♦ Preoperative
Imaging
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): Pay particular attention to the optimal sequence and communicate the information to the radiologist (otherwise radiology will default to the postcontrast image). Make sure the radiology staff realize that the scan is for image guidance so that thin slices are used for image acquisition.
- Computed tomography (CT): In certain situations, CT may be indicated. CT often gives better special localization than MRI. In addition, CT scans can be obtained more rapidly than MRIs. Sometimes, CT is the only option (i.e., patient has a pacemaker).
- Planning: Since the images need to be preloaded into an imaging station (i.e., Stealth Station or BrainLab), there is time to plan the target and entry point. An inline view is recommended to follow the tract of the biopsy needle to ensure that vessels and eloquent structures are avoided.
Surgery
- Anesthesia: in some situations, it may be performed under monitored anesthesia care, but general anesthesia is recommended when possible.
- Equipment: A dedicated biopsy kit is made for this procedure. Make sure the equipment is inventoried before surgery.
- Pinning: The biopsy arm attaches to the Mayfield pins. The biopsy arm will guide the trajectory, so plan how the biopsy arm will need to lay to give a free range of trajectories. This is a crucial step.
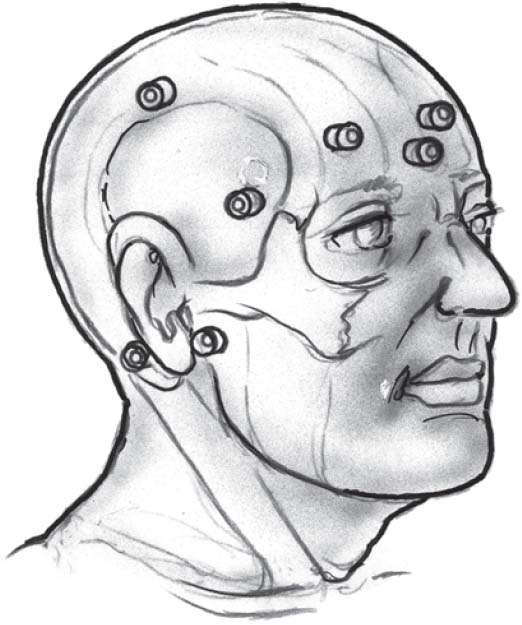
- Trajectory: Register the fiducials on the patient’s head (Fig. 55.1) and then complete the assembly of the biopsy arm. Then identify the entry site and trajectory. The sagittal, coronal, axial, and target views on the image station are suggested. The target view usually needs the cross-hairs to be lined up or two circles brought together to help determine trajectory. Sometimes, the alignment can be difficult and the manipulation of the arm should be broken into each plane (sagittal, axial, and coronal) to guide the required movements.
- Opening—two methods:
- Burr hole opening over entry site: this allows for direct visualization of the cortex to avoid veins.
- Twist burr hole: Using the large size reducers in the arm, place a twist burr hole (usually requires a power drill). Note that a stop on the drill bit is useful to avoid risk of plunging into the brain.
- Burr hole opening over entry site: this allows for direct visualization of the cortex to avoid veins.
- Biopsy: Make sure the needle is registered and pass the needle in the set trajectory. Premeasure the needle prior to entering to ensure that the registered depth corresponds to your measurement.
- Recommend making quadrants for the cores (i.e., imagine taking a core at 12:00, 3:00, 6:00, and 9:00)
- When taking cores, be careful not to aspirate too much.
- Recommend making quadrants for the cores (i.e., imagine taking a core at 12:00, 3:00, 6:00, and 9:00)
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue