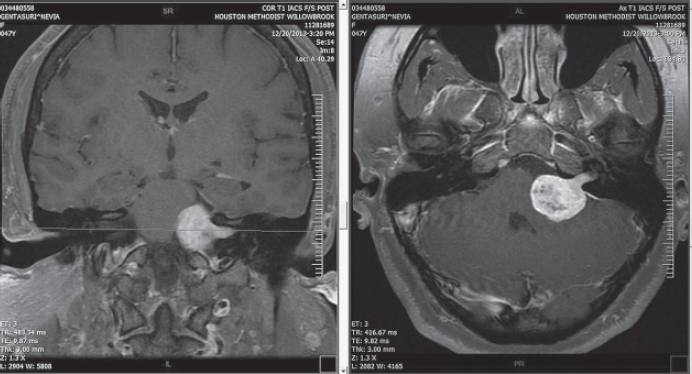
A. The first symptom in 90% of patients is unilateral hearing loss.
B. Headaches, clumsy gait, and mental confusion may occur.
C. The seventh cranial nerve is frequently involved preoperatively.
D. Essentially everyone who has been treated for an acoustic neuroma experiences difficulty with balance and/or dizziness to some degree.
E. Sporadic defects in tumor suppressor genes may give rise to these tumors.
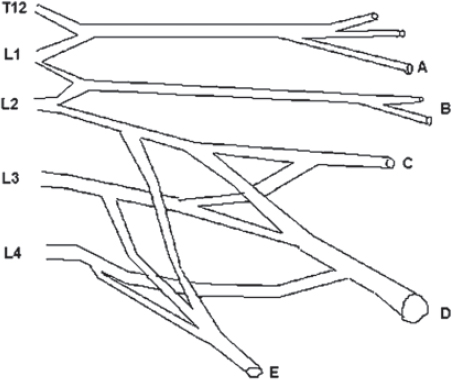
Match these brachial plexus structures with the appropriate letter in the diagram:
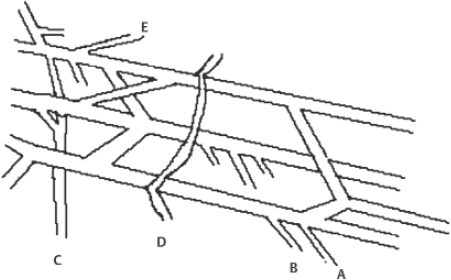
60. Medial brachial cutaneous nerve
61. Long thoracic nerve
62. Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve
63. Suprascapular nerve
64. Median pectoral nerve
65. The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is responsible for the binocular coordination of the following eye movements EXCEPT:
A. Lateral
B. Vertical
C. Vergence
D. Oblique
E. Horizontal
66. Which of the following is a distinguishing factor between Apert’s and Crouzon’s syndrome?
A. Pattern of inheritance
B. Association with bilateral coronal synostosis
C. Severity of mental retardation
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
67. TRH is a secretagogue for
A. prolactin.
B. ACTH.
C. GH.
D. TSH.
68. Which of the following nerves is responsible for movement of the ring finger?
A. Radial only
B. Radial and median
C. Radial, median, and ulnar
D. Radial, median, and axillary
E. Musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar
69. Which of the following immunohistochemical profiles has been shown to be expressed in 100% of primary glioblastoma?
A. Survivin
B. MMP-9
C. EGFR
D. MDM2
E. Fas (APO-1/CD95)
70. This triangle is defined laterally by the greater superficial petrosal nerve and medially by the petrosal sinus.
A. Lateral triangle
B. Paramedial triangle
C. Glasscock’s triangle
D. Kawase’s triangle
E. Parkinson’s triangle
71. Which is FALSE regarding the hormone prolactin (PRL)?
A. Its releasing hormone is located in the arcuate nucleus.
B. Normal levels are 5–25 ng per mL.
C. Levels may be increased after syncope.
D. Levels are increased after tonic clonic seizure activity.
E. Levels are increased after nonepileptic seizures.
72. Which of the following circumventricular organs is a central receptor site for angiotensin II?
A. Organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis
B. Median eminence of the tuber cinereum
C. Subcommissural organ
D. Subfornical organ
E. Area postrema
73. All of the following are true of the sinuvertebral nerve EXCEPT:
A. It is a branch from the posterior division of the spinal nerve proximal to the dorsal root ganglion.
B. It may enter the intervertebral foramen.
C. It supplies most of the innervation to the posterior aspect of the disk.
D. It may have a proprioceptive and/or nociceptive function.
E. It has been shown to consist of two roots at cervical levels.
74. All of the following are true of conduction aphasia EXCEPT:
A. It is caused by a lesion of the arcuate fasciculus.
B. There is fluent paraphasic speech with intact repetition.
C. It may be caused by occlusion of a middle cerebral artery(MCA) posterior temporal branch.
D. Patients may mimic Wernicke’s disease, but are able to understand.
E. Patients are aware of the problem.
75. Which statement is true about the aneurysm shown here?
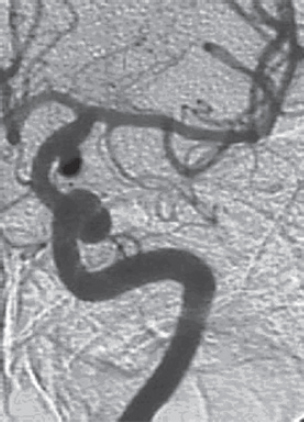
A. It arises from the cavernous internal carotid artery.
B. It measures ~6–8 mm.
C. It usually presents pituitary dysfunction.
D. All of the above statements are true.
E. None of the above statements are true.
76. What does the Torg-Pavlov ratio measure?
A. Vertebral blood flow
B. Carotid blood flow
C. Cervical stenosis
D. Thoracic stenosis
77. Which of the following is FALSE when comparing primary and secondary glioblastoma?
A. Primary glioblastoma has an incidence that is about 10 times higher than secondary glioblastoma.
B. The mean age at presentation in primary glioblastoma is much younger (45 years) than in secondary glioblastoma (62 years).
C. Primary glioblastoma is more common in males when compared with secondary glioblastoma.
D. The median survival at presentation is longer in secondary glioblastoma as compared with primary glioblastoma.
E. Loss of heterozygosity on 10p or 10q is one of the most common genetic mutations in primary glioblastoma.
78. Cell bodies of nerve fibers in the medial brachial cutaneous nerve are found in the
A. dorsal root ganglia only.
B. anterior horn only.
C. sympathetic chain ganglia and dorsal root ganglia.
D. lateral horn and sympathetic chain ganglia.
E. None of the above
79. The perforant path is the main
A. inhibitory pathway of the hippocampus.
B. excitatory pathway of the hippocampus.
C. inhibitory pathway of the hypothalamus.
D. excitatory pathway of the hypothalamus.
E. None of the above
80. Which triangle has its base at the petrous apex?
A. Parkinson’s triangle
B. Kawase’s triangle
C. Glasscock’s triangle
D. Inferior medial triangle
E. Paramedial triangle
81. The most common type of headache is
A. cluster.
B. tension.
C. migraine.
D. postconcussive.
82. The trochlear nerve can be found in which cistern?
A. Cerebellomedullary
B. Interpeduncular
C. Ambient
D. Chiasmatic
E. Pontine
83. Which scalene muscle(s) insert on the first rib?
A. Anterior scalene
B. Anterior and medial
C. Medial and posterior
D. Anterior and posterior
E. Anterior, medial, and posterior
84. A lesion of the left geniculocalcarine tract and the corpus callosum is most likely to cause
A. pure word blindness.
B. pure word deafness.
C. mutism.
D. anomic aphasia.
E. global aphasia.
85. All of the following are true regarding hemispherectomy EXCEPT:
A. Improvement in IQ is often seen postoperatively.
B. Behavior is improved after surgery.
C. It is not necessary to preserve the septum pellucidum.
D. The foramen of Monro is often plugged with a piece of temporalis muscle.
E. Patients are usually uncommunicative for about a week after surgery.
86. The principle behind multiple subpial transection for epilepsy is that
A. horizontal fibers have a limited functional role.
B. vertical fibers have a limited functional role.
C. the pia has a limited functional role.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
87. The presenting symptom of a hypothalamic hamartoma is most commonly
A. headache.
B. vomiting.
C. visual field disturbance.
D. sexual precocity.
88. All of the following are true of the tumor in this pathology slide EXCEPT:
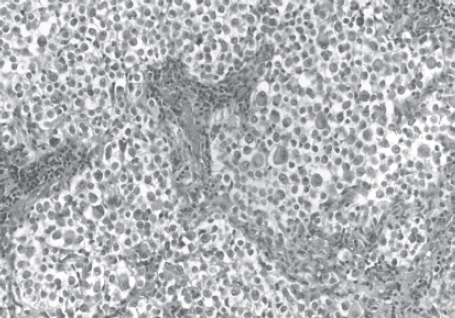
A. It is found in superficial brain regions.
B. It shows intracellular accumulation of lipids.
C. It corresponds to WHO grade II.
D. It carries a dismal prognosis.
E. It presents in patients with a long history of seizures.
89. Schaffer collaterals carry
A. excitatory input from CA1.
B. excitatory input from CA3.
C. inhibitory input from CA1.
D. inhibitory input from CA3.
90. Which of the following muscles would you expect to find weak given the finding on this scan?
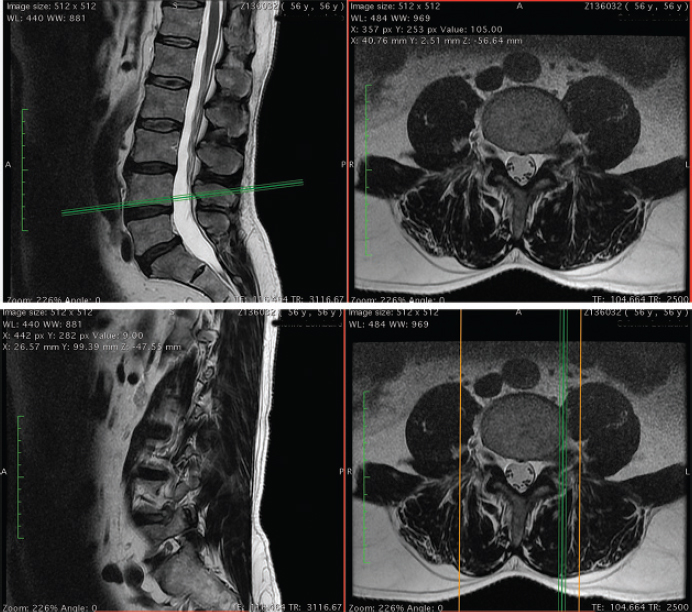
A. Gastrocnemius
B. Tibialis anterior
C. Extensor hallucis longus
D. Iliopsoas
E. None of the above
91. Which is the optimal approach for resection of the lesion in the scan shown previously for Question 90?
A. Midline laminectomy approach
B. Paramedian partial facetectomy approach
C. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion
D. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion
E. A and C
92. All of the following structures are supplied by the anterior spinal artery EXCEPT:
A. Pyramids
B. Medial lemniscus
C. Fibers of cranial nerve XII
D. Gracile and cuneate nuclei
E. Anterior two-thirds of the spinal cord
93. During a clinic appointment, the patient is asked to sit with the arms dependent, hold her breath, and tilt her head back and turn it to the side. Meanwhile the doctor is checking for presence or absence of a radial pulse. What is being described?
A. Allen’s test
B. Ayer’s test
C. Adson’s test
D. Addis test
E. Dix–Hallpike maneuver
94. The corticobulbar tract is located in which area of the internal capsule?
A. Anterior limb
B. Posterior limb
C. Retrolenticular limb
D. Sublenticular limb
E. Genu
95. The medial forebrain bundle interconnects the following areas EXCEPT:
A. Septal nuclei
B. Raphe nuclei
C. Locus ceruleus
D. Medulla
E. Hypothalamus
96. Cerebellar tonsillar displacement is seen in
A. Chiari I.
B. Chiari II.
C. Crouzon’s syndrome.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
97. The most severe forms of hypothalamic cachexia are seen in lesions of the
A. lateral hypothalamus.
B. anterior hypothalamus.
C. posterior hypothalamus.
D. ventromedial hypothalamus.
E. suprachiasmatic hypothalamus.
98. The region of the cortex most closely associated with the conscious perception of smell is the
A. temporal cortex.
B. cingulate cortex.
C. prefrontal cortex.
D. posterior parietal cortex.
99. Which amino acids are precursors for catecholamines?
A. Phenylalanine and tyrosine
B. Phenylalanine and tryptophan
C. Tyrosine and tryptophan
D. Arginine and tyrosine
E. Phenylalanine and arginine
100. Which of the following pathological diagnoses is most likely associated with this hemorrhagic lesion?
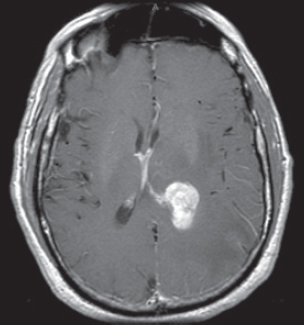
A. Melanoma
B. Choriocarcinoma
C. Breast carcinoma
D. Renal cell carcinoma
E. Choroid plexus papilloma
101. In contrast to primary glioblastomas, the most common genetic mutation seen in secondary glioblastomas is
A. loss of heterozygosity 10q.
B. TP53 mutation.
C. EGFR amplification.
D. p16INK4a deletion.
E. PTEN mutations (25%).
102. The straight sinus is formed from the union of the
A. internal cerebral vein and basal vein.
B. inferior sagittal sinus and vein of Galen.
C. basal vein and great cerebral vein.
D. inferior sagittal vein and basal vein.
E. precentral cerebellar vein and internal cerebral vein.
103. A lesion of the vestibular labyrinth that causes images in the visual fields to move back and forth is best described as
A. ocular flutter.
B. ocular dysmetria.
C. ocular bobbing.
D. oscillopsia.
E. opsoclonus.
104. Atropine mainly affects which type of synapses?
A. Parasympathetic preganglionic
B. Parasympathetic postganglionic
C. Sympathetic postganglionic
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
105. Wernicke’s encephalopathy is due to deficiency of
A. vitamin B1.
B. vitamin B2.
C. vitamin B6.
D. vitamin B12.
E. None of the above
106. The solitary pathways are concerned with
A. taste.
B. thoracic viscera.
C. sudden changes in blood pressure.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
107. The greatest difference between diffuse astrocytomas (WHO grade II) and anaplastic astrocytomas (WHO grade III) is
A. MIB-1 fraction.
B. the presence of mitotic activity.
C. the presence of necrosis.
D. angiogenesis.
E. the presence of gemistocytes.
108. The most common intraconal orbital mass is the
A. neurilemmoma.
B. fibrous histiocytoma.
C. hemangiopericytoma.
D. cavernous hemangioma.
109. HIV-infected individuals have an increased risk of cerebrovascular events, such as stroke, when the following risk factors are present EXCEPT:
A. Intravenous drug abuse
B. Low CD4 cell count
C. Exposure to abacavir
D. Exposure to highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)
E. CD4 cell count ≤ 200 cells/μL before the start of HAART
110. The location of the apex in most arteriovenous malformations is
A. cortical.
B. insular.
C. parietal.
D. occipital.
E. periventricular.
111. In catecholamine biosynthesis, the rate-limiting step during conditions of neuronal activation is
A. dopamine β-hydroxylase.
B. tyrosine hydroxylase.
C. aromatic amino acid decarboxylase.
D. monoamine oxidase.
E. phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase.
112. The venous angle is seen angiographically by the junction of which two veins?
A. Septal and caudate
B. Septal and terminal
C. Terminal and caudate
D. Internal cerebral and terminal
E. Basal and internal cerebral
113. Ocular bobbing may be seen in which of the following?
A. Hydrocephalus
B. Pontine infarct
C. Hepatic encephalopathy
D. Trauma
114. The most likely diagnosis for this lesion seen on CT is
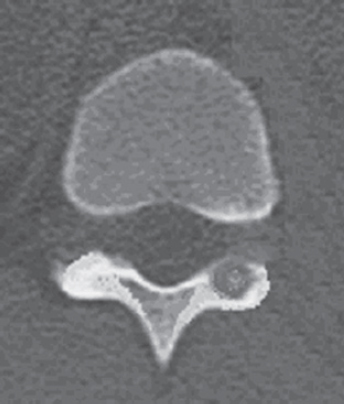
A. aneurysmal bone cyst.
B. epidermoid granuloma.
C. osteosarcoma.
D. hemangioma.
E. osteoid osteoma.
115. The striae medullares (rhombencephali) arise from
A. the septal nuclei.
B. the habenular trigone.
C. the arcuate nuclei.
D. the amygdala.
E. None of the above
116. The delivery of nutrients and removal of wastes from the vertebral disk is dependent on
A. arterioles and venules.
B. capillaries penetrating the disk.
C. diffusion.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
117. Which of the following statements is true of the olivocochlear bundle?
A. It is part of the ascending auditory pathway to the dorsal cochlear nucleus.
B. It can be seen readily in brainstem sections of the upper pons.
C. It communicates directly with the medial lemniscus.
D. Stimulation of it inhibits acoustic fiber responses to auditory stimuli.
E. It arises from the inferior olivary nucleus and projects to the cochlea.
118. Which of the following orbital tumors is at highest risk of tumor seeding and recurrence during removal?
A. Cavernous hemangioma
B. Pleomorphic adenoma of the lacrimal gland
C. Neurilemmoma
D. Hemangiopericytoma
E. Fibrous histiocytoma
119. The pterygoid plates are made up of which bones?
A. Sphenoid and temporal
B. Sphenoid and vomer
C. Palatine and sphenoid
D. Palatine
E. None of the above
120. Brodmann area 44 is a part of
A. Wernicke’s area.
B. Visual cortex.
C. Broca’s area.
D. Prefrontal area.
E. Frontal eye field.
121. Which one of the following is NOT a characteristic of hydromyelia?
A. The fluid collection may communicate with the fourth ventricle.
B. The fluid collection may be noncommunicating with the fourth ventricle.
C. The fluid collection is typically not lined by ependymal cells.
D. It may be associated with hydrocephalus.
E. It may be associated with Chiari malformation.
122. Which of the following arteries supplies the deep cerebellar nuclei?
A. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery
B. Superior cerebellar artery
C. Thalamogeniculate branches
D. Posterior choroidal artery
E. None of the above
123. In the comatose patient, extensor movements of the arms and weak flexor movements of the legs are most likely to occur with a lesion
A. above the red nucleus.
B. at the red nucleus.
C. between the red nucleus and above the vestibular nuclei.
D. at the vestibular nuclei.
E. below the vestibular nuclei.
124. “Crocodile tears” or lacrimation from gustatory stimulation is classically described as the result of aberrant regeneration of fibers from
A. cranial nerve III reaching the ciliary ganglion.
B. cranial nerve V reaching the ciliary ganglion.
C. cranial nerve VII reaching the ciliary ganglion.
D. cranial nerve III reaching the sphenopalatine ganglion.
E. cranial nerve VII reaching the sphenopalatine ganglion.
125. Syringomyelia affecting the lower cervical area may result in attenuation or abolition of which of the following somatosensory evoked potentials?
A. N13
B. N20
C. P40
D. N22
E. None of the above
126. If an instrumentation system is too stiff, disuse osteoporosis can occur around the instrumentation. This statement is related to
A. Sherrington’s law.
B. Flourens’ law.
C. Wolff’s law.
D. Delpech’s principle.
E. Jackson’s law.
127. In comparison to chordomas, chondrosarcomas
A. arise more laterally.
B. result in more neurological deficits at presentation.
C. are nearly always S-100 positive.
D. display all of the above features.
E. display none of the above features.
128. Which of the following conditions would benefit most from thalamotomy?
A. Medically refractory essential tremor
B. Rigidity associated with Parkinson’s disease
C. Intention tremor from cerebellar stroke
D. Bradykinesia associated with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP)
E. Dyskinesia associated with striatonigral degeneration
129. Which of the following is the best measure of the “equator” of the spinal cord when performing a cordotomy for pain management?
A. Just ventral to the dentate ligament
B. Just dorsal to the dentate ligament
C. At the attachment of the dentate ligament
D. The midway point between the exit of the dorsal and ventral rootlets
E. Approximately 5 mm from the anterior spinal artery
130. When is the earliest time after radiation therapy that one would expect to observe the changes appearing on this T2-weighted MRI taken in a patient who underwent a tumor resection?
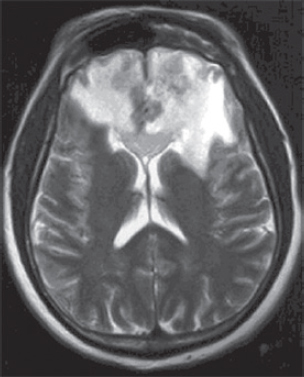
A. 1 month
B. 3 months
C. 14 months
D. 48 months
E. 72 months
131. Levels of L-dopa are virtually unmeasurable in the central nervous system under basal conditions because
A. the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase is low.
B. L-dopa is localized in vesicles.
C. the activity of aromatic amino acid decarboxylase is high.
D. dopamine β hydroxylase is localized in the vesicles.
E. the activity of tyrosine hydroxylase is high.
132. The facial nucleus and the spinal trigeminal nucleus and tract are supplied by which artery?
A. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)
B. Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)
C. Superior cerebellar artery (SCA)
D. Basilar
133. Which of the following statements regarding the length constant of a nerve fiber is true?
A. The length constant is directly proportional to the membrane resistance.
B. It is the distance along a fiber where a change in the membrane potential by a given current decays to half its original value.
C. The length constant is directly proportional to the axial resistance.
D. The length constant is greater in unmyelinated than myelinated fibers.
E. None of the above
134. Dysfunction of which cell is the main problem in Raynaud’s phenomenon?
A. Red blood cell
B. Sympathetic neuron
C. Platelet
D. Mast cell
E. Fibroblast
135. Epidural hematomas in children are the result of
A. arterial injury.
B. bone oozing.
C. bleeding from the periosteal surface.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
136. Spondylolysis most often occurs at
A. L1.
B. L2.
C. L3.
D. L4.
137. The finding seen in the photograph is caused by damage to
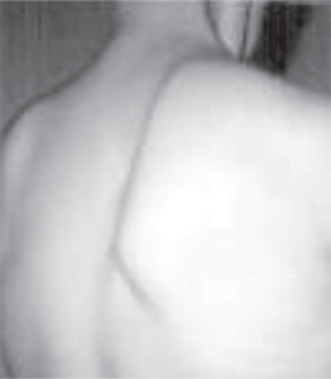
A. a nerve arising from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus.
B. a nerve arising from the roots of the brachial plexus.
C. the dorsal scapular nerve.
D. the thoracodorsal nerve.
E. None of the above
138. The typical target for thalamotomy for reduction of tremor is
A. Vim.
B. Vop.
C. Voa.
D. VC.
E. None of the above
139. Which of the following structures are derived from the telencephalon?
A. Caudate
B. Putamen
C. Amygdala
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
140. The precuneus (Brodmann areas 7 and 31) is located
A. on the medial surface of the frontal lobe.
B. in the secondary visual cortex.
C. within the occipital lobe.
D. on the medial surface of the parietal lobe.
E. on the medial surface of the occipital lobe.
141. Given the imaging provided, the indications for surgery include all of the following EXCEPT:
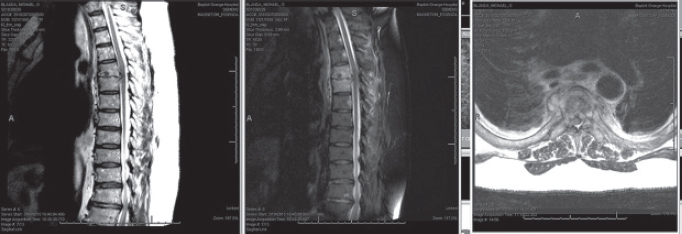
A. Failure of medical treatment
B. Open biopsy
C. Significant bony or paraspinal abscess with sepsis
D. Significant bony destruction on CT scan due to limited penetration of medical treatment
E. Sensory deficit along the rib cage
142. Neural crest derivatives include all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Schwann cells
B. Bipolar cells
C. Leptomeninges
D. Chromaffin cells of the suprarenal medulla
E. Parafollicular cells
143. Which of the following is located in the bony modiolus of the cochlea?
A. Scala vestibuli
B. Cochlear duct
C. Organ of corti
D. Spiral ganglion
E. Basilar membrane
144. Damage to this area leaves the patient transiently mute, with complete recovery in a few weeks.
A. Broca’s area
B. Wernicke’s area
C. Arcuate fasciculus
D. Uncinate fasciculus
145. The foramen spinosum is located in
A. the sphenoid bone anterior to the greater and lesser superficial petrosal nerves.
B. the sphenoid bone between to the greater and lesser superficial petrosal nerves.
C. the temporal bone posterior to the greater and lesser superficial petrosal nerves.
D. the temporal bone between the greater and lesser superficial petrosal nerves.
E. None of the above
146. Spondyloptosis corresponds to Meyerding grade
A. I.
B. II.
C. III.
D. IV.
E. V.
147. Golgi tendon organs are
A. sensitive to stretch.
B. in series with extrafusal fibers.
C. encapsulated.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
148. During a thalamotomy procedure, which of the following indicates that the electrode is in the correct location?
A. Low frequency (2 Hz) stimulation causes driving of the tremor.
B. The patient reports contralateral paresthesias.
C. High-frequency (50 Hz) stimulation results in tremor suppression.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
149. Olfactory glomeruli are made up of
A. granule and tufted cells.
B. granule and mitral cells.
C. tufted and mitral cells.
D. granule cells only.
E. None of the above
150. The sylvian triangle is defined by points along which artery/arteries?
A. MCA only
B. MCA and ACA
C. ACA, MCA, and PCA
D. MCA and PCA
151. Select the FALSE statement regarding monoamine oxidase (MAO).
A. MAOA has a high affinity for norepinephrine and serotonin.
B. MAOA is selectively inhibited by clorgyline.
C. MAOB has a high affinity for o-phenylethylamines.
D. MAOA and MAOB are associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane.
E. MAOB is selectively inhibited by deprenyl.
152. The superior part of the fourth ventricle is derived from which of the following vesicles?
A. Metencephalon
B. Myelencephalon
C. Mesencephalon
D. Prosencephalon
E. None of the above
153. This structure is a projection of the spiral limbus that overlies the hair cells of the organ of Corti.
A. Tectorial membrane
B. Basilar membrane
C. Vestibular membrane
D. Reissner’s membrane
E. None of the above
154. Which fibers are associated with the gag reflex?
A. Spinal trigeminal nucleus projections to the nucleus ambiguus
B. Solitary projections to the nucleus ambiguus
C. Solitary projections to the salivatory nucleus
D. Salivatory nucleus projections to the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
155. A 64-year-old man presents to the clinic with severe back pain going down the left lateral leg (see X-ray). He states that the pain is worst when he reaches and bends to the right. He is most comfortable when he is lying still. He has attempted and failed conservative therapy of medication and physical therapy. If surgery is offered, what would be the best choice from the following options?
A. Lumbar laminectomy of L4–S1
B. Lumbar hemilaminectomy at L4 on left side
C. Pedicle screw fusion of L4–L5
D. Pedicle screw fusion of L3–S1
E. Pedicle screw fusion of L3–L4
156. Which of the following receptors is activated by baclofen and is insensitive to bicuculline?
A. GABA-A
B. GABA-B
C. GABA-C
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
157. All of the following structures pass through the annulus of Zinn (tendinous ring) EXCEPT:
A. Cranial nerve III, superior division
B. Nasociliary nerve
C. Cranial nerve IV
D. Cranial nerve III, inferior division
Match the organisms associated with the lesion shown here, given the patient presentation:
A. Proteus
B. Streptococcus
C. Staphylococcus
D. Pseudomonas
158. Sixteen year-old boy who sustained a parietal skull fracture after a motorcycle accident
159. Sixty-year-old woman with chronic ear infection
160. Three-month-old baby with irritability and decreased oral intake
161. Tranylcypromine is
A. an inhibitor of MAOA.
B. an inhibitor of MAOB.
C. an inhibitor of COMT.
D. a reuptake inhibitor of serotonin.
E. an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase.
162. Which is the embryological structure that becomes the ventral white commissure in the adult?
A. Basal plate
B. Floor plate
C. Alar plate
D. Basal plate
163. Which of the following is FALSE regarding the syndrome that has a prominent feature illustrated in this CT scan?
A. There is involvement of the upper eyelid.
B. Radiotherapy is not effective.
C. Hemiparesis is contralateral to the facial lesion.
D. The triad classically consists of nevus flammeus, venous malformation, and glaucoma.
E. Abnormalities of chromosome 9 are seen.
164. CSF is produced by
A. choroid plexus.
B. ependymal surface.
C. brain parenchyma.
D. bulk flow from the brain.
E. All of the above
165. In patients with known systemic cancer, what percentage of single brain lesions are cerebral abscesses or primary brain tumors?
A. Less than 0.1%
B. 1%
C. 15%
D. 30%
E. 50%
166. Vigabatrin has anticonvulsant properties related to its interference of
A. GABA breakdown.
B. GABA synthesis.
C. GABA reuptake.
D. All of the above
167. The indusium griseum is a remnant of
A. the habenula.
B. the hippocampus.
C. the hypothalamus.
D. the gyrus of Heschl.
E. None of the above
168. A patient who had a thalamotomy for Parkinsonian tremor earlier in the month has noticed weakness of the arm. The most likely explanation for this is that the lesion placed during the thalamotomy was too
A. medial.
B. lateral.
C. anterior.
D. posterior.
E. mild.
169. Which immunosuppressive agent works at the level of the T cells by inhibiting expression of interleukin (IL)-2?
A. Azathioprine
B. Cyclosporine
C. Methotrexate
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
170. Posterior thalamo-perforating arteries are the perforators that arise from which artery?
A. Pcom
B. Pcom and P1
C. P1 and P2
D. P2
E. P1
171. Which nucleus of the hypothalamus gives rise to dopamine innervation of the median eminence?
A. Supraoptic
B. Dorsomedial
C. Lateral
D. Arcuate
E. Ventromedial
172. The alar plate gives rise to all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Gracile and cuneate nuclei
B. Inferior olivary nuclei
C. Solitary nucleus
D. Spinal trigeminal nucleus
173. Normal thoracic kyphosis is generally accepted to vary from
A. 10–35°.
B. 20–45°.
C. 30–55°.
D. 40–65°.
E. 50–70°.
174. In preparation for placement of a ventriculostomy catheter, a resident measures a point 2.5 cm from the midline and 1 cm anterior to the coronal suture. The point that is being measured is
A. Keen’s point.
B. Kocher’s point.
C. McEwen’s point.
D. Barker’s point.
E. Sylvian point.
175. A 60-year-old man with this MRI finding is most likely to present with the following signs on examination:
A. Bilateral limb ataxia
B. Ipsilateral Horner’s syndrome
C. Contralateral abducens palsy
D. Ipsilateral tongue paralysis
E. None of the above
176. All of the following epilepsy drugs have hepatic enzyme-inducing properties EXCEPT:
A. Carbamazepine
B. Phenytoin
C. Clonazepam
D. Primidone
177. The interposed nuclei project to
A. the contralateral red nucleus.
B. the ipsilateral red nucleus.
C. the contralateral thalamus.
D. the ipsilateral thalamus.
E. None of the above
178. All of the following symptoms may improve after pallidotomy EXCEPT:
A. Drug-induced dyskinesias
B. Painful dystonias
C. On/off fluctuations
D. Bradykinesia
E. Postural instability
179. With regard to neurological manifestations of HIV disease, which of the following is true?
A. Neurological involvement in HIV infection is more frequent in adults than in children.
B. Neurological complications occur in less than 20% of patients with HIV infection.
C. Neurological complications are the presenting feature of AIDS in 20% of cases.
D. At autopsy, the prevalence of neuropathological abnormalities is ~20%.
E. An ongoing increase in HIV-associated CNS disease has been observed in very recent years
180. AICA originates from the
A. vertebral artery.
B. distal one-third of the vertebral artery.
C. proximal two-thirds of the basilar artery.
D. posterior cerebral artery.
E. distal two-thirds of the basilar artery.
181. Which is FALSE regarding serotonin?
A. It is metabolized to melatonin in the pineal gland.
B. The majority of body stores of serotonin are found in the central nervous system.
C. Two critical enzymes take part in its synthesis.
D. Tryptophan is the precursor amino acid.
E. It has an indole structure.
182. The basal plate gives rise to all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Oculomotor nucleus
B. Trochlear nucleus
C. Substantia nigra
D. Red nucleus
183. Which of the following are more expressed in painful degenerative disk disease as compared with disk herniation?
A. Tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin (IL)-8
B. IL-1β and IL-6
C. IL-6 and IL-12
D. IL-3 and IL-4
E. None of the above
184. During the abdominal portion of the operation for a ventroperitoneal (VP) shunt, if the surgeon is below the arcuate line, which structures would lie behind the rectus abdominis?
A. External oblique aponeurosis
B. Internal oblique aponeurosis
C. Transversus abdominis aponeurosis
D. Transversalis fascia
E. None of the above
185. Which of the following posterior fossa tumors has the tendency to arise from the floor of the fourth ventricle?
A. Medulloblastoma
B. Ependymoma
C. Astrocytoma
D. Hemangioblastoma
E. None of the above
186. Which of the following is true of Lissauer’s tract?
A. Its fibers are derived from the lateral division of the dorsal roots.
B. It contains Aδ fibers.
C. It contains C fibers.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
187. The limen insula can be found
A. in the occipital lobe.
B. at the junction of the insula and the frontal lobe.
C. within the third ventricle.
D. in cross sections through the pons.
E. in none of the above.
188. During pallidotomy when the surgeon believes the electrode is near the target, a high-frequency stimulation is performed to insure that the electrode is not too close to the
A. thalamus.
B. internal capsule.
C. optic tract.
D. amygdala.
189. The apex of the thoracic curvature typically lies at
A. T3.
B. T5.
C. T7.
D. T9.
E. T11.
190. An important landmark for identifying the junction of the tegmentum and the cerebral peduncle is the
A. anterior pontomesencephalic vein.
B. lateral mesencephalic vein.
C. precentral cerebellar vein.
D. vein of Galen.
E. superior vermian vein.
191. This amino acid is not only a precursor to GABA but is also a neurotransmitter.
A. Glycine
B. Glutamate
C. Arginine
D. Tyrosine
E. Tryptophan
192. Which of the following is FALSE regarding stiff person syndrome?
A. It is transmitted in an autosomal recessive pattern.
B. The stiffness primarily affects the truncal muscles.
C. Chronic pain and impaired mobility are common symptoms.
D. Lumbar hyperlordosis is often seen.
E. Patients have high glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody titers.
193. All of the following inflammatory factors are expressed at high levels in degenerative disk disease EXCEPT:
A. Interleukin (IL)-1β
B. IL-3
C. IL-6
D. IL-8
E. Tumor necrosis factor-α
194. In phenylketonuria, the deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase results in decreased levels of
A. dopamine.
B. norepinephrine.
C. serotonin.
D. None of the above
195. Classic phenylketonuria is characterized by all EXCEPT:
A. Low levels of prolactin
B. Increased gray matter volume in the ventral part of the striatum
C. A diet low in phenylalanine as a major part of disease management
D. Neurological symptoms such as intellectual disability, tremors, seizures, and jerky movements
E. Occurs in 1 in 10,000 to 15,000 newborns
196. Which of the following findings is LEAST likely to be associated with this MRI scan?
A. Elevated serum angiotensin-converting enzyme
B. Eosinophilic granuloma
C. Meningitis
D. Elevated adrenocorticotrophic hormone
E. Sarcoidosis
197. A central facial palsy would involve
A. only the ipsilateral upper face.
B. only the ipsilateral lower face.
C. only the contralateral upper face.
D. only the contralateral lower face.
E. None of the above
198. Palatal nystagmus is most likely due to a lesion of
A. the dorsal spinocerebellar tract.
B. the corticospinal tract.
C. the middle cerebellar peduncle.
D. the central tegmental tract.
199. The single best predictor for patients with esthesioneuroblastoma is
A. completeness of primary tumor excision and extent of involvement at presentation.
B. TP53 overexpression.
C. the presence of Homer–Wright rosettes on pathology.
D. neuron-specific enolase expression.
E. destruction of the cribriform plate.
200. During a lateral suboccipital approach for tumor resection, cerebellar retraction may be excessive if the BSAEP indicates
A. increased latency in wave 3.
B. decreased latency in wave 4.
C. decreased latency in wave 5.
D. increased latency in wave 4.
E. increased latency in wave 5.
201. The best-characterized glutamate-containing neurons are found in the
A. Purkinje cells of the cerebellum.
B. pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex.
C. pyramidal cells of the hippocampus.
D. septal region.
E. lateral entorhinal cortex.
202. All of the following statements are true of nuclear chain fibers EXCEPT:
A. They receive group Ia primary afferent fibers.
B. They receive group II secondary afferent fibers.
C. They are associated with flower spray endings.
D. They are associated with static gamma efferent fibers.
E. They respond to muscle tension.
203. Patients who continue to display mental status changes after correction of diabetic ketoacidosis should be investigated for
A. cysticercosis.
B. histoplasmosis.
C. Lyme disease.
D. mucormycosis.
E. hydatid disease.
204. Which of the following is FALSE with regard to shunt nephritis?
A. It is a well-described complication of VP shunts.
B. It is due to deposition of immune complexes in the glomeruli of kidneys.
C. The diagnosis is suspected with hematuria, elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and decreased complement levels.
D. Proper treatment entails removing the entire shunt.
E. There is an elevated peripheral WBC count.
205. Regarding DNET, which of the following is FALSE?
A. Male predominance has been noted.
B. It is a surgically curable cause of partial seizures.
C. There is an abundance of mitoses with no necrosis.
D. It is a mixed glial and neuronal neoplasm.
E. It shows on CT scans as a hypodense pseudocystic lesion.
206. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of a hypertensive patient who sustained recurrent falling episodes and complains of headache with the MRI findings shown here?
A. Transsphenoidal resection
B. Bromocriptine
C. Angiography
D. Ophthalmologic evaluation
E. Transcranial resection
207. The saccule sends fibers to the _______vestibular ganglion which project to the _______vestibular nucleus.
A. Superior, superior
B. Superior, inferior
C. Inferior, superior
D. Inferior, inferior
E. None of the above
208. Which of the following tracts traverse the restiform body?
A. Olivocerebellar
B. Reticulocerebellar
C. Dorsal spinocerebellar
D. All of the above
209. A favorable prognosis in neuroblastomas is related to
A. n-Myc amplification.
B. 1p deletion.
C. TrkA expression.
D. older age.
E. None of the above
210. For microvascular decompression in a patient with trigeminal neuralgia, the first bur hole is best placed at the
A. mastoid tip.
B. key hole.
C. asterion.
D. bregma.
E. lambda.
211. The definitive marker for cholinergic neurons is
A. acetyl CoA.
B. acetylcholinesterase.
C. choline acetyltransferase.
D. choline.
E. sensitivity to hemicholinium-3.
212. Tanycytes are most likely to be found in
A. the wall of the third ventricle.
B. a high-grade glioma.
C. a low-grade glioma.
D. the cauda equina.
E. None of the above
Match the statement with the appropriate structure on the diagram:
213. Genitofemoral nerve
214. Innervates the sartorius muscle
215. Enables leg abduction
216. Meralgia paresthetica
217. The vagus nerve leaves the medulla
A. between the pyramid and the olive.
B. between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle.
C. from the same sulcus as CN XII.
D. from the dorsomedial sulcus.
E. from none of the above.
218. Bilateral damage to the medial basal occipitotemporal cortex results in
A. astereognosis.
B. prosoprognosia.
C. alexia without agraphia.
D. auditory agnosia.
E. autotopagnosia.
219. Neuroblastomas may present with
A. spinal cord compression.
B. Ondine’s curse.
C. opsoclonus syndrome.
D. diarrhea.
E. All of the above
220. One of the most significant prognostic indicators for successful prolactinoma surgery is
A. the results of the Goldman perimetry field.
B. being male.
C. the preoperative prolactin level.
D. the age of the patient.
E. being female.
221. Nitric oxide synthase is responsible for
A. conversion of R-arginine into nitrous oxide (NO).
B. conversion of citrulline into NO.
C. production of NO and L-arginine.
D. production of NO and citrulline.
222. Which Rexed lamina is homologous to the spinal trigeminal tract?
A. I
B. II
C. III and IV
D. VII
E. IX
223. The most common presentation of vein of Galen malformation in the neonate is
A. an intracranial bruit with heart failure.
B. subarachnoid hemorrhage.
C. hydrocephalus.
D. developmental delay.
E. ocular symptoms.
224. Which of the following associations based on this MRI scan is FALSE?
A. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
B. Progressive ascending paraplegic syndrome
C. The definitive therapy is microsurgical elimination.
D. Tendency to bleed in elderly patients
E. It may represent a vascular anomaly.
225. The arcuate eminence is the bony landmark of
A. the superior petrosal sinus.
B. the superior semicircular canal.
C. the middle meningeal artery.
D. the vein of Labbé.
226. Which of the following is true of the medial posterior choroidal artery?
A. It is a branch of the posterior cerebral artery.
B. It supplies the choroid plexus of the third ventricle.
C. It supplies the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricles.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
227. The calamus scriptorius can be found
A. in the third ventricle.
B. in the fourth ventricle.
C. in the lateral ventricle.
D. at the cauda equina.
E. in none of the above.
228. Brain waves that are characteristic of deep sleep and have a frequency of 1 to 3 per second are
A. α waves.
B. β waves.
C. theta waves.
D. delta waves.
E. None of the above
229. Which cranial nerves innervate muscles that attach to the styloid process?
A. VII, IX, X
B. IX, X
C. IX, X, XII
D. VII, X
E. VII, IX, XII
230. The sagittal vertical axis offset is a measure of sagittal balance performed by using the following:
A. C7 plumb line
B. Cobb angle
C. Pelvic tilt
D. Sacral slope
E. None of the above
231. Allodynia is a condition in which
A. a painful response is produced by an innocuous mechanical stimulus.
B. a painful response is felt in an amputated limb.
C. a painful response is felt on the opposite side of the body.
D. there is sensitization of spinocerebellar neurons.
E. all of the above may occur.
232. The nucleus dorsalis of Clarke corresponds to which Rexed lamina?
A. I
B. II
C. III and IV
D. VII
E. IX
233. All of the following are true of encephaloceles EXCEPT:
A. Occipital encephaloceles are the most common type.
B. Frontoethmoidal (sincipital) are the most common type in southeast Asia and among Australian aborigines.
C. Parietal encephaloceles are associated with Chiari II malformation in up to one-third of cases.
D. Basal encephaloceles are associated with defects along the sphenoid bone.
E. Children with basal encephaloceles have a low risk of developing meningitis.
234. On a horizontal section of the brain, the anterior limb of the internal capsule can be found between
A. the thalamus and the globus pallidus.
B. the caudate nucleus and the corpus striatum.
C. the caudate and the thalamus.
D. the thalamus and the putamen
E. None of the above
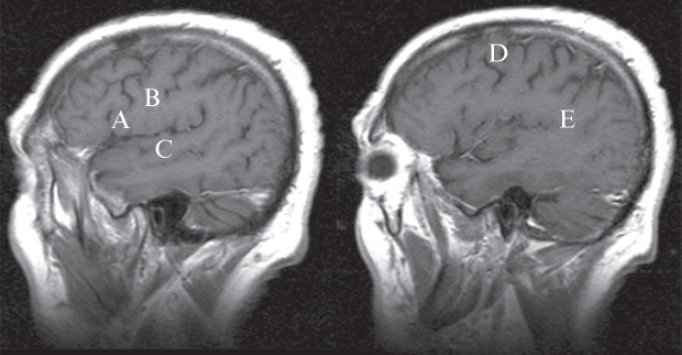
Match the following structures with their appropriate location on the MRI:
235. Supplementary motor cortex
236. Operculum
237. Premotor cortex
238. Heschl’s gyrus
239. Which of the following are true of the greater occipital nerve?
A. It emerges inferior to the inferior obliquus capitis muscle.
B. It is accompanied by the occipital artery.
C. It is a sensory nerve.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
240. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding arachidonic acid metabolism?
