Small Ventricles
Bronwyn E. Hamilton, MD
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
Normal Variant (Young Brain)
CSF Shunts and Complications
Cerebral Edema, Traumatic
Herniation Syndromes, Intracranial
Less Common
Encephalitis (Miscellaneous)
Intracranial Hypotension
Intracranial Hypertension, Idiopathic
Intracranial Hypertension, Secondary
HIE, NOS
Meningitis
Rare but Important
Brain Death
Inborn Errors of Metabolism (Acute Presentation)
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Clinical presenting features usually help define the category of disease in question
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Normal Variant (Young Brain)
Ventricles in children, young adults can normally appear quite small
CSF Shunts and Complications
CSF diversion
± Reduced ventricular compliance
Compliance changes caused by
Ependymal scar/adhesions
Cause shunted ventricle to collapse
Cerebral Edema, Traumatic
Low density parenchyma with sulcal & ventricular effacement
Hyperdense cerebellum, “reversal sign”
Herniation Syndromes, Intracranial
Ventricular effacement common
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Encephalitis (Miscellaneous)
White matter T2 hyperintensity & edema
Mild restriction on DWI common
Intracranial Hypotension
“Slumping” midbrain, acquired tonsillar herniation/ectopia, enhancing dura
Intracranial Hypertension, Idiopathic
“Pseudotumor cerebri”
Dilated optic nerve sheaths, basal cisterns effaced, small ventricles
Intracranial Hypertension, Secondary
Etiology: Any causes of high intracranial pressure or diffuse edema: Trauma, venous outflow obstruction, anoxic or metabolic encephalopathy, mass, brain death
HIE, NOS
Global anoxic/ischemic event results in DWI changes
Basal ganglia > diffuse cortex bright
Diffuse white matter restriction (may be subacute manifestation)
DWI abnormalities evolve slower than thromboembolic infarction
Meningitis
Mild hydrocephalus > > > small ventricles
Image Gallery
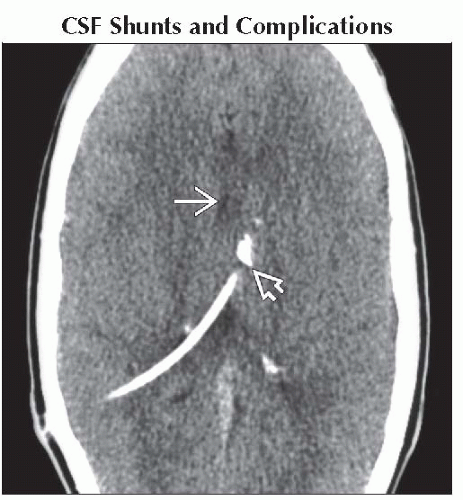 Axial NECT shows small ventricles
 & indeterminate shunt position & indeterminate shunt position 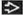 . Symptomatic ventricular collapse is known as “slit-like ventricle syndrome” & suggests overshunting. . Symptomatic ventricular collapse is known as “slit-like ventricle syndrome” & suggests overshunting.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|