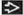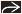Solitary Cystic Parenchymal Mass, General
Anne G. Osborn, MD, FACR
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Common
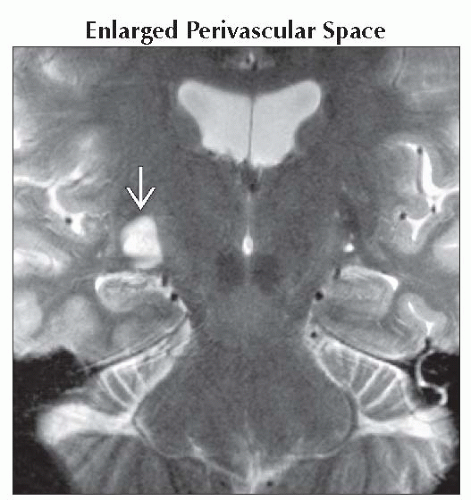
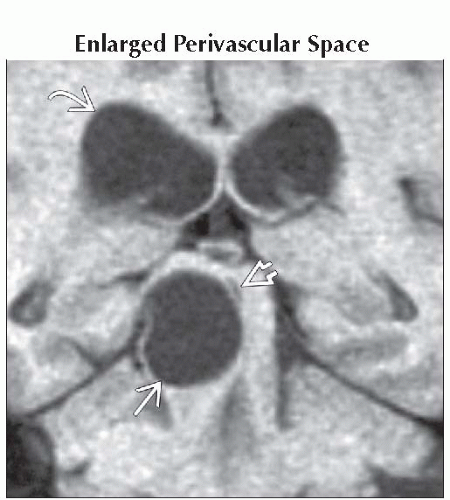
Enlarged Perivascular Space
Encephalomalacia
Neurocysticercosis
Porencephalic Cyst
Glioblastoma Multiforme
Metastasis
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Abscess
Less Common
Intracerebral Hematoma (Resolving)
Multiple Sclerosis
Ganglioglioma
DNET
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma
Hemangioblastoma
Meningioma (Cystic)
Epidermoid Cyst
Dermoid Cyst
Neuroglial Cyst
Ependymoma, Supratentorial
Rare but Important
Parasites, Miscellaneous
Schwannoma (Cystic)
Neurenteric Cyst
Desmoplastic Infantile Ganglioglioma
ESSENTIAL INFORMATION
Key Differential Diagnosis Issues
Definition
Includes all cyst-like parenchymal masses
Excludes extra-axial cysts
Cisternal (e.g., arachnoid cyst), intraventricular (ependymal cyst)
Includes “pseudoparenchymal” lesions that can invaginate into brain, mimic cystic parenchymal mass
Epidermoid, dermoid cysts; cystic meningioma
Key clinical issue: Effect of age on diagnosis
Most common in child
Encephalomalacia, infection (abscess, parasite), neoplasm (primary > > metastatic)
Most common in adult
Enlarged perivascular space, encephalomalacia, neoplasm (GBM, metastasis), infection (abscess, parasite)
Key imaging issues
Is cystic mass exactly like CSF?
Enlarged perivascular space, encephalomalacia, porencephalic or neuroglial cyst
Is cystic mass hypodense to parenchyma but hyperdense compared to CSF?
Cystic neoplasm, abscess, tumefactive demyelination, epidermoid or neurenteric cyst, parasites
Is density/signal intensity of surrounding brain abnormal?
Encephalomalacia, infection, neoplasm
Does lesion enhance?
Yes: Neoplasm, abscess, resolving (subacute) hematoma, tumefactive demyelination
No: Enlarged perivascular space (PVS), encephalomalacia, porencephalic or neuroglial cyst
Does cyst have mural nodule?
Neurocysticercosis (NCC), neoplasm
Helpful Clues for Common Diagnoses
Enlarged Perivascular Space
Multiple lesions, clusters of variable-sized cysts > > solitary enlarged PVS
Well-delineated round/ovoid
Basal ganglia > white matter, midbrain, temporal lobe, dentate nucleus
Follows CSF density/signal intensity
Encephalomalacia
Trauma, infarct, surgery
Follows CSF
Adjacent parenchyma often hyperintense on T2WI, FLAIR
Neurocysticercosis
Multiple small > solitary small or large cyst ± visible scolex
Cyst fluid typically proteinaceous, not exactly like CSF
± Enhancement, edema
Look for multiple parenchymal calcifications (“starry sky”)
Porencephalic Cyst
CSF-containing cyst contiguous with ventricle
Glioblastoma Multiforme
95% central necrosis ± hemorrhage
Thick, irregular rim enhancement
Metastasis
Rim enhances
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
Child, young adult
Cerebellar cyst + mural nodule
Abscess
Appearance depends on stage
Rim enhancement typical in late cerebritis, capsule stages
Helpful Clues for Less Common Diagnoses
Intracerebral Hematoma (Resolving)
Slightly hyperdense to CSF on NECT
Hyperintense on T1-, T2WI
Rim enhancement common
Multiple Sclerosis
“Tumefactive” MS has “horseshoe-shaped” enhancing rim
Ganglioglioma
Cortically based cyst + enhancing nodule
± Ca++; may remodel skull
DNET
NECT: Cortically based hypodense mass
Hyperdense to CSF
MR: “Bubbly” appearance
Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma
Cortically based cyst + nodule
Look for adjacent “dural tail”
Hemangioblastoma
Middle-aged adult
Posterior fossa cyst + enhancing nodule that abuts pia
Epidermoid Cyst
Irregular “cauliflower-like” margins
Sylvian fissure, quadrigeminal mass can mimic intra-axial mass
Looks like CSF on NECT
Does not suppress on FLAIR, restricts on DWI
Dermoid Cyst
Fat ± Ca++
Look for fat “droplets” (rupture)
Neuroglial Cyst
Well-delineated CSF-like parenchymal cyst
No enhancement
Ependymoma, Supratentorial
1/3 of ependymomas
80% parenchymal, not necessarily related to ventricular wall
Usually large, ± cysts, hemorrhage
Ca++ seen in 50%
Variable heterogeneous enhancement of cyst wall, solid component
Helpful Clues for Rare Diagnoses
Parasites, Miscellaneous
Solitary or conglomerate cyst(s)
Some (e.g., hydatid cyst) very large
Schwannoma (Cystic)
Only 1-2% of schwannomas are in brain parenchyma
Peripheral cyst + enhancing nodule
Neurenteric Cyst
Most are extra-axial, posterior fossa
Do occur in supratentorial brain (rare)
Well-delineated cyst hyperintense to CSF
Desmoplastic Infantile Ganglioglioma
Infant with cystic supratentorial mass
Dural-based enhancing mural component
Image Gallery
 (Left) Axial FLAIR MR in a patient with history of remote right MCA infarct shows cystic encephalomalacia
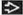 with spongiosis and gliosis, seen here as FLAIR hyperintensity with spongiosis and gliosis, seen here as FLAIR hyperintensity  surrounding the infarcted brain. (Right) Axial CECT in a patient with history of systemic cysticercosis and seizure shows a large CSF-like right temporal lobe cyst surrounding the infarcted brain. (Right) Axial CECT in a patient with history of systemic cysticercosis and seizure shows a large CSF-like right temporal lobe cyst  . No other lesions were identified. . No other lesions were identified.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|