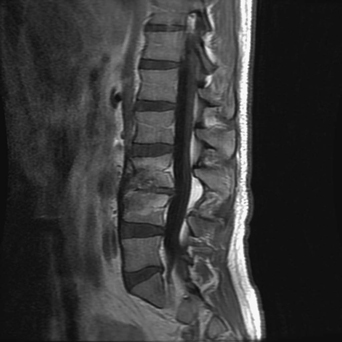
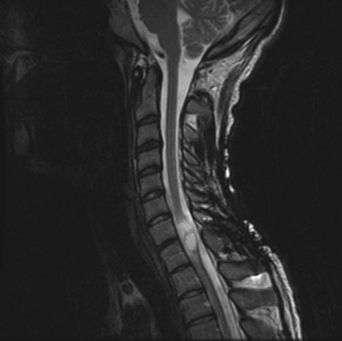
7 A 17-year-old boy was in a motor vehicle accident and became paraplegic. He had a cervical fusion for stabilization and then extensive rehabilitation. During his rehabilitation course, a urinary tract infection seeded his epidural space, causing a discitis and osteomyelitis (Fig. 7-1). This was treated with prolonged intravenous antibiotics. A couple years after his accident, he began experiencing worsening hand weakness, paresthesias, and hyperhidrosis. FIGURE 7-1 Lumbar MRI with L3-L4 osteomyelitis and discitis. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the cervical spine shows an intramedullary fluid-filled cavity at C7-T1 (Fig. 7-2). There is also some metallic artifact seen around the posterior elements from the patient’s previous fusion. Posttraumatic syrinx
Spinal Trauma
Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Spinal Trauma
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








