♦ Preoperative
Operative Planning
Imaging
- Gadolinium-enhanced brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): determine lesion location along the medial, middle, or lateral third of the sphenoid ridge; determine extent of disease affecting optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic canal, orbit, superior orbital fissure, cavernous sinus, carotid artery, and middle cerebral artery (MCA) branches
- Computed tomography (CT): evaluate for hyperostosis or erosion
- Acquire preoperative gadolinium-enhanced MRI scan for intraoperative image guidance
- Consider preoperative cerebral angiography and embolization if large flow voids are identified on MRI; this permits a better understanding of the anatomy of large vessels in relation to the tumor
Classification
- Based on location along sphenoid wing (clinoidal, middle, or lateral)
- Clinoidal lesions subdivided by Al-Mefty1 into group I (origin: inferior clinoid), II (origin: lateral or superior clinoid), or III (origin: optic foramen)
- Group I lesions adhere to the adventitia of the carotid artery preventing dissection of tumor from the vessels; group II lesions possess an arachnoid plane between vessels and the tumors permitting dissection from vessels; group III lesions present early secondary to their location
- Resection of tumor that has invaded the cavernous sinus significantly increases the risk of cranial nerve deficits
Extent of Resection
- Extent of resection based on Simpson grade correlates with recurrence of disease
- Postoperative radiation therapy significantly decreases recurrence and progression
- Preoperative evaluation to document existence of visual field and cranial nerve deficits
Routine Equipment
- Major craniotomy tray
- Microsurgery tray
- Mayfield head holder
- High-speed drill
- Operating microscope
- Fibrin glue
- Bipolar cautery
Special Equipment
- Image guidance system
- Leyla bar or Greenberg system for self retaining retractors
- Ultrasonic aspirator (Cavitron ultrasound surgical aspirator)
- Intraoperative monitoring: somatosensory evoked potentials, electroencephalography
- Aneurysm clips
Operating Room Set-up
- Headlights
- Loupes
- Bipolar and monopolar cautery
- Image guidance equipment
Anesthetic Issues
- Antibiotics: cefazolin, 2 g intravenous (IV) at least 30 minutes prior to incision and then every 4 hours, or vancomycin, 1 g IV 30 minutes prior to incision and then every 12 hours
- Dexamethasone (10 mg IV) preoperative
- Antiepileptic medication (phenytoin 15 mg/kg IV during surgery to achieve therapeutic level)
- Mannitol (1 g/kg IV infusion at incision)
- Arterial line and either good peripheral venous or central venous access
♦ Intraoperative
Positioning
- After intubation, the patient is positioned supine. The Mayfield clamp is applied as for a pterional craniotomy. A small shoulder roll is placed under the ipsilateral shoulder.
- The head is slightly extended and then rotated 30 degrees to the side contralateral to the lesion
Preparation of Operative Field
- An incision is marked as for a pterional craniotomy
Incision
- Incise the skin as in a pterional craniotomy; preserve the superficial temporal artery (STA)
Craniotomy (Fig. 40.1)
- Meningiomas involving the middle or lateral third of the sphenoid wing: a frontotemporosphenoidal craniotomy is completed. Extradural drilling of the sphenoid ridge and hyperostotic bone is completed. This extradural drilling aids devascularization of the tumor.
- Clinoidal meningiomas: a frontotemporosphenoidal craniotomy with an orbitozygomatic extension is completed. Removal of the posterior orbital roof, posterolateral orbital wall, and optic canal unroofing is completed.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>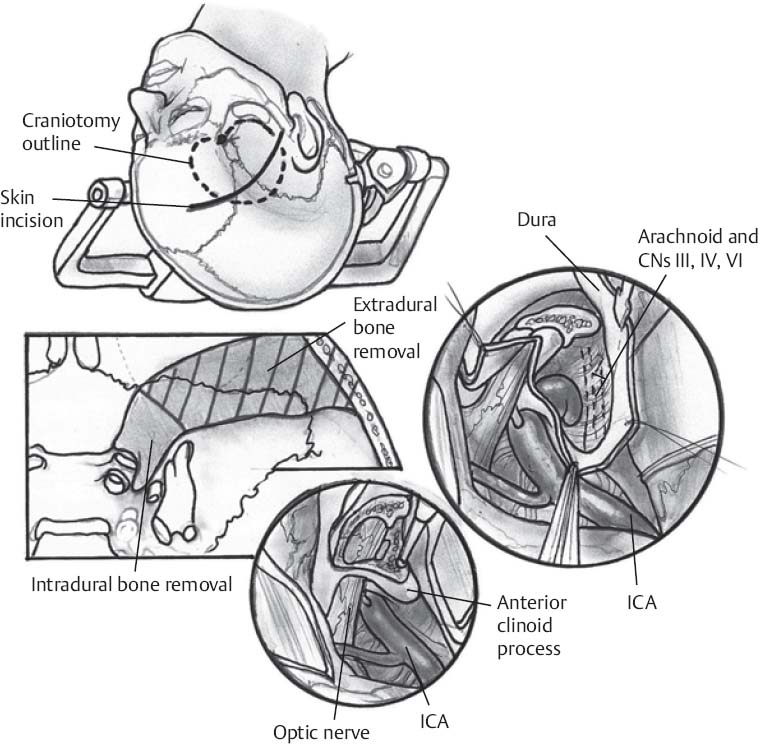 Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue







