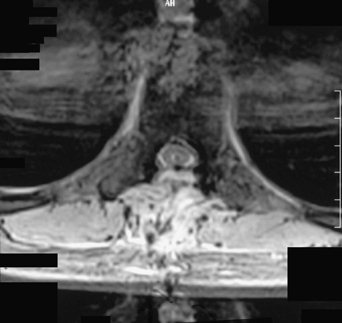
35 A 48-year-old woman had worsening weakness and numbness of her left hand and leg (4+/5), hyperreflexia. Her entire neuraxis was imaged, and the only finding was a high thoracic syrinx. Postoperative axial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the thoracic spine (Fig. 35-1) shows the syringosub-arachnoid shunt draining the syrinx. FIGURE 35-1 Syringosubarachnoid shunt draining a thoracic syrinx. Syrinx Intraoperatively, an arachnoid web was found, which was lysed. A syringosubarachnoid shunt was placed. A syrinx occurs when a cyst forms within the spinal cord. This can be found with Chiari I malformations, or as a complication of trauma, tumor, meningitis, or hemorrhage. Sometimes the cause is not found. We have seen in our case series a patient who developed spinal cord injury, arachnoiditis, and a syrinx after hydrogen peroxide was accidentally injected into his lumbar drain intraoperatively. Although one cannot completely reverse the toxic effect of this action, immediate intervention could include widening the durotomy and copious irrigation with preservative-free normal saline. Syrinx patients can experience pain, difficulty with temperature sensation, and weakness. MRI is the most sensitive test for diagnosis. If symptomatic, treatment is usually directed at the primary etiology, but if none is found, the cyst can be shunted. Mallucci CL, Stacey RJ, Miles JB, Williams B. Idiopathic syringomyelia and the importance of occult arachnoid webs, pouches, and cysts. Br J Neurosurg 1997;11:306–309
Syrinx
Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Treatment
Discussion
SUGGESTED READING
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Syrinx
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








