Fig. 14.1
The schematic diagram of lesion loci. a Group A (axial and coronal views). CC corpus callosum; Cd caudate nucleus ; GRe gyrus rectus; Ic internal capsule; LV lateral ventricle; NAc nucleus accumbens ; OT optical tract; Pu putamen; RN red nucleus; Th thalamus; hash (#) indicates initial lesion. b Group B (axial and sagittal views). CC corpus callosum; Cd caudate nucleus ; GRe gyrus rectus; Ic internal capsule; LV lateral ventricle; NAc nucleus accumbens ; OT optical tract; Pu putamen; RN red nucleus; Th thalamus; hash (#) indicates initial lesion. c Group C (axial, sagittal, and coronal views). CC corpus callosum; Cd caudate nucleus ; GRe gyrus rectus; Ic internal capsule; LV lateral ventricle; NAc Nucleus accumbens; OT optical tract; Pu putamen; RN red nucleus; Th thalamus; hash (#) indicates initial lesion. d D group (axial, sagittal, and coronal views). CC corpus callosum; Cd caudate nucleus ; GRe gyrus rectus; Ic internal capsule; LV lateral ventricle; NAc Nucleus Accumbens ; OT optical tract; Pu putamen; RN red nucleus; Th thalamus; hash (#) indicates initial lesion
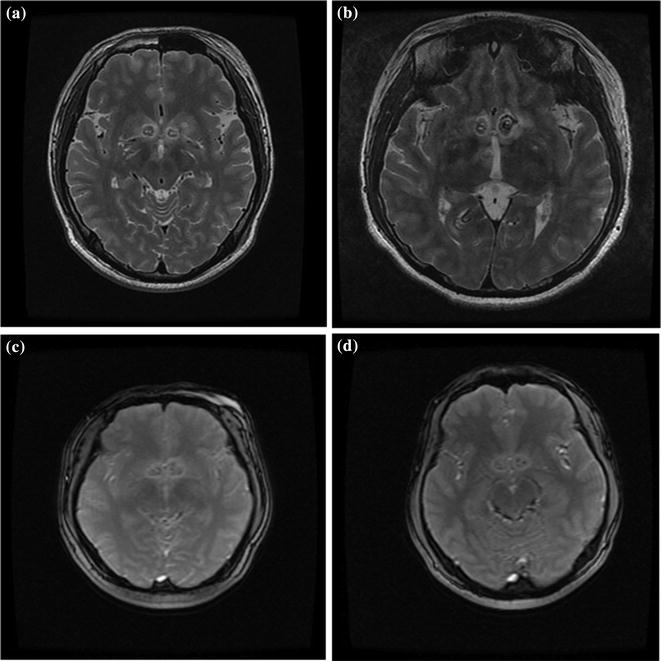
Fig. 14.2
Post-operative MRI images of patients. Postoperative MRI scans showing the condition of the lesion foci in four patients belonging to four different surgical groups. a MRI of a patient from group A (axial views, T2-weighted image). b MRI of a patient from group B (axial views, T2-weighted image). c MRI of a patient from group C (axial views, T1-weighted image). d MRI of a patient from group D (axial views, T1-weighted image)
Using stereotactic technology, we precisely planted an electrode in the target region, and then stimulated it to affect functioning of the related cerebral nuclei, improve the symptom, and control the condition. DBS has the following advantages: non–destructive (DBS does not cause much damage to the brain tissue, is very safe, and electrodes can be planted bilaterally at the same time), adjustability (the disease can be best controlled by adjusting the parameters for DBS), and reversibility (the adverse reaction related to DBS can be relieved by adjusting the parameters).
The distinguishing feature of our center’s DBS for drug addiction is that we can simultaneously stimulate the NAc and anterior limb of internal capsule (ALIC) using a single electrode. We applied the path analysis function of the image analysis software in the stereotactic system to place the far-end contacts of an electrode in the NAc and the proximal contact of electrode in the ALIC. Therefore, we can stimulate both the regions simultaneously. We have included the ALIC in our research considering the compulsivity of drug addiction [10] and the effectiveness of ALIC therapy for OCD [19, 20] (Figs. 14.3 and 14.4).
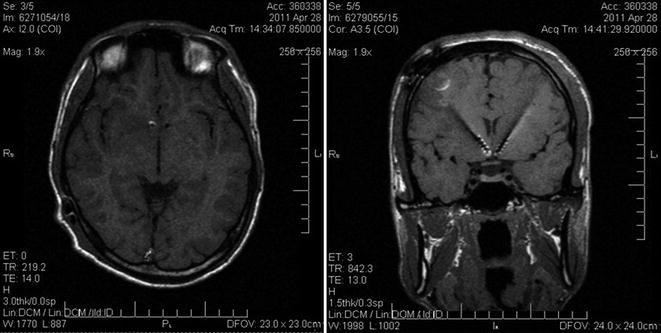
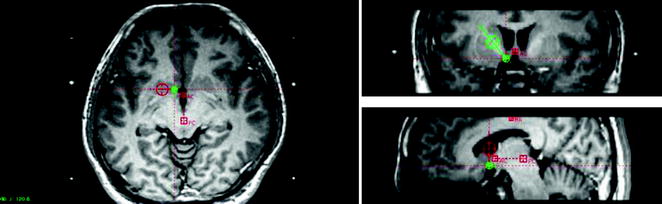

Fig. 14.3
Post-operative MRI of a patient subjected to NAc-ALIC DBS for drug addiction

Fig. 14.4
Schematic diagram of NAc-ALIC DBS
The centers of the small and big circles indicate the NAc and ALIC, respectively.
14.5 How to Perform the Surgery
14.5.1 Aim
The aim of stereotactic surgery for drug addiction is to directly affect the key cerebral nuclei involved in drug addiction in order to control functioning of the addiction circuit, thereby weakening the psychological dependence on drugs and finally avoiding relapse to ensure complete recovery from addiction.
14.5.2 Indications
1.
Patients diagnosed with drug addiction in accordance with the Chinese Classification and Diagnostic Criteria of Mental Disorders (Revision of Second Edition; CCMD-II-R).
2.
Patients with a history of drug abuse >3 years with at least three relapses despite systematic conservative treatments.
3.
Patients aged between 18 and 70 years.
4.
Patients and their families volunteer to undergo surgery, and agree to comply with the treatment.
5.
Patients have completed the physiological detoxification treatment (discontinued all drugs for at least 7–10 days and acute withdraw symptoms have disappeared, with negative results for the morphine urine and naloxone tests).
14.5.3 Contraindications
1.
Patients who are reluctant to give up drugs and are forced to stay in hospital by their family.
2.
Patients who have contraindications for stereotactic neurosurgery.
3.
Patients who have obvious mental disorders, personality disorders, and social disability in accordance with the diagnostic standard of CCMD-II-R.
4.
Patients who have severe communicable diseases, such as AIDS, syphilis, and viral hepatitis.
5.
Patients who have obvious learning difficulties or concomitant degenerative brain diseases.
14.5.4 Preoperative Assessment
Collection for basic information
The collection includes patients’ history of drug abuse, kind of drug, drug dosage, history of treatment, height, weight, and other indexes of health condition.
Assessment for mental condition
Note: Considering the actual situation, at least choose one to two scales in each of following aspect:
1.
Assessment for addiction severity
Opiate Addiction Severity Inventory (OASI)
Opiate Withdrawal Scale (OWS)
2.
Assessment for general mental condition
Symptom Checklist 90 (SCL-90)
3.
Assessment for neuropsychological function
Personality
Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI)
Eysenck Personality Questionnaire (EPQ)
16 Personality Factor Questionnaire (16PF)
Mood
Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)
Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI)
Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA)
Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD)
Cognition
Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-Revised by China (WAIS-RC)
Raven Standard Progressive Matrices Test-Revised by China (RSPM-RC)
Wechsler Memory Scale-Revised by China (WMS-RC)
Clinical Memory Scale (CMS)
4.
Assessment for life quality and social function
Short Form 36 Health Survey Questionnaire (SF-36)
Quality of life Scale for Drug Addicts (QOL-DA)
14.5.5 Preoperative Preparation
1.
Patients have completed the physiological detoxification treatment.
2.
Morphine urine test and naloxone test are negative.
3.
MRI or CT of the brain to screen intracranial organic lesions.
4.




Preoperative assessment (see Sect. 14.5.4)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