A. Aspirin inhibits both cyclooxygenase (COX) isoforms.
B. Arachidonic acid is a substrate for production of ceramide.
C. Thromboxane synthesis inhibitors lead to depletion of arachidonic acid.
D. Arachidonic acid is a substrate for COX I.
E. Prostaglandin H2PGH2 is a product of the COX enzyme.
241. The basal ganglia output for eye movements is the
A. subthalamic nucleus.
B. substantia nigra pars compacta.
C. substantia nigra pars reticulata.
D. globus pallidus interna.
E. globus pallidus externa.
242. Which area receives dorsal roots?
A. Dorsal lateral sulcus
B. Dorsal intermediate sulcus
C. Ventral lateral sulcus
D. Dorsal median sulcus
E. Ventral intermediate sulcus
243. Which statement is true in the case of a 4-year-old with the MRI scan findings shown here?
A. Biopsy is usually indicated to confirm the diagnosis.
B. Hyperfractionated radiation therapy has not been shown to improve survival.
C. It represents 30% of pediatric CNS tumors.
D. There is no proven chemotherapeutic regimen.
E. Most lesions will regress spontaneously.
244. Which of the following formulas is correct in terms of the relationship of pelvic tilt (PT), pelvic incidence (PI), and sacral slope (SS)?
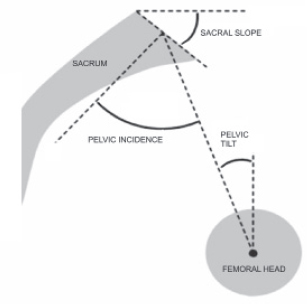
A. PT = PI + SS
B. PI = PT + SS
C. SS = PI + PT
D. PT = PI − SS
245. The scan shown here was taken from a patient with a prolactin level of 267 mg/dL.
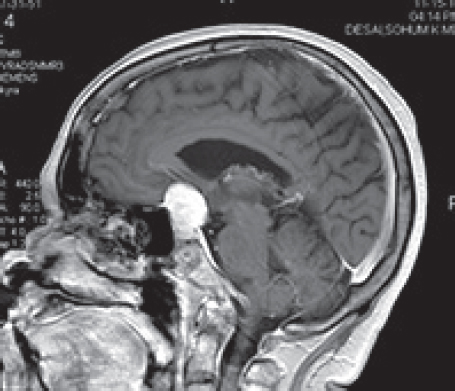
Which of the following is FALSE?
A. Men may not seek early attention despite loss of libido and potency, headache, or fatigue.
B. When visual loss or disturbing endocrine symptoms are present most seek medical attention.
C. A useful endocrine test is determination of the basal serum prolactin level.
D. The normal level ranges from 5 to 20 ng/mL.
E. When the level of prolactin is normal post-treatment, ovulation and menstruation return in < 50% of women in galactorrhea cases.
246. Increased prolactin is typically seen in all the following physiological states EXCEPT:
A. Exercise
B. Stress
C. Sleep
D. Pregnancy
E. Delivery
247. With surgical resection of the mass (shown above with Question 245), cure can be achieved in what percentage of patients?
A. 10%
B. 20%
C. 40%
D. 70%
248. All of the following are true of Lhermitte–Duclos disease EXCEPT:
A. It is also called dysplastic gangliocytoma of the cerebellum.
B. There is demyelination of granular cell layer of the cerebellum.
C. There is thickening of one or more cerebellar folia.
D. Calcification and hydrocephalus may occur in this disorder.
E. A laminated pattern of folia on T2-MRI scans is suggestive of the disease.
249. Which of the following is consistent with the diagnosis of typical trigeminal neuralgia?
A. Unilateral symptoms
B. Sensory deficit
C. Decreased corneal reflex
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
250. n-Butyl cyanoacrylate is used for
A. cranioplasty.
B. endovascular procedures.
C. topical wound dressings.
D. vasospasm in the ICU.
E. spinal fusion.
251. A 24-year-old man is brought into the emergency room after sustaining a motorcycle accident. He has a scalp wound that is bleeding profusely. His eyes open only after his name is loudly called; however, he is confused when asked about the details of the accident. He obeys commands in all extremities. In this case, the GCS score is
A. 15.
B. 14.
C. 13.
D. 12.
E. 11.
252. The ciliospinal center of Budge can be found at which spinal cord level?
A. Midcervical
B. Upper thoracic
C. Lower thoracic
D. Lumbar
253. The serum level of phenytoin is increased by all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Cimetidine
B. Chloramphenicol
C. Valproic acid
D. Uremia
E. Aspirin
254. Which of the following deficits or findings in lateral medullary syndrome is contralateral to the primary pathology?
A. Pain and temperature of the body
B. Pain and temperature of the face
C. Horner’s syndrome
D. Falling
E. None of the above
255. Which of the following fractures is most commonly associated with anterior cord syndrome?
A. Clay shoveler’s fracture
B. Wedge fracture
C. Teardrop fracture
D. Chance fracture
E. None of the above
256. With regard to surgical techniques on pituitary tumors, which of the following is FALSE?
A. Lacerations in the gland with attendant subcapsular bleeding make it difficult if not impossible to detect the subtle differences between the normal gland and a small tumor.
B. Prolactin microadenomas are usually situated medially in the gland.
C. Larger pituitary tumors usually erode the floor of the sella turcica, and in these cases the tumor may extrude into the operative wound upon removal of the floor of the sella and opening of the dura mater.
D. Frequently, the pituitary gland is compressed and flattened against the dorsum sellae or diaphragma sellae by tumor.
E. Reported incidence of postoperative CSF rhinorrhea is ~3%.
257. All of the following structures are derived from ectoderm EXCEPT:
A. Pia
B. Dura
C. Arachnoid
D. Glia
258. The most common primary tumor of the septum pellucidum is
A. meningioma.
B. oligodendroglioma.
C. astrocytoma.
D. ependymoma.
E. None of the above
259. Which of the following is the most common conflicting vessel in trigeminal neuralgia?
A. AICA
B. PICA
C. SCA
D. Satellite veins
E. None of the above
260. The ELANA technique may be helpful in
A. vertebrobasilar ischemia.
B. controlling ICP
C. vasospasm.
D. tumor biology.
E. None of the above
261. This cervical spine MRI scan demonstrates